Abnormal Development - Hypoxia
| Embryology - 25 Feb 2026 |
|---|
| Google Translate - select your language from the list shown below (this will open a new external page) |
|
العربية | català | 中文 | 中國傳統的 | français | Deutsche | עִברִית | हिंदी | bahasa Indonesia | italiano | 日本語 | 한국어 | မြန်မာ | Pilipino | Polskie | português | ਪੰਜਾਬੀ ਦੇ | Română | русский | Español | Swahili | Svensk | ไทย | Türkçe | اردو | ייִדיש | Tiếng Việt These external translations are automated and may not be accurate. (More? About Translations) |
| Educational Use Only - Embryology is an educational resource for learning concepts in embryological development, no clinical information is provided and content should not be used for any other purpose. |
Introduction
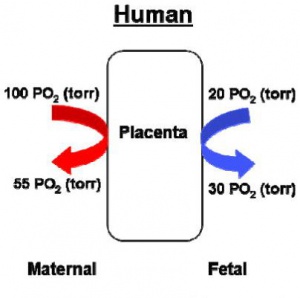
Hypoxia (hypoxiation or anoxemia) is the condition of reduced oxygen content. Postnatally, environmental hypoxia can effect the function/survival of many systems, while prenatal hypoxia (including birth) has been shown to have many detrimental effects for the growing fetus/neonate. It should be noted that normal prenatal development typically occurs in an environment that is hypoxic compared to the maternal or postnatal environment. The hypoxia discussed here refers to reduced maternal oxygen or fetal hypoxia below that occurring in normal development. Exposure to altitude hypoxia normally results in physiological responses that act to preserve maternal and fetal oxygenation.
Maternal smoking, in addition to vasoconstriction, has associated carbon monoxide inhalation that has also been suggested to interfere with delivery of oxygen to the fetus. (More? smoking)
Historically, hypoxia was identified in growing mice and rats as influencing the growth of caudal vertebrae.[1] More recently hypoxia has now been shown to influence many different developing systems including neural, heart and skeletal systems.
Some Recent Findings
|
|
| More recent papers |
|---|
|
This table allows an automated computer search of the external PubMed database using the listed "Search term" text link.
More? References | Discussion Page | Journal Searches | 2019 References | 2020 References Search term: Fetal Hypoxia | Maternal Hypoxia | Developmental Hypoxia | |
| Older papers |
|---|
| These papers originally appeared in the Some Recent Findings table, but as that list grew in length have now been shuffled down to this collapsible table.
See also the Discussion Page for other references listed by year and References on this current page. |
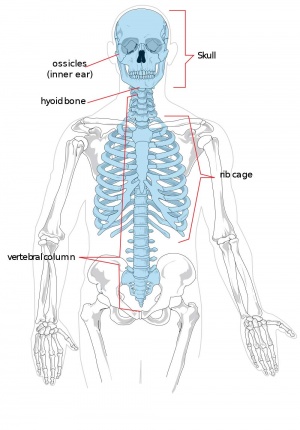
Musculoskeletal Effects
- Links: axial skeleton
Cardiac Effects
Neural Effects
Animal Models
References
- ↑ Hunter C & Clegg EJ. (1973). The effects of hypoxia on the caudal vertebrae of growing mice and rats. J. Anat. , 116, 227-44. PMID: 4783417
- ↑ Ritchie HE, Oakes DJ, Kennedy D & Polson JW. (2017). Early Gestational Hypoxia and Adverse Developmental Outcomes. Birth Defects Res , 109, 1358-1376. PMID: 29105381 DOI.
- ↑ Giampietro PF, Raggio CL, Blank RD, McCarty C, Broeckel U & Pickart MA. (2013). Clinical, genetic and environmental factors associated with congenital vertebral malformations. Mol Syndromol , 4, 94-105. PMID: 23653580 DOI.
Journals
Reviews
Herrera EA, Krause B, Ebensperger G, Reyes RV, Casanello P, Parra-Cordero M & Llanos AJ. (2014). The placental pursuit for an adequate oxidant balance between the mother and the fetus. Front Pharmacol , 5, 149. PMID: 25009498 DOI.
Stanek J. (2013). Hypoxic patterns of placental injury: a review. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. , 137, 706-20. PMID: 23627456 DOI.
Tal R. (2012). The role of hypoxia and hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha in preeclampsia pathogenesis. Biol. Reprod. , 87, 134. PMID: 23034156 DOI.
Jean D & Moore LG. (2012). Travel to high altitude during pregnancy: frequently asked questions and recommendations for clinicians. High Alt. Med. Biol. , 13, 73-81. PMID: 22724609 DOI.
Mwaniki MK, Atieno M, Lawn JE & Newton CR. (2012). Long-term neurodevelopmental outcomes after intrauterine and neonatal insults: a systematic review. Lancet , 379, 445-52. PMID: 22244654 DOI.
Bosco C & Diaz E. (2012). Placental hypoxia and foetal development versus alcohol exposure in pregnancy. Alcohol Alcohol. , 47, 109-17. PMID: 22241888 DOI.
Webster WS & Abela D. (2007). The effect of hypoxia in development. Birth Defects Res. C Embryo Today , 81, 215-28. PMID: 17963271 DOI.
Articles
Search Pubmed
Search Pubmed: Maternal Hypoxia
External Links
External Links Notice - The dynamic nature of the internet may mean that some of these listed links may no longer function. If the link no longer works search the web with the link text or name. Links to any external commercial sites are provided for information purposes only and should never be considered an endorsement. UNSW Embryology is provided as an educational resource with no clinical information or commercial affiliation.
- Victor Chang Cardiac Research Institute - Dunwoodie Lab
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2026, February 25) Embryology Abnormal Development - Hypoxia. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Abnormal_Development_-_Hypoxia
- © Dr Mark Hill 2026, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G