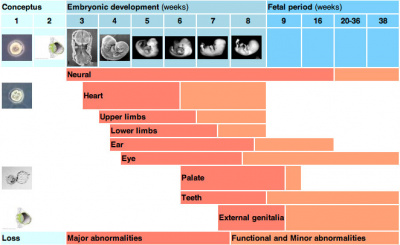
Neural Development
- 3DMRI - Three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging. A new technique that allows 3D analysis of embryonic structures. (More? Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
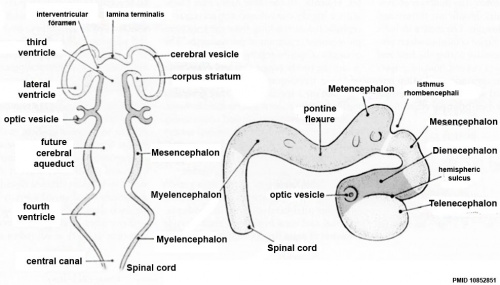
- 3rd ventricle - a fluid-filled space formed from neural tube lumen, located within the diencephalon (from the primary vesicle prosencephalon, forebrain).
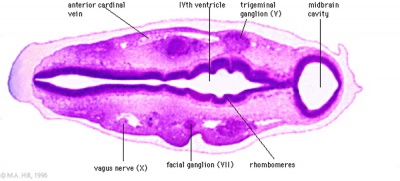
- 4th ventricle - a fluid-filled space formed from neural tube lumen, located within the rhombencephalon (from the primary vesicle, hindbrain).
- adenohypophysis - (anterior pituitary) = 3 parts pars distalis, pars intermedia, pars tuberalis.
- afferent - refers to the direction of conduction from the periphery toward the central nervous system. Efferent is in the opposite direction.
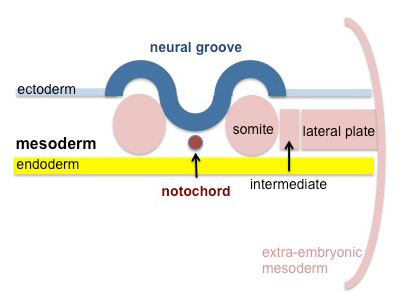
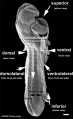
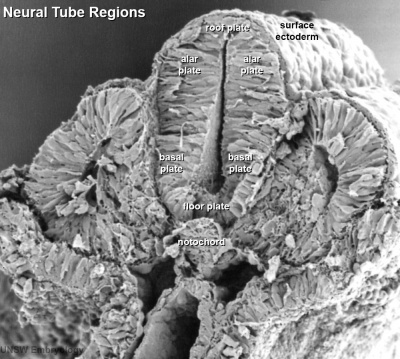
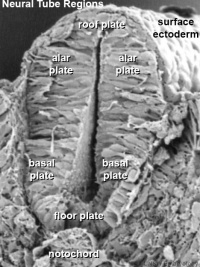
- alar plate - embryonic dorsolateral region of the neural tube forming at spinal cord level dorsal horns (afferent) and brain level different structures.
- anlage - (German = primordium) structure or cells that will form a future adult structure.
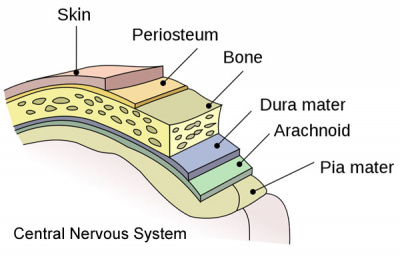
- arachnoid mater - (G.) spider web-like used in reference to the middle layer of the brain meninges.
- astrocytes - cells named by their "star-like" branching appearance, are the most abundant glial cells in the brain, important for the blood-brain barrier.
- basal ganglia - (basal nuclei) neural structure derived from the secondary vesicle telencephalon (endbrain) structure from the earlier primary vesicle prosencephalon (forebrain).
- basal plate - embryonic ventrolateral region of the neural tube forming at spinal cord level ventral horns (efferent) and brain level different structures.
