Fetal Development
| Embryology - 27 Apr 2024 |
|---|
| Google Translate - select your language from the list shown below (this will open a new external page) |
|
العربية | català | 中文 | 中國傳統的 | français | Deutsche | עִברִית | हिंदी | bahasa Indonesia | italiano | 日本語 | 한국어 | မြန်မာ | Pilipino | Polskie | português | ਪੰਜਾਬੀ ਦੇ | Română | русский | Español | Swahili | Svensk | ไทย | Türkçe | اردو | ייִדיש | Tiếng Việt These external translations are automated and may not be accurate. (More? About Translations) |
Introduction
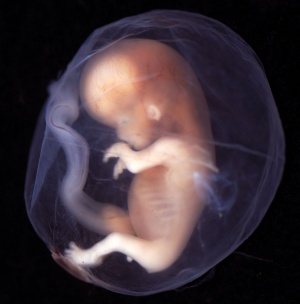
| <html5media height="400" width="360">File:fetal growth.mp4</html5media> | This page shows some key events of human development during the fetal period (weeks 9 to 37) following fertilization. The long Fetal period (4x the embryonic period) is a time of extensive growth in size and mass as well as ongoing differentiation of organ systems established in the embryonic period. Clinically this period is generally described as the Second Trimester and Third Trimester. Many of the critical measurements of growth are now carried out by ultrasound and this period ends at birth.
|
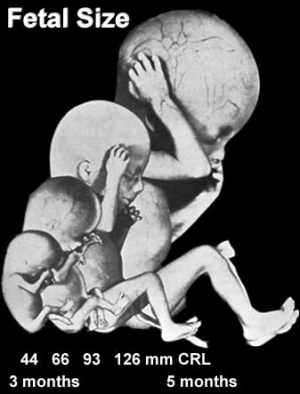
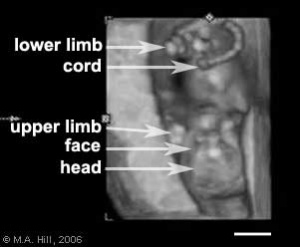
| Changing fetal proportions, not size growth. | Use the links below to get more detailed information about this period of development. |

|
In 1949 the embryologist George Streeter[1] used the replacement of cartilage within the humerus by bone marrow as an arbitrary definition of the embryo to fetus transition.
|
| Fetal Links: fetal | Week 10 | Week 12 | second trimester | third trimester | fetal neural | Fetal Blood Sampling | fetal growth restriction | birth | birth weight | preterm birth | Developmental Origins of Health and Disease | macrosomia | BGD Practical | Medicine Lecture | Science Lecture | Lecture Movie | Category:Human Fetus | Category:Fetal | |||
|
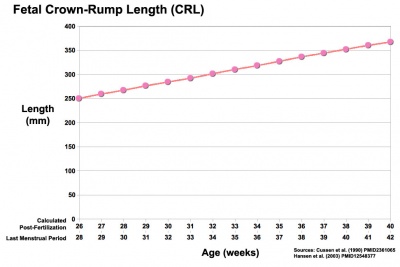
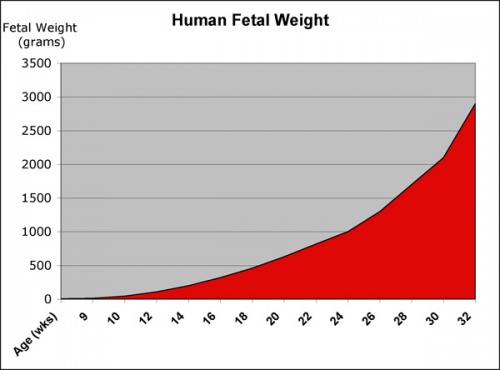
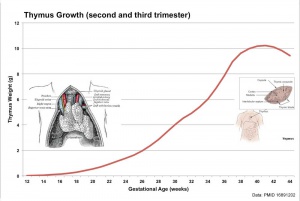
- Fetal Graphs: Crown-Rump Length (CRL) | Third trimester CRL | Head Circumference | Head Circumference 2nd Trimester | Liver Weight | Pancreas Weight | Thymus Weight | Small Intestine Length | Large Intestine Length | Length and Weight Changes | Fetal Development
Some Recent Findings
|
| More recent papers |
|---|
|
This table allows an automated computer search of the external PubMed database using the listed "Search term" text link.
More? References | Discussion Page | Journal Searches | 2019 References | 2020 References Search term: Fetal Development | Foetal Development | Second Trimester | Third Trimester |
| Older papers |
|---|
| These papers originally appeared in the Some Recent Findings table, but as that list grew in length have now been shuffled down to this collapsible table.
