Amniocentesis
| Embryology - 27 Apr 2024 |
|---|
| Google Translate - select your language from the list shown below (this will open a new external page) |
|
العربية | català | 中文 | 中國傳統的 | français | Deutsche | עִברִית | हिंदी | bahasa Indonesia | italiano | 日本語 | 한국어 | မြန်မာ | Pilipino | Polskie | português | ਪੰਜਾਬੀ ਦੇ | Română | русский | Español | Swahili | Svensk | ไทย | Türkçe | اردو | ייִדיש | Tiếng Việt These external translations are automated and may not be accurate. (More? About Translations) |
Introduction
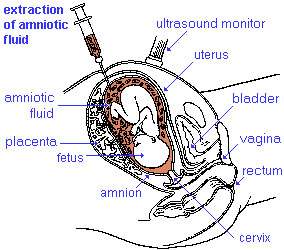
|
Amniocentesis is a prenatal diagnostic test carried out mainly between 14th to 18th week of pregnancy (GA week 14 to 18).
In amniocentesis, amniotic fluid is taken from the uterus, sent to a diagnostic laboratory and embryonic cells isolated from the amniotic fluid. No anaesthetic is required, and a result is usually obtained in about three to four weeks. When the test is carried out by an obstetrician experienced in the technique, the risk of a miscarriage related to the test can be about 1 %. A recent study of the published literature, showed a procedure-related risk of miscarriage following amniocentesis was 0.35% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.07 to 0.63).[1]. A more detailed Cochrane review of amniocentesis and chorionic villus sampling has also bee carried out.[2] This technique has not yet been fully replaced for primary screening by cell-free DNA analysis.[3] |
Some Recent Findings
|
| More recent papers |
|---|
|
This table allows an automated computer search of the external PubMed database using the listed "Search term" text link.
More? References | Discussion Page | Journal Searches | 2019 References | 2020 References Search term: Amniocentesis |
| Older papers |
|---|
|
Testing Comparison
A Chochrane review (2003) comparing prenatal diagnosis showed that early amniocentesis is not a safe as mid-trimester amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling, because of increased pregnancy loss and the increased risk of Talipes equinovarus.[13]
Cells floating in the fluid can be isolated for genetic analysis and the amniotic fluid can also be often assessed for both quality and quantity. The amniotic fluid volume increases as the fetus grows and rate of change varies during the pregnancy.
- up to 8 weeks - increases at the rate of 10 ml/week
- 8 to 13 weeks - increases at the rate of 25 ml/week
- 13 to 21 weeks - increases at the rate of 60 ml/week
- 21 to 33 weeks - amniotic volume increase starts decreasing and eventually plateaus.
- 34 weeks (GA) - peaks at about 800 mL.
- 40 weeks (GA) - about 600 mL at term.
Fluid Facts
- Circulated by fetal inhaling and swallowing.
- Replaced by fetal exhalation and urination.
- Magnesium low levels associated with preeclampsia and diabetes.
- normal magnesium value at 16 weeks (GA) is 1.65 ± 0.16 mg/dL in amniotic fluid and 1.97 ± 0.23 mg/dL in serum.[14]
Amniotic Fluid Stem Cells
It has been shown that human amniotic fluid stem cells (hAFSCs) can be retrieved directly from a small amount of mid-term pregnancy amniotic fluid that can be obtained at the time of diagnostic amniocentesis.[7] These are generally considered as mesenchymal stem cells.
- Links: Stem Cell
Movie
A typical example of ultrasound guided amniotic fluid sampling (amniocentesis) at 16 weeks of pregnancy (Royal Berkshire, Published on Oct 21, 2013).
<html5media width="480" height="360">https://www.youtube.com/embed/aDH0XR_Ko-U</html5media>
- Links: Movie - CVS | YouTube video
Historic
First used as a test of fetal sex in 1955Serr DM, Sachs L & Danon M. (1955). The diagnosis of sex before birth using cells from the amniotic fluid (a preliminary report). Bull Res Counc Isr , 5B, 137-8. PMID: 12307916 , two years later in 1957 was then published as a wider prenatal diagnostic test.[15]
References
- ↑ Beta J, Lesmes-Heredia C, Bedetti C & Akolekar R. (2018). Risk of miscarriage following amniocentesis and chorionic villus sampling: a systematic review of the literature. Minerva Ginecol , 70, 215-219. PMID: 29161799 DOI.