- brachial plexus - mixed spinal nerves innervating the upper limb form a complex meshwork (crossing).
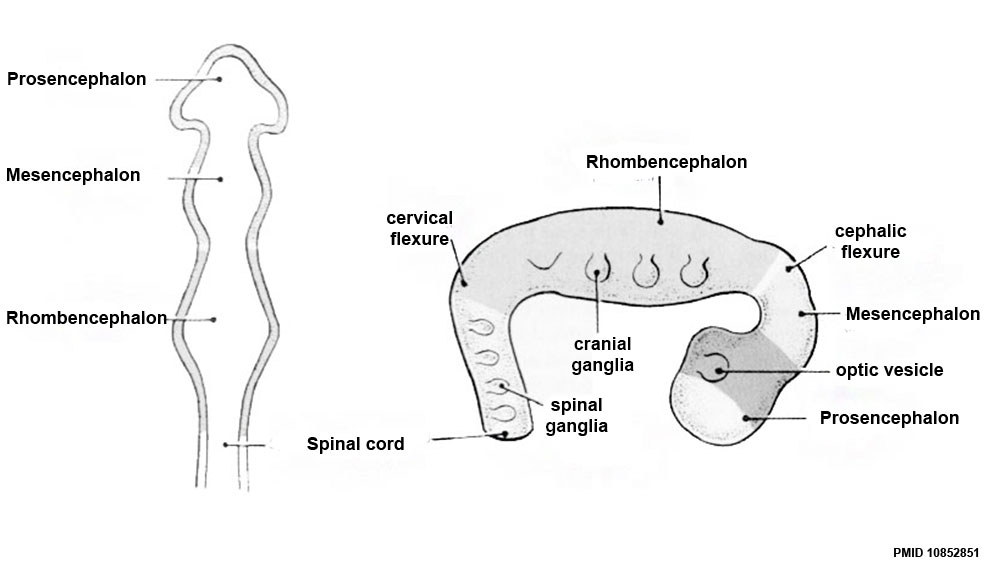
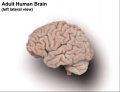
- brain - general term for the central nervous system formed from 3 primary vesicles.
- buccopharyngeal membrane - (oral membrane) at cranial (mouth) end of gastrointestinal tract (GIT) where surface ectoderm and GIT endoderm meet. (see also cloacal membrane).
- cauda equina - (horse's tail) caudal extension of the mature spinal cord.
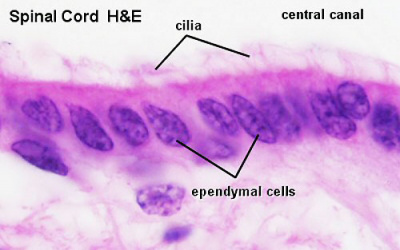
- central canal - lumen, cavity of neural tube within the spinal cord. Space is continuous with ventricular system of the brain.
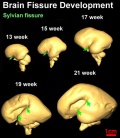
- central cerebral sulcus - (central fissure, fissure of Rolando, Rolandic fissure) fold in the cerebral cortex associated with the sensorimotor cortex.
- cerebral aqueduct - ventricular cavity within the mesencephalon.
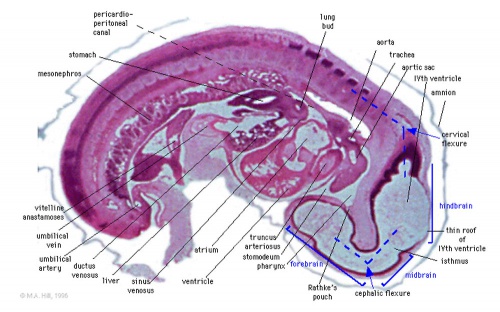
- cervical flexure - most caudal brain flexure (of 3) between spinal cord and rhompencephalon.