See also the Discussion Page for other references listed by year and References on this current page.
|
Reading
|
|
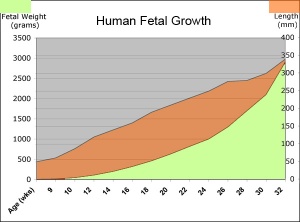
| Fetal Development - Length - Weight | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Gestational age | Fertilization age | Length | Mass |
| (LMP) (GA weeks) | (weeks) | (cm) | (g) |
| 8 (embryonic) | 6 | 1.6 (crown to rump) | 1 |
| 9 | 7 | 2.3 | 2 |
| 10 | 8 | 3.1 | 4 |
| 11 (fetal) | 9 | 4.1 | 7 |
| 12 | 10 | 5.4 | 14 |
| 13 (second trimester) | 11 | 7.4 | 23 |
| 14 | 12 | 8.7 | 43 |
| 15 | 13 | 10.1 | 70 |
| 16 | 14 | 11.6 | 100 |
| 17 | 15 | 13 | 140 |
| 18 | 16 | 14.2 | 190 |
| 19 | 17 | 15.3 | 240 |
| 20 | 18 | 16.4 25.6 (crown to heel) |
300 |
| 21 | 19 | 26.7 | 360 |
| 22 | 20 | 27.8 | 430 |
| 23 | 21 | 28.9 | 501 |
| 24 | 22 | 30 | 600 |
| 25 | 23 | 34.6 | 660 |
| 26 | 24 | 35.6 | 760 |
| 27 | 25 | 36.6 | 875 |
| 28 (third trimester) | 26 | 37.6 | 1005 |
| 29 | 27 | 38.6 | 1153 |
| 30 | 28 | 39.9 | 1319 |
| 31 | 29 | 41.1 | 1502 |
| 32 | 30 | 42.4 | 1702 |
| 33 | 31 | 43.7 | 1918 |
| 34 | 32 | 45 | 2146 |
| 35 | 33 | 46.2 | 2383 |
| 36 | 34 | 47.4 | 2622 |
| 37 | 35 | 48.6 | 2859 |
| 38 | 36 | 49.8 | 3083 |
| 39 | 37 | 50.7 | 3288 |
| 40 | 38 | 51.2 | 3462 |
| 41 | 39 | 51.7 | 3597 |
| 42 | 40 | 51.5 | 3685 |
| References [8][9][10] | |||
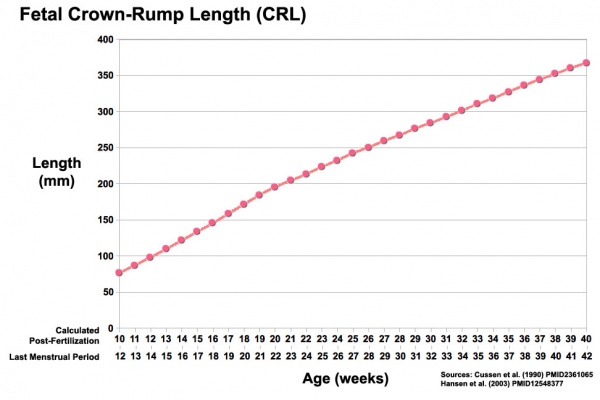
Ultrasound CRL Data
The collapsed table below shows measurement data from a recent ultrasound study.[11]
| Fertilization and Gestational Age - Crown-Rump Length (ultrasound) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Second Trimester
- Second Trimester
- Week 12 - CRL 85 mm, femur length 15 mm, biparietal diameter 25 mm.
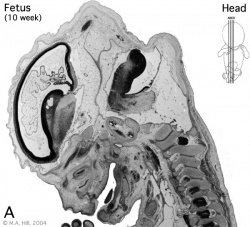
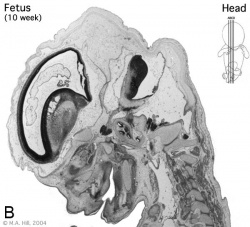
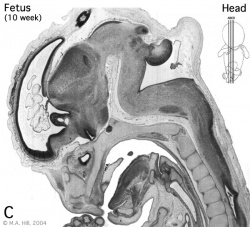
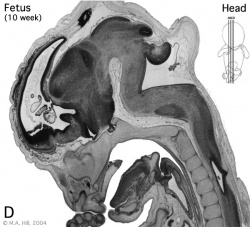
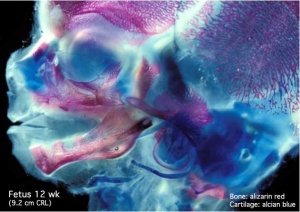
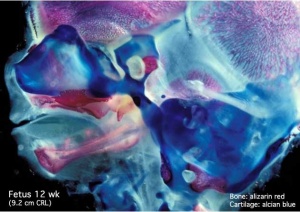
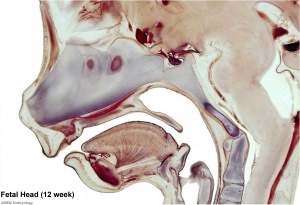
Begin by working through the features present in the early 10 week female fetus. Then look in detail at the head development in a 12 week fetus.