- ↑ Alfirevic Z, Navaratnam K & Mujezinovic F. (2017). Amniocentesis and chorionic villus sampling for prenatal diagnosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev , 9, CD003252. PMID: 28869276 DOI.
- ↑ Gray KJ & Wilkins-Haug LE. (2018). Have we done our last amniocentesis? Updates on cell-free DNA for Down syndrome screening. Pediatr Radiol , 48, 461-470. PMID: 29550862 DOI.
- ↑ Jummaat F, Ahmad S & Mohamed Ismail NA. (2019). 5-Year review on amniocentesis and its maternal fetal complications. Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig , 40, . PMID: 31539354 DOI.
- ↑ Salomon LJ, Sotiriadis A, Wulff CB, Odibo A & Akolekar R. (2019). Risk of miscarriage following amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling: systematic review of the literature and updated meta-analysis. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol , , . PMID: 31124209 DOI.
- ↑ Kim SR, Choi EJ, Kim YJ, Kim TY & Lee YJ. (2018). Prenatally Diagnosed Rare Trisomy 16 Mosaicism in Human Amniotic Fluid Cells in the Second Trimester: A Case Report. Dev Reprod , 22, 199-203. PMID: 30023470 DOI.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Geffen KT, Ben-Zvi O, Weitzner O, Peleg A, Biron-Shental T & Sukenik-Halevy R. (2017). The yield and complications of amniocentesis performed after 24 weeks of gestation. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. , 296, 69-75. PMID: 28540575 DOI.
- ↑ Orczyk-Pawilowicz M, Jawien E, Deja S, Hirnle L, Zabek A & Mlynarz P. (2016). Metabolomics of Human Amniotic Fluid and Maternal Plasma during Normal Pregnancy. PLoS ONE , 11, e0152740. PMID: 27070784 DOI.
- ↑ Oh KJ, Park JS, Norwitz ER, Kim SM, Kim BJ, Park CW, Jun JK & Syn HC. (2012). Proteomic biomarkers in second trimester amniotic fluid that identify women who are destined to develop preeclampsia. Reprod Sci , 19, 694-703. PMID: 22534327 DOI.
- ↑ Visnjevac J, Mikić AN, Nikolić A & Visnjevac N. (2010). [Comparative analysis of amniotic fluid lamellar body count and foam stability test as indices of fetal lung maturity]. Med. Pregl. , 63, 747-52. PMID: 21553448
- ↑ Weisz B, Book M, Lipitz S, Katorza E, Achiron R, Grossman Z & Shrim A. (2011). Fetal outcome and amniocentesis results in pregnancies complicated by varicella infection. J Obstet Gynaecol Can , 33, 720-724. PMID: 21749748 DOI.
- ↑ McIntosh JJ, McHugh K & Haas DM. (2012). Difficulties in establishing routine amniocentesis for preterm labor evaluation. J. Matern. Fetal. Neonatal. Med. , 25, 313-4. PMID: 21663523 DOI.
- ↑ Alfirevic Z, Sundberg K & Brigham S. (2003). Amniocentesis and chorionic villus sampling for prenatal diagnosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev , , CD003252. PMID: 12917956 DOI.
- ↑ Bocos Terraz JP, Izquierdo Álvarez S, Bancalero Flores JL, González López A & Escanero Marcén JF. (2011). Magnesium concentration in amniotic fluid in the early weeks of the second trimester of pregnancy. BMC Res Notes , 4, 185. PMID: 21672230 DOI.
- ↑ PARRISH HM, LOCK FR & ROUNTREE ME. (1957). Lack of congenital malformations in normal human pregnancies after transabdominal amniocentesis. Science , 126, 77. PMID: 13442649
Reviews
Evans MI, Wapner RJ. Invasive prenatal diagnostic procedures 2005. Semin Perinatol. 2005 Aug;29(4):215-8.
Ball RH. Invasive fetal testing. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2004 Apr;16(2):159-62.