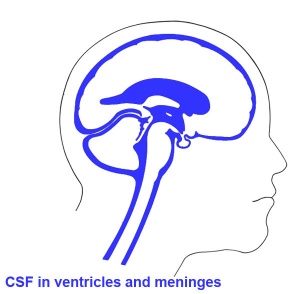
- choroid plexus - specialized vascular plexus responsible for secreting ventricular fluid that with further additions becomes cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
- cloacal membrane - at caudal (anal) end of gastrointestinal tract (GIT) where surface ectoderm and GIT endoderm meet forms the openings for GIT, urinary, reproductive tracts. (see also buccopharyngeal membrane).
- connectome - term describing the detailed map of neural connections in the central nervous system.
- cortex - - CNS structure derived from the secondary vesicle telencephalon (endbrain) from the earlier primary vesicle prosencephalon (forebrain).
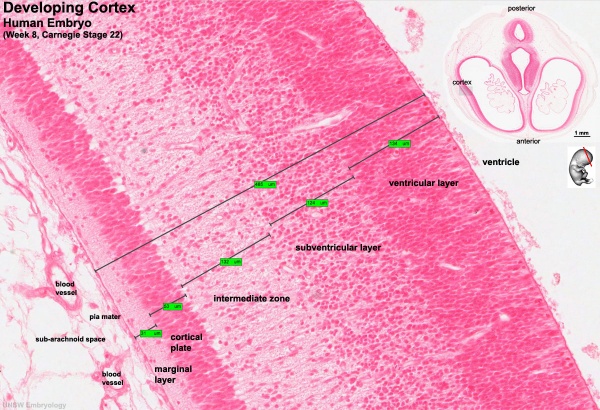
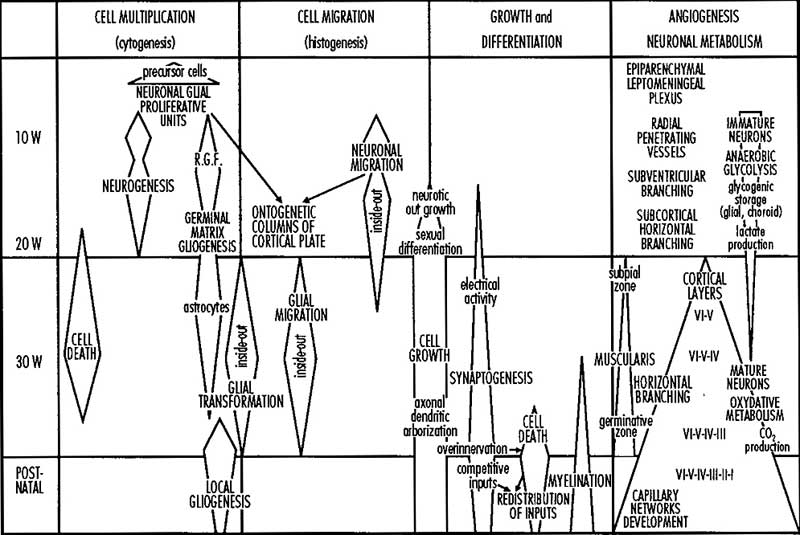
- cortical plate - outer neural tube region which post-mitotic neuroblasts migrate too along radial glia to form adult cortical layers.
- cranial flexure - (=midbrain flexure) most cranial brain flexure (of 3) between mesencephalon and prosencephalon.
- diencephalon - the caudal portion of forebrain after it divides into 2 parts in the 5 secondary vesicle brain (week 5). (cavity- 3rd ventricle) Forms the thalmus and other nuclei in the adult brain. (sc-My-Met-Mes-Di-Tel)
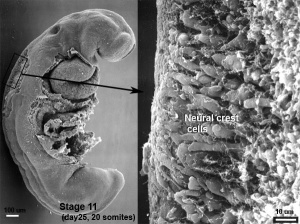
- dorsal root ganglia - (spinal ganglia) sensory ganglia derived from the neural crest lying laterally paired and dorsally to the spinal cord (in the embryo found ventral to the spinal cord). Connects centrally with the dorsal horn of the spinal cord.
- dura mater- "tough" (Latin, mater = mother) used in reference to the tough outer layer of the brain meninges.