Week 13 to Week 16
(GA Week 15-18)
- Growth - rapid growth continues
- Head - head has straightened up
- eyes at the front part of the face but still widely separated
- outer ear has moved (relatively) from upper part of neck to the side of the head
- Musculoskeletal - ossification is proceeding
- skeleton now visible on an x-ray
- Integumentary - body is covered with lanugo
Week 17 to Week 20
(GA Week 19-21)
- Growth - Length growth begins to slow.
- body parts have acquired their relative proportions.
- Integumentary - vernix caseosa
- sebaceous glands begin to secrete and vernix caseosa comes to cover the skin to prevent damage by amniotic fluid.
- Neural - Spinal cord myelinization begins
- Adipose Tissue - brown fat is forming
- Musculoskeletal - active movements of the fetus in the uterus (kicks)
Week 21 to Week 25
(GA Week 23-27)
- Integumentary / Vision - eyelids and eyebrows developed
- lanugo a darker color and vernix caseosa is thicker.
- skin is sometimes very wrinkled (high growth, lack of subcutaneous fat)
- fingernails are visible
- Growth - face and body are usually as they will be at birth.
- Fetuses born after the 25th week of gestation are generally viable
|
|
|
|
Then look in detail at the head development in a 12 week fetus showing both forms of ossification in the skull.
|
|
|
Timeline
| Links: human timeline | first trimester timeline | second trimester timeline | third trimester timeline | ||
| Event | ||
| Clinical second trimester |  Week 12 - CRL 85 mm, femur length 15 mm, biparietal diameter 25 mm Week 12 - CRL 85 mm, femur length 15 mm, biparietal diameter 25 mm
Hearing Week 12-16 - Capsule adjacent to membranous labrynth undegoes vacuolization to form a cavity (perilymphatic space) around membranous labrynth and fills with perilymph
Respiratory Month 3-6 - lungs appear glandular, end month 6 alveolar cells type 2 appear and begin to secrete surfactant Tongue Week 12 - first differentiated epithelial cells (Type II and III) Genital female genital canal (80 days) formed with absorption of the median septum | |
| tongue Week 12 to 13 - maximum synapses between cells and afferent nerve fibers
hearing outer ear Week 13 - Meatal plug disc-like, innermost surface in contact with the primordial malleus, contributes to the formation of the tympanic membrane. | ||
| tongue Week 14 to 15 - taste pores develop, mucous
ovary 100 days - primary follicles present nail toenails appear Head Development facial skeleton remodelling begins Hearing - Inner Ear Development Week 14 GA 16 - neural-crest-derived melanocytes, now intermediate cells of the stria vascularis, tightly integrate with Na+ /K+ -ATPase-positive marginal cells, which started to express KCNQ1 in their apical membrane.[12] | ||
| Pancreas glucagon detectable in fetal plasma.
spleen Week 15 -alpha-smooth muscle actin (alpha-SMA)-positive reticulum cells scattered around the arterioles.[13] | ||
| 14 cm |  Hearing Week 16-24 - Centres of ossification appear in remaining cartilage of otic capsule form petrous portion of temporal bone. Continues to ossify to form mastoid process of temporal bone. Hearing Week 16-24 - Centres of ossification appear in remaining cartilage of otic capsule form petrous portion of temporal bone. Continues to ossify to form mastoid process of temporal bone.
