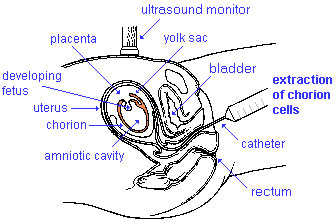
Chorionic villus sampling
| Embryology - 3 Mar 2026 |
|---|
| Google Translate - select your language from the list shown below (this will open a new external page) |
|
العربية | català | 中文 | 中國傳統的 | français | Deutsche | עִברִית | हिंदी | bahasa Indonesia | italiano | 日本語 | 한국어 | မြန်မာ | Pilipino | Polskie | português | ਪੰਜਾਬੀ ਦੇ | Română | русский | Español | Swahili | Svensk | ไทย | Türkçe | اردو | ייִדיש | Tiếng Việt These external translations are automated and may not be accurate. (More? About Translations) |
Introduction
Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS)test is done in the 10th to 12th week after the first day of the mother's last menstrual period (GA week 10 to 12).
The chorionic villus sampling test is done by looking at cells taken from the chorionic membrane or placenta. No anaesthetic is required, and a test result is usually available in two to three weeks.
When the test is carried out by an obstetrician experienced in the technique, the risk of miscarriage related to the test is about 2 %. (Modified from: Checking your baby's health before birth. State Health Publication Number (PA) 94-090). A recent study of the published literature showed a procedure-related risk of miscarriage following CVS was 0.35% (95% CI: -0.31 to 1.00).[1] A more detailed Cochrane review of amniocentesis and chorionic villus sampling has also bee carried out.[2]
Potential disadvantages include maternal cell contamination, placental mosaicism and failure to obtain an adequate specimen. This may result in the need for a repeat procedure or amniocentesis.
Some Recent Findings
|
| More recent papers |
|---|
|
This table allows an automated computer search of the external PubMed database using the listed "Search term" text link.
More? References | Discussion Page | Journal Searches | 2019 References | 2020 References Search term: Chorionic villus sampling | CVS |
| Older papers |
|---|
| These papers originally appeared in the Some Recent Findings table, but as that list grew in length have now been shuffled down to this collapsible table.
See also the Discussion Page for other references listed by year and References on this current page.
|
Movie
A typical example of ultrasound guided chorionic villus sampling (CVS) at 12 weeks of pregnancy (Royal Berkshire, Published on Oct 21, 2013).
<html5media width="480" height="360">https://www.youtube.com/embed/FVaPqKrZm4E</html5media>
- Links: Movie - Amniocentesis | YouTube CVS video
References
- ↑ Beta J, Lesmes-Heredia C, Bedetti C & Akolekar R. (2018). Risk of miscarriage following amniocentesis and chorionic villus sampling: a systematic review of the literature. Minerva Ginecol , 70, 215-219. PMID: 29161799 DOI.
- ↑ Alfirevic Z, Navaratnam K & Mujezinovic F. (2017). Amniocentesis and chorionic villus sampling for prenatal diagnosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev , 9, CD003252. PMID: 28869276 DOI.
- ↑ Salomon LJ, Sotiriadis A, Wulff CB, Odibo A & Akolekar R. (2019). Risk of miscarriage following amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling: systematic review of the literature and updated meta-analysis. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol , , . PMID: 31124209 DOI.
- ↑ Niederstrasser SL, Hammer K, Möllers M, Falkenberg MK, Schmidt R, Steinhard J, Klockenbusch W & Schmitz R. (2017). Fetal loss following invasive prenatal testing: a comparison of transabdominal chorionic villus sampling, transcervical chorionic villus sampling and amniocentesis. J Perinat Med , 45, 193-198. PMID: 27416616 DOI.
- ↑ Yong PJ, McFadden DE & Robinson WP. (2011). Developmental origin of chorionic villus cultures from spontaneous abortion and chorionic villus sampling. J Obstet Gynaecol Can , 33, 449-452. PMID: 21639964 DOI.
- ↑ Adeniji B, Williams J, Solt I, Morales C, Alanakian A & Rotmensch S. (2011). Clinical trial of multiplanar real-time 4- versus 2-dimensional sonographic guidance for transcervical chorionic villus sampling. J Ultrasound Med , 30, 309-12. PMID: 21357552
Reviews
Filocamo M & Morrone A. (2011). Lysosomal storage disorders: molecular basis and laboratory testing. Hum. Genomics , 5, 156-69. PMID: 21504867
Minna T, Mika G, Tiina L, Marjo M, Sture A, Olavi Y, Annukka R, Vilho H, Jorma P & Mika N. (2011). Risk for placental abruption following amniocentesis and chorionic villus sampling. Prenat. Diagn. , 31, 410-2. PMID: 21413037 DOI.