- efferent - refers to the direction of conduction from the central nervous system toward the periphery. Afferent is in the opposite direction.
- ependyma - epithelia of remnant cells after neurons and glia have been generated and left the ventricular zone.
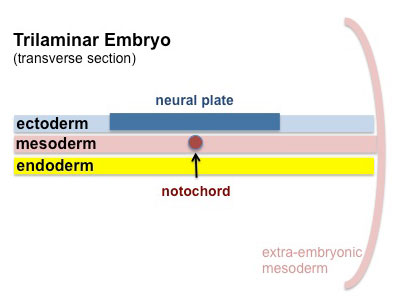
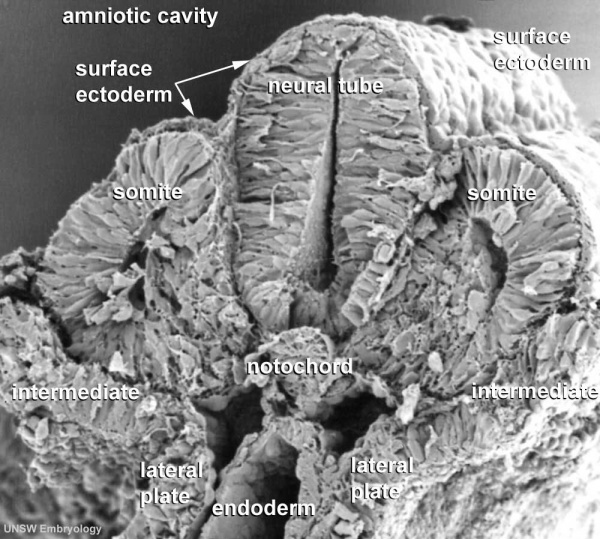
- floorplate - early forming thin region of neural tube closest to the notochord.
- ganglia - (pl. of ganglion) specialized neural cluster within either the CNS or PNS.
- glia - supporting, non-neuronal cells of the nervous system. Generated from the same neuroepithelial stem cells that form neurons in ventricular zone of neural tube. Form astrocytes, oligodendrocytes.
- grey matter - neural regions containing cell bodies (somas) of neurons. In the brain it is the outer layer, in the spinal cord it is inner layer. (see white matter white matter).
- growth factor - usually a protein or peptide that will bind a cell membrane receptor and then activates an intracellular signaling pathway. The function of the pathway will be to alter the cell directly or indirectly by changing gene expression. (eg SHH).
- HOX - (homeobox) family of transcription factors that bind DNA and activate gene expression. Expression of different Hox genes along neural tube defines rostral-caudal axis and segmental levels.
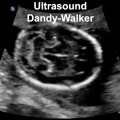
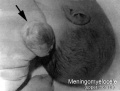
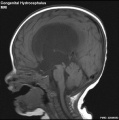
- hydrocephalus - abnormality as the result of an imbalance between the rate at which the CSF is being formed and the rate at which the CSF is passing through the arachnoidal villi back into the blood (hydrocephalus rate is a function of the degree of imbalance in these two). Very small imbalance exhibit subtle, if any, symptoms. Large imbalances will have rapidly evolving symptoms of unmistakable import.
- isthmus- (G. narrow passage).
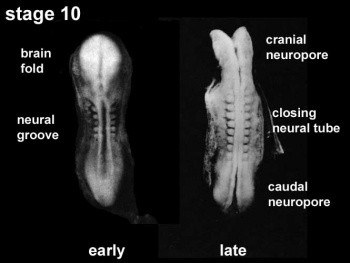
- lamina terminalis - anterior region of brain where cranial neuropore closes.
- lumbar plexus - mixed spinal nerves innervating the lower limb form a complex meshwork (crossing).
- mantle layer - layer of cells generated by first neuroblasts migrating from the ventricular zone of the neural tube. Layers are rearranged during development of the brain and spinal cord. (Ven-Man-Mar-CP)
- marginal zone - layer of processes from neuroblasts in mantle layer. (Ven-Man-Mar-CP)
- mater - (Latin, mater = mother) used in relation to the 3 layers of the meninges.