pituitary adenohypophysis fully differentiated respiratory Week 16 to 25 lung histology - canalicular Hearing - Outer Ear Development Week 16.5 - External auditory meatus is fully patent throughout its length, lumen is still narrow and curved. Hearing - Inner Ear Development Week 16 GA 18 - cells in the outer sulcus express KCNJ10 and gap junction proteins GJB2/CX26 and GJB6/CX30, but these are not expressed in the spiral ligament.[12] gap junction cartoon neural - Cerebrum development of the periinsular sulci (week 16-17, GA 18-19 weeks)[14]
primary follicles begin to form in the ovary and are characterized by an oocyte glandular urethra forms and skin folds present | |
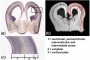 Neural - Brain development histology week 17 Neural - Brain development histology week 17
Cerebellum Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) can study the developing cerebellum from 17 to 18 weeks (GA 19 to 20 weeks). tooth Week 17 - First papilla of the permanent dentition appear (first molar) immediately behind the second milk molar, milk teeth are well advanced (Fetus 180 mm). | ||
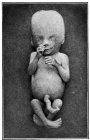 tongue Week 18 - substance P detected in dermal papillae, not in taste bud primordia tongue Week 18 - substance P detected in dermal papillae, not in taste bud primordia
integumentary vernix caseosa covers skin spleen Week 18 - alpha-SMA-positive reticulum cells increase in number and began to form a reticular framework. An accumulation of T and B lymphocytes occurred within the framework, and a primitive white pulp was observed around the arterioles.[13] Hearing - Outer Ear Development week 18 - External auditory meatus is already fully expanded to its complete form. neural - Cerebrum central sulci and opercularization of the insula (week 18-20, GA 20-22 weeks)[14] | ||
| neural week 19 neuronal migration ends and the radial glial cells that aided the migration now become transformed into astrocytes and astrocytic precursors.[15] | ||
| pituitary week 20 to 24 growth hormone levels peak, then decline
integumentary lanugo, skin hair integumentary 5 months - Hair growth initiated at base of cord, lateral outgrowths form associated sebaceous glands; Other cords elongate and coil to form sweat glands; Cords in mammary region branch as they elongate to form mammary glands. touch pacinian corpuscle begin to develop[16] | ||
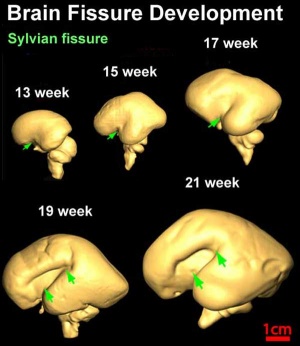
 Neural brain cortical sulcation - sylvian fissure, interhemispheric fissure, callosal sulcus, parietooccipital fissure, and hippocampic fissures present[17] Neural brain cortical sulcation - sylvian fissure, interhemispheric fissure, callosal sulcus, parietooccipital fissure, and hippocampic fissures present[17]
spleen - Week 22 - antigenic diversity of the reticular framework was observed, and T and B lymphocytes were segregated in the framework. T lymphocytes were sorted into the alpha-smooth muscle actin-positive reticular framework, and the periarteriolar lymphoid sheath (PALS) was formed around the arteriole. B lymphocytes aggregated in eccentric portions to the PALS and formed the lymph follicle (LF). The reticular framework of the LF was alpha-SMA-negative. [13] neural - Cerebrum covering of the posterior insula (week 22-24, GA 24-26 weeks)[14] | ||
| respiratory Week 24 to 40 lung histology - terminal sac
spleen Week 24 - marginal zone appeared in the alpha-smooth muscle actin-positive reticular framework around the white pulp.[13] tooth Week 24 - Permanent incisors and canines appear. Earliest potential survival expected if born ovary follicles can consist of growing oocytes surrounded by several layers of granulosa cells | ||
| respiratory end month 6 alveolar cells type 2 appear and begin to secrete surfactant
neural - Cerebrum closure of the laeteral sulcus (Sylvian fissure or lateral fissure) (week 25-26, GA 27-28 weeks)[14] | ||
| touch pacinian corpuscle well developed[16] | ||
Third Trimester
Third trimester Crown-Rump Length
- Vibration acoustically of maternal abdominal wall induces startle respone in fetus.
- Month 7 - respiratory bronchioles proliferate and end in alveolar ducts and sacs.
- Week 37 to 38 Birth.
Week 26 to Week 29
(GA Week 28-31)
- Integumentary / Vision - eyes are opened again and eyebrows and eyelashes are well formed
- pupillary membrane disappears.
- Integumentary - hair grows, subcutaneous adipose tissue deposits round the whole body, becomes chubby and plump
Week 30 to Week 34
(GA Week 32-36)
- Integumentary - body becomes chubby and the skin is pink
- fingernails have reached the ends of the fingers
- toenails are visible
- Genital - testicles descend
Timeline
| Links: human timeline | first trimester timeline | second trimester timeline | third trimester timeline | ||
| Event | ||
| Clinical third trimester |  hearing 3rd Trimester - vibration acoustically of maternal abdominal wall induces startle respone in fetus. hearing 3rd Trimester - vibration acoustically of maternal abdominal wall induces startle respone in fetus.