Articles
Fajnzylber E, Hotz VJ & Sanders SG. (2010). An economic model of amniocentesis choice. Adv Life Course Res , 15, 11-26. PMID: 21516255 DOI.
Search PubMed
Search PubMed: Amniocentesis | Amniotic fluid
- ART - Assisted Reproductive Technology a general term to describe all the clinical techniques used to aid fertility.
- blastomere biopsy - An ART preimplantation genetic diagnosis technique carried out at cleavage stage (day 3), excluding poor quality embryos, detects chromosomal abnormalities of both maternal and paternal origin. May not detect cellular mosaicism in the embryo.
- blastocyst biopsy - An ART preimplantation genetic diagnosis technique carried out at blastocyst stage (day 4-5), removes several trophoblast (trophoderm) cells, detects chromosomal abnormalities of both maternal and paternal origin and may detect cellular mosaicism.
- cell-free fetal deoxyribonucleic acid - (cfDNA) refers to fetal DNA circulating and isolated from the plasma portion of maternal blood. Can be performed from GA 10 weeks as a first-tier test or as a second-tier test, with women with increased probability on combined first trimester screening offered cfDNA or diagnostic testing.
- false negative rate - The proportion of pregnancies that will test negative given that the congenital anomaly is present.
- false positive rate - The proportion of pregnancies that will test positive given that the congenital anomaly is absent.
- free β human chorionic gonadotrophin - beta-hCG subunit of hCG used as a diagnostic marker for: early detection of pregnancy, Trisomy 21, spontaneous abortion, ectopic pregnancy, hydatidiform mole or choriocarcinoma.
- multiples of the median - (MoM) A multiple of the median is a measure of how far an individual test result deviates from the median and is used to report the results of medical screening tests, particularly where the results of the individual tests are highly variable.
- negative predictive value - The probability that a congenital anomaly is absent given that the prenatal screening test is negative.
- Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing - (NIPT) could refer to ultrasound or other imaging techniques, but more frequently used to describe analysis of cell-free fetal DNA circulating in maternal blood.
- polar body biopsy - (PB biopsy) An ART preimplantation genetic diagnosis technique that removes either the first or second polar body from the zygote. As these are generated by oocyte meiosis they detects chromosomal abnormalities only on the female genetics.
- positive predictive value - The probability that a congenital anomaly is present given that the prenatal screening test is positive.
- pre-implantation genetic diagnosis - (PGD, pre-implantation genetic screening) a diagnostic procedure for embryos produced through Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART, in vitro fertilisation, IVF) for genetic diseases that would generate developmental abnormalities or serious postnatal diseases.
- prenatal screening sensitivity - (detection rate) The probability of testing positive on a prenatal screening test if the congenital anomaly is present.
- prenatal screening specificity - The probability of testing negative on a prenatal screening test if the congenital anomaly is absent.
- quadruple test (maternal serum testing of a-fetoprotein Template:AFP, free B-hCG or total hCG, unconjugated estriol, and inhibin A) is a fetal chromosomal anomaly test usually carried out later in pregnancy (GA 14 to 20 weeks).
- single nucleotide polymorphisms - (SNPs) the variation in a single DNA nucleotide that occurs at a specific position in the genome.
- triple test - (maternal serum testing of a-fetoprotein Template:AFP, free B-hCG or total hCG, and unconjugated estriol) is a fetal chromosomal anomaly test usually carried out later in pregnancy (GA 14 to 20 weeks).
| Other Terms Lists |
|---|
| Terms Lists: ART | Birth | Bone | Cardiovascular | Cell Division | Endocrine | Gastrointestinal | Genital | Genetic | Head | Hearing | Heart | Immune | Integumentary | Neonatal | Neural | Oocyte | Palate | Placenta | Radiation | Renal | Respiratory | Spermatozoa | Statistics | Tooth | Ultrasound | Vision | Historic | Drugs | Glossary |
External Links
External Links Notice - The dynamic nature of the internet may mean that some of these listed links may no longer function. If the link no longer works search the web with the link text or name. Links to any external commercial sites are provided for information purposes only and should never be considered an endorsement. UNSW Embryology is provided as an educational resource with no clinical information or