- meninges - mesenchyme surrounding neural tube forms 3 layer (Dura-, pia-, arachnoid- mater) connective tissue sheath of nervous system. (D-P-A-cns)
- mesencephalon - (midbrain), the middle portion of the 3 primary vesicle brain (week 4). (sc-R-M-P)
- metencephalon - the cranial portion of hindbrain after it divides into 2 parts in the 5 secondary vesicle brain (week 5). Forms the pons and cerebellum in the adult brain. (sc-My-Met-Mes-Di-Tel)
- microglia - CNS innate immune cells that have a macrophage function, derive from yolk sac progenitor cells migrating into the CNS. microglia
- myelencephalon - the caudal portion of hindbrain after it divides into 2 parts in the 5 secondary vesicle brain (week 5). Forms the medulla in the adult brain. (sc-My-Met-Mes-Di-Tel)
- neural tube - neural plate region of ectoderm pinched off to form hollow ectodermal tube above notochord in mesoderm.
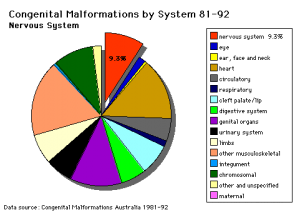
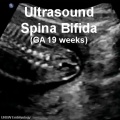
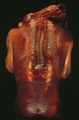
- neural tube defect - (NTD) any developmental abnormality that affects neural tube development. Commonly failure of neural tube closure.
- neuroblast - undifferentiated neuron found in ventricular layer of neural tube.
- neurohypophysis - (posterior pituitary; pas nervosa)
- neuromere - (prosomere) the model units for segmental brain development regions based upon a series of neural tube transverse subunits.
- neuron - The cellur "unit" of the nervous system, transmitting signals between neurons and other cells. The post-mitotic cells generated from neuroepithelial stem cells (neuroblasts) in ventricular zone of neural tube.
- neuropore - opening at either end of neural tube cranial (rostral, anterior) neuropore closes (day 25) about 2 days before caudal (posterior) that closes at somite level 32 to 34. Neural Tube Defects (NTDs) can be due to failure of these two neuropores to close.
- notochord - rod of cells lying in mesoderm layer ventral to the neural tube, induces neural tube and secretes sonic hedgehog which "ventralizes" the neural tube.
- olfactory bulb - (cranial nerve I, CN I) bipolar neurons from nasal epithelium project axons through cribiform palate into olfactory bulb of the brain associated with smell.
- optic nerve - (cranial nerve II, CN II) retinal ganglion neurons project from the retina as a tract into the brain (at the level of the diencephalon) associated with vision.
- optic vesicle - diencephalon region of neural tube outgrowth that forms the primordia of the retina associated with vision.
- opercularization - during fetal development of the sensorimotor cortex, the insula (located deep within the lateral sulcus) begins to invaginate from the surface of the immature cerebrum, until at term, the opercula completely cover the insula.
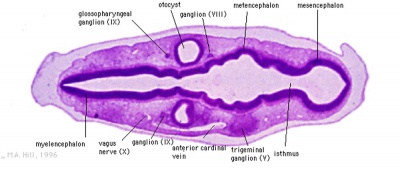
- otocyst - (otic vesicle) sensory placode that sinks into mesoderm to form spherical vesicle (stage 13/14 embryo) that will form components of the inner ear associated with hearing.
- pharyngeal arch - (branchial arch, Gk. gill) form the main structures of the head and neck. Humans have 5 arches appearing in week 4 that form 4 external swellings, each arch has a pouch, membrane and cleft.
- pharynx - uppermost end of GIT, beginning at the buccopharyngeal membrane and at the level of the pharyngeal arches.
- pia mater - (G.) (L. pius = soft, faithful + mater = mother) delicate vascular membrane which adheres to surface of brain and spinal cord, faithfully following their contours, the inner layer of the brain meninges.