| |
| respiratory Month 7 - respiratory bronchioles proliferate and end in alveolar ducts and sacs | ||
|
tooth Week 29 - Permanent premolars (correspond to the milk molars) appear. | ||
|
Genital male gonad (testes) descending | ||
| nail fingernails reach digit tip | ||
| neural brain cortical sulcation - primary sulci present[17] | ||
| neural brain cortical sulcation - insular, cingular, and occipital secondary sulci present[17] | ||
 Nail Development toenails reach digit tip Nail Development toenails reach digit tip
Lens Development - lens growth and interocular distance plateaus after 36 weeks of gestation[18] | ||
| Birth |  Clinical Week 40 Clinical Week 40
Heart pressure difference closes foramen ovale leaving a fossa ovalis thyroid TSH levels increase, thyroxine (T3) and T4 levels increase to 24 h, then 5-7 days postnatal decline to normal levels adrenal - zona glomerulosa, zona fasiculata present | |
- Links: Third Trimester
Growth
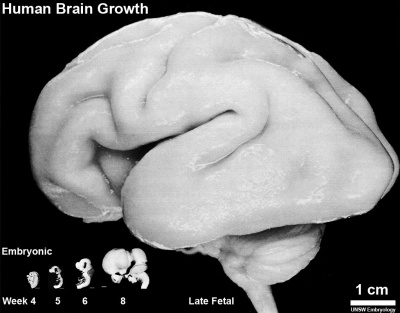
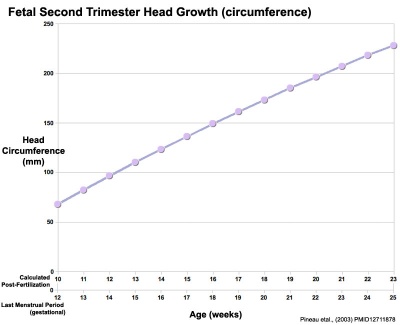
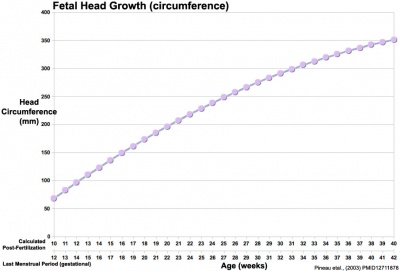
Fetal Head Growth
| Second trimester | Second and third trimesters |
|---|---|
|
|
Fetal Neural
| Fetal Fissure Development | Timeline Neural Development |
|---|---|
|
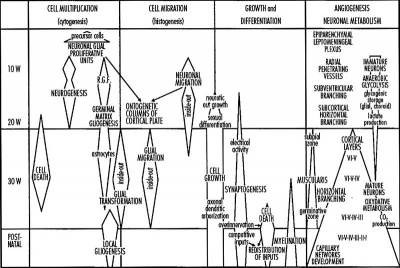
|
| Links: Scaled Fissures 13-21 weeks | Fissures 13-21 weeks | Brain Sylvian Fissure | Scaled Brain and Ventricles 13-21 weeks | Scaled Brain, Ventricles and Ganglia 13-21 weeks | Limbic Tract 13-19 weeks | Brain and Ventricles 13-21 weeks | Sylvian Fissure Movie | Neural System Development | Magnetic Resonance Imaging | Timeline human development |
- Links: Neural System Development
|}
Fetal Endocrine
Pituitary Hormones
- HPA axis established by week 20
- Pituitary functional throughout fetal development
Thyroid Hormone
- required for metabolic activity, also in the newborn
- important for neural development
Parathyroid Hormone
- newborn has total calcium levels (approx 20 grams) accumulated mainly in the 3rd trimester (weeks 28–40)
- fetal parathyroid hormone (PTH) potentially available from 10–12 weeks and PTH does not cross the placenta
- fetus relatively hypercalcemic, active transplacental transport of Ca2+ to fetus
- maternal serum - calcium ions (Ca2+), inorganic phosphate (Pi) and PTH concentrations are within the non-pregnant normal range throughout pregnancy.
- maternal bone turnover increases in the 3rd trimester.
(Based on Endocrinology - Materno—fetal calcium balance)
Pancreatic Hormones
- maternal diabetes can affect fetal pancreas development (increase in fetal islet beta cells).
Gonadal Hormones
- testosterone - required during fetal development for external genital development and internal genital tract in male.
- estrogens - secreted inactive precursor converted to active form by placenta.