Farina A. (2011). Nonabortal pregnancy complications of chorionic villous sampling. Curr. Opin. Obstet. Gynecol. , 23, 129-34. PMID: 21297473 DOI.
Articles
Search PubMed
Search PubMed: Chorionic villus sampling
Search Entrez: Search All Databases - CVS
- ART - Assisted Reproductive Technology a general term to describe all the clinical techniques used to aid fertility.
- blastomere biopsy - An ART preimplantation genetic diagnosis technique carried out at cleavage stage (day 3), excluding poor quality embryos, detects chromosomal abnormalities of both maternal and paternal origin. May not detect cellular mosaicism in the embryo.
- blastocyst biopsy - An ART preimplantation genetic diagnosis technique carried out at blastocyst stage (day 4-5), removes several trophoblast (trophoderm) cells, detects chromosomal abnormalities of both maternal and paternal origin and may detect cellular mosaicism.
- cell-free fetal deoxyribonucleic acid - (cfDNA) refers to fetal DNA circulating and isolated from the plasma portion of maternal blood. Can be performed from GA 10 weeks as a first-tier test or as a second-tier test, with women with increased probability on combined first trimester screening offered cfDNA or diagnostic testing.
- false negative rate - The proportion of pregnancies that will test negative given that the congenital anomaly is present.
- false positive rate - The proportion of pregnancies that will test positive given that the congenital anomaly is absent.
- free β human chorionic gonadotrophin - beta-hCG subunit of hCG used as a diagnostic marker for: early detection of pregnancy, Trisomy 21, spontaneous abortion, ectopic pregnancy, hydatidiform mole or choriocarcinoma.
- multiples of the median - (MoM) A multiple of the median is a measure of how far an individual test result deviates from the median and is used to report the results of medical screening tests, particularly where the results of the individual tests are highly variable.
- negative predictive value - The probability that a congenital anomaly is absent given that the prenatal screening test is negative.
- Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing - (NIPT) could refer to ultrasound or other imaging techniques, but more frequently used to describe analysis of cell-free fetal DNA circulating in maternal blood.
- polar body biopsy - (PB biopsy) An ART preimplantation genetic diagnosis technique that removes either the first or second polar body from the zygote. As these are generated by oocyte meiosis they detects chromosomal abnormalities only on the female genetics.
- positive predictive value - The probability that a congenital anomaly is present given that the prenatal screening test is positive.
- pre-implantation genetic diagnosis - (PGD, pre-implantation genetic screening) a diagnostic procedure for embryos produced through Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART, in vitro fertilisation, IVF) for genetic diseases that would generate developmental abnormalities or serious postnatal diseases.
- prenatal screening sensitivity - (detection rate) The probability of testing positive on a prenatal screening test if the congenital anomaly is present.
- prenatal screening specificity - The probability of testing negative on a prenatal screening test if the congenital anomaly is absent.
- quadruple test (maternal serum testing of a-fetoprotein Template:AFP, free B-hCG or total hCG, unconjugated estriol, and inhibin A) is a fetal chromosomal anomaly test usually carried out later in pregnancy (GA 14 to 20 weeks).
- single nucleotide polymorphisms - (SNPs) the variation in a single DNA nucleotide that occurs at a specific position in the genome.
- triple test - (maternal serum testing of a-fetoprotein Template:AFP, free B-hCG or total hCG, and unconjugated estriol) is a fetal chromosomal anomaly test usually carried out later in pregnancy (GA 14 to 20 weeks).
| Other Terms Lists |
|---|
| Terms Lists: ART | Birth | Bone | Cardiovascular | Cell Division | Endocrine | Gastrointestinal | Genital | Genetic | Head | Hearing | Heart | Immune | Integumentary | Neonatal | Neural | Oocyte | Palate | Placenta | Radiation | Renal | Respiratory | Spermatozoa | Statistics | Tooth | Ultrasound | Vision | Historic | Drugs | Glossary |
External Links
External Links Notice - The dynamic nature of the internet may mean that some of these listed links may no longer function. If the link no longer works search the web with the link text or name. Links to any external commercial sites are provided for information purposes only and should never be considered an endorsement. UNSW Embryology is provided as an educational resource with no clinical information or commercial affiliation.
- Medline Plus - Chorionic villus sampling
- WHO - Oladapo OT. Amniocentesis and chorionic villus sampling for prenatal diagnosis: RHL commentary (last revised: 1 April 2009). The WHO Reproductive Health Library; Geneva: World Health Organization.
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2026, March 3) Embryology Chorionic villus sampling. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Chorionic_villus_sampling
- © Dr Mark Hill 2026, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G