- placode - specialized regions of ectoderm which form components of the sensory apparatus.
- pontine flexure - middle brain flexure (of 3) between cervical and cranial flexure in opposite direction, also generates thin roof of rhombencephalon and divides it into myelencephalon and metencephalon. ( sc-^V^ )
- posterior insula - during sensorimotor cortex development this region is composed of the anterior and posterior long insular gyri and the postcentral insular sulcus, which separates them.
- prosencephalon - (forebrain), the most cranial portion of the 3 primary vesicle brain (week 4). (sc-R-M-P)
- prosomere - (neuromere) a model for segmental brain development based upon a series of neural tube transverse subunits. PMID 12948657
- Rathke's pouch - a portion of the roof of the pharynx pushes upward towards the floor of the brain forming the anterior pituitary (adenohypophysis, pars distalis, pars tuberalis pars intermedia). Where it meets a portion of the brain pushing downward forming the posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis, pars nervosa). Rathke's pouch eventually looses its connection with the pharynx.
- rhombencephalon - (hindbrain), the most caudal portion of the 3 primary vesicle brain (week 4). (sc-R-M-P)
- rhombic lip - metencephalon posterior part extending from the roof of the fourth ventricle to dorsal neuroepithelial cells that contributes to the cerebellum.
- roofplate - early forming thin region of neural tube closest to the overlying ectoderm.
- spinal cord - caudal end of neural tube that does not contribute to brain. Note: the process of secondary neuralation contributes the caudal end of the spinal cord.
- spinal ganglia - (dorsal root ganglia, drg) sensory ganglia derived from the neural crest lying laterally paired and dorsally to the spinal cord (in the embryo found ventral to the spinal cord). Connects centrally with the dorsal horn of the spinal cord.
- spinal nerve - mixed nerve (motor and sensory) arising as latera pairs at each vertebral segmental level.
- sonic hedgehog - (shh) secreted growth factor that binds patched (ptc) receptor on cell membrane. SHH function is different for different tissues in the embryo. In the nervous system, it is secreted by the notochord, ventralizes the neural tube, inducing the floor plate and motor neurons.
- sulcus - (L. furrow) groove.
- sulcus limitans - longitudinal lateral groove in neural tube approx. midway between roofplate and floorplate. Groove divides alar (dorsal) and basal (ventral) plate regions.
- telencephalon - the cranial portion of forebrain after it divides into 2 parts in the 5 secondary vesicle brain (week 5). (cavity- lateral ventricles and some of 3rd ventricle) Forms the cerebral hemispheres in the adult brain. (sc-My-Met-Mes-Di-Tel)
- thalamus - (G. thalamos= bedchamber) cns nucleus, lateral to 3rd ventricle, paired (pl thalami).
- thyroid hormone - hormone required for brain development. T3 (3,5,3′-triiodothyronine) binding to nuclear receptors then act as a transcription factor in both neurons and glial cells. iodine deficiency
- transcription factor - a factor (protein or protein with steroid) that binds to DNA to alter gene expression, usually to activate. (eg steroid hormone+receptor, Retinoic acid+Receptor, Hox, Pax, Lim, Nkx-2.2)
- trigeminal ganglion - (cranial nerve V, CN V) first arch ganglion, very large and has 3 portions.
- vagal ganglion - (cranial nerve X, CN X) fourth and sixth arch ganglion, innervates the viscera and heart.
- ventricles - the fluid-filled interconnected cavity system with the brain. Fluid (cerebrospinal fluid, CSF) is generated by the specialized vascular network, the choroid plexus. The ventricles are directly connected to the spinal canal (within the spinal cord).
- ventricular zone - Neuroepithelial cell layer of neural tube closest to lumen. Neuroepithelial cells generate neurons, glia and ependymal cells. (Ven-Man-Mar-CP)
- vestibulocochlear nerve - (cranial nerve VIII, CN VIII, also called statoacoustic)
- white matter - - neural regions containing processes (axons) of neurons. In the brain it is the inner layer, in the spinal cord it is outer layer. (see grey matter).
|