- Links: Endocrine System Development | Endocrinology - Control of steroid production in the fetal gonads | Neuroscience - The Effect of Sex Hormones on Neural Circuitry
Fetal Respiratory
- week 4 - 5 embryonic
- week 5 - 17 pseudoglandular
- week 16 - 25 canalicular
- week 24 - 40 terminal sac
- late fetal - 8 years alveolar
Fetal Genital
- ovary and testis development
- external genital development
- testis descent
| Tests descent beginning | Tests descent end |
|---|---|
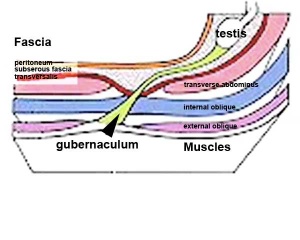
|
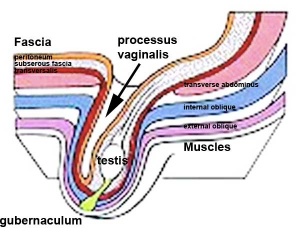
|
- Links: Genital System Development
Fetal Renal
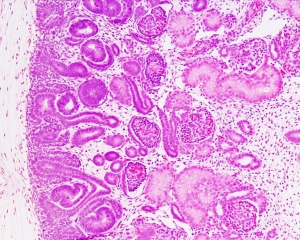
- week 32-34 nephron development completed
- term birth nephron number per kidney about 1 million (300,000 to 2 million)
Nephron development has four identifiable developmental stages:
- Vesicle (V) stage (13-19 weeks, second trimester)
- S-shaped body (S) stage ( 20-24 weeks, second trimester)
- Capillary loop (C) stage (25-29 weeks, third trimester)
- Maturation (M) stage (infants aged 1-6 months, neonatal and postnatal)
- Links: Fetal Renal | renal
Fetal Gastrointestinal
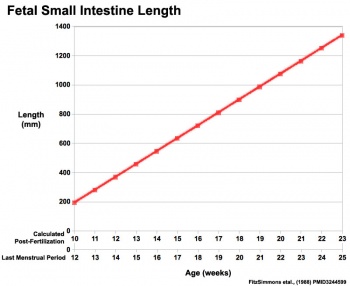
|
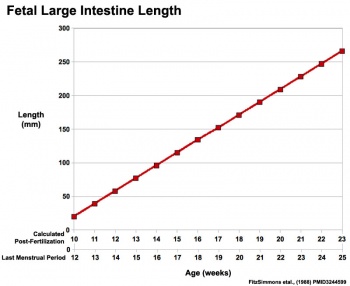
|
Fetal developmental features include: the growth and rotation of intestines initially herniated outside the ventral body wall; changes in mesenteries; development of the blood supply and tract wall.
The initial functions of the tract with amionic fluid swallowing and the accumulation of both secretions and swallowed components within the large intestine as meconium.
- Links: intestine | gastrointestinal
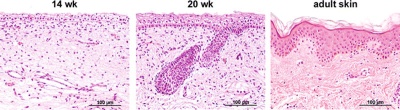
Fetal Integumentary
- Links: integumentary
Fetal Palate
Levator veli palatini skeletal muscle contacted by the lesser palatine nerve.[19] The lesser palatine nerve (posterior palatine nerve) is a branch of the maxillary nerve (CN V2), one of two palatine nerves that descends through the greater palatine canal, and emerges by the lesser palatine foramen
- Links: palate
Fetal Surgical Procedures
There are a range of fatal abnormalities that are potentially amenable to surgical intervention, see recent review link Maternal-Fetal Surgical Procedures.[20]
Some examples include:
- Cardiac Malformations
- Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia
- Myelomeningocele/Spina Bifida
- Obstructive Uropathy
- Sacrococcygeal Teratoma
- Thoracic Lesions
- Twin-Twin Transfusion Syndrome
Maternal
There are many maternal physiological changes during and after pregnancy. This section introduces just the anatomical changes that must occur to simply accomodate the growing fetus.
<html5media width="480" height="360">https://www.youtube.com/embed/yE-l1stWkT4</html5media>
Make Room for Baby! (2017)
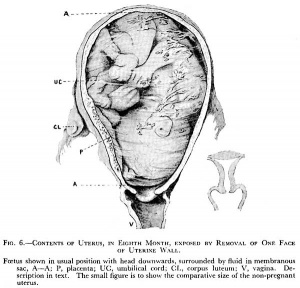
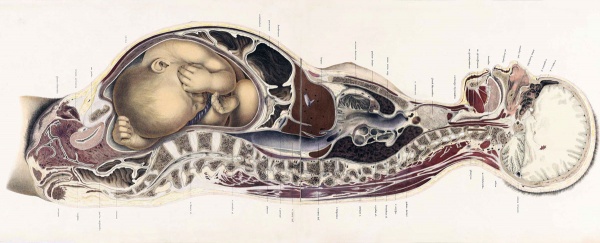
The Position of the Uterus and Fetus at Term (1872).[21]
- Links: Maternal Development | MP4 | Museum of Science and Industry, Chicago - Make Room for Baby! | YouTube
References
- ↑ Streeter GL. Developmental horizons in human embryos (fourth issue). A review of the histogenesis of cartilage and bone. (1949) Carnegie Instn. Wash. Publ. 583, Contrib. Embryol., 33: 149-169. PMID: 18144445
- ↑ Turk E, van den Heuvel MI, Benders MJ, de Heus R, Franx A, Manning JH, Hect JL, Hernandez-Andrade E, Hassan SS, Romero R, Kahn RS, Thomason ME & van den Heuvel MP. (2019). Functional connectome of the fetal brain. J. Neurosci. , , . PMID: 31685648 DOI.
- ↑ Khan S, Vasung L, Marami B, Rollins CK, Afacan O, Ortinau CM, Yang E, Warfield SK & Gholipour A. (2019). Fetal brain growth portrayed by a spatiotemporal diffusion tensor MRI atlas computed from in utero images. Neuroimage , 185, 593-608. PMID: 30172006 DOI.
- ↑ Verbruggen SW, Kainz B, Shelmerdine SC, Hajnal JV, Rutherford MA, Arthurs OJ, Phillips ATM & Nowlan NC. (2018). Stresses and strains on the human fetal skeleton during development. J R Soc Interface , 15, . PMID: 29367236 DOI.
- ↑ Maged A, Youssef G, Hussien A, Gaafar H, Elsherbini M, Elkomy R, Eid M, Abd El-Hamid N & Abdel-Razek AR. (2019). The role of three-dimensional ultrasonography fetal lung volume measurement in the prediction of neonatal respiratory function outcome. J. Matern. Fetal. Neonatal. Med. , 32, 660-665. PMID: 28969488 DOI.
- ↑ Sulak O, Ozgüner G & Malas MA. (2011). Size and location of the kidneys during the fetal period. Surg Radiol Anat , 33, 381-8. PMID: 21110022 DOI.
- ↑ Ishimoto H & Jaffe RB. (2011). Development and function of the human fetal adrenal cortex: a key component in the feto-placental unit. Endocr. Rev. , 32, 317-55. PMID: 21051591 DOI.
- ↑ Cussen L, Scurry J, Mitropoulos G, McTigue C & Gross J. (1990). Mean organ weights of an Australian population of fetuses and infants. J Paediatr Child Health , 26, 101-3. PMID: 2361065
- ↑ Hansen K, Sung CJ, Huang C, Pinar H, Singer DB & Oyer CE. (2003). Reference values for second trimester fetal and neonatal organ weights and measurements. Pediatr. Dev. Pathol. , 6, 160-7. PMID: 12548377 DOI.
- ↑ Archie JG, Collins JS & Lebel RR. (2006). Quantitative standards for fetal and neonatal autopsy. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. , 126, 256-65. PMID: 16891202 DOI.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Westerway SC, Davison A & Cowell S. (2000). Ultrasonic fetal measurements: new Australian standards for the new millennium. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol , 40, 297-302. PMID: 11065037
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Locher H, de Groot JC, van Iperen L, Huisman MA, Frijns JH & Chuva de Sousa Lopes SM. (2015). Development of the stria vascularis and potassium regulation in the human fetal cochlea: Insights into hereditary sensorineural hearing loss. Dev Neurobiol , 75, 1219-40. PMID: 25663387 DOI.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 13.3 Satoh T, Sakurai E, Tada H & Masuda T. (2009). Ontogeny of reticular framework of white pulp and marginal zone in human spleen: immunohistochemical studies of fetal spleens from the 17th to 40th week of gestation. Cell Tissue Res. , 336, 287-97. PMID: 19255788 DOI.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 14.2 14.3 Afif A, Bouvier R, Buenerd A, Trouillas J & Mertens P. (2007). Development of the human fetal insular cortex: study of the gyration from 13 to 28 gestational weeks. Brain Struct Funct , 212, 335-46. PMID: 17962979 DOI.
- ↑ Kadhim HJ, Gadisseux JF & Evrard P. (1988). Topographical and cytological evolution of the glial phase during prenatal development of the human brain: histochemical and electron microscopic study. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. , 47, 166-88. PMID: 3339373
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 Hewer EE. The development of nerve endings in the human foetus. (1935) J Anat. 69(3):369-79. PMID 17104543
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 17.2 Garel C, Chantrel E, Brisse H, Elmaleh M, Luton D, Oury JF, Sebag G & Hassan M. (2001). Fetal cerebral cortex: normal gestational landmarks identified using prenatal MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol , 22, 184-9. PMID: 11158907
- ↑ Paquette LB, Jackson HA, Tavaré CJ, Miller DA & Panigrahy A. (2009). In utero eye development documented by fetal MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol , 30, 1787-91. PMID: 19541779 DOI.
- ↑ Kishimoto H, Yamada S, Kanahashi T, Yoneyama A, Imai H, Matsuda T, Takeda T, Kawai K & Suzuki S. (2016). Three-dimensional imaging of palatal muscles in the human embryo and fetus: Development of levator veli palatini and clinical importance of the lesser palatine nerve. Dev. Dyn. , 245, 123-31. PMID: 26509917 DOI.
- ↑ Maternal-Fetal Surgical Procedures. Walsh WF, Chescheir NC, Gillam-Krakauer M, et al. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2011 Apr. (Comparative Effectiveness Technical Briefs, No. 5.) Report | Comparative Effectiveness Research, Health Care
- ↑ Braune W. An atlas of topographical anatomy after plane sections of frozen bodies. (1877) Trans. by Edward Bellamy. Philadelphia: Lindsay and Blakiston.
Journals
Reviews
Farley D & Dudley DJ. (2009). Fetal assessment during pregnancy. Pediatr. Clin. North Am. , 56, 489-504, Table of Contents. PMID: 19501688 DOI.
Grivell RM, Wong L & Bhatia V. (2009). Regimens of fetal surveillance for impaired fetal growth. Cochrane Database Syst Rev , , CD007113. PMID: 19160321 DOI.
Articles
Search PubMed
Search Pubmed: human fetal development | fetal development | Second Trimester | Third Trimester
Carnegie Fetal
| Carnegie Collection - Fetal | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serial No. | Size CRL (mm) | Grade | Fixative | Embedding Medium | Plane | Thinness (µm) | Stain | Point Score | Sex | Year | Notes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 95 | 40 | catalogued as CRL 40 but development suggests 50 stage. Spinal cord - Kunitomo (1920)[1] Colon - Lineback (1920)[2] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 96 | 50 | Brain venous sinuses - Streeter (1915)[3] Spinal cord - Kunitomo (1920)[1] Brain vascular - Streeter (1921)[4] Brain weight - Jenkins (1921)[5] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 142 | 125 | Spinal cord - Kunitomo (1920)[1] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 145 | 33 | Spinal cord - Kunitomo (1920)[1] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 184 | 50 | 34 vertebrae, 31 spinal ganglia, Spinal cord - Kunitomo (1920)[1] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 211 | 33 | 34 vertebra, 31 spinal ganglia, Spinal cord - Kunitomo (1920)[1] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 217 | 45 | Male | Genital - Spaulding (1921)[6] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 300 | 73 | 85 days, Bone ossification - Mall (1906)[7] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 362 | 30 | Spinal cord - Kunitomo (1920)[1] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 448 | 52 | Colon - Lineback (1920)[2] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 449 | 36 | Spinal cord - Kunitomo (1920)[1] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 538 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 590 | 21 to 23 | Male | Genital - Spaulding (1921)[6] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 607 | 37 | Male | Genital - Spaulding (1921)[6] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 625 | 220 | Temporomandibular joint - Moffatt (1957)[8] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 662 | 80 | Spinal cord - Kunitomo (1920)[1] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 693 | 45 | Male | Genital - Spaulding (1921)[6] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 847 | 58.8 | Male | Genital - Spaulding (1921)[6] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 858 | 57.25 | Temporomandibular joint - Moffatt (1957)[8] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 922 | 37 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 928 | 120 | Spinal cord - Kunitomo (1920)[1] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 948 | 45 | Male | Genital - Spaulding (1921)[6] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 972 | 37 | 34 vertebrae, 30 spinal ganglia, Spinal cord - Kunitomo (1920)[1] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1318 | 37 | Temporomandibular joint - Moffatt (1957)[8] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1388 | 51 | Female | Genital - Spaulding (1921)[6] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1455 | 78.5 | Temporomandibular joint - Moffatt (1957)[8] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1591 | 36 | subcutaneous vascular plexus - Finley (1923)[9] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1656 | 67 | 34 vertebrae, Spinal cord - Kunitomo (1920)[1] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1686 | 40 | Male | Genital - Spaulding (1921)[6] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3990 | 49 | Temporomandibular joint - Moffatt (1957)[8] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4473 | 43 | 20 | Spinal cord meninges - Sensenig (1951)[10] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4475 | 48 | 20 | Spinal cord meninges - Sensenig (1951)[10] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5652 | 49 | Temporomandibular joint - Moffatt (1957)[8] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6581 | 75 | Temporomandibular joint - Moffatt (1957)[8] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7218 | 80 | 20 um | Spinal cord meninges - Sensenig (1951)[10] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1597b | 47 | Female | Genital - Spaulding (1921)[6] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2250a | 40 | Female | Genital - Spaulding (1921)[6] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2250b | 36 | Female | Genital - Spaulding (1921)[6] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| This table currently contains only has embryo number information.
Abbreviations
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
External Links
External Links Notice - The dynamic nature of the internet may mean that some of these listed links may no longer function. If the link no longer works search the web with the link text or name. Links to any external commercial sites are provided for information purposes only and should never be considered an endorsement. UNSW Embryology is provided as an educational resource with no clinical information or commercial affiliation.
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 27) Embryology Fetal Development. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Fetal_Development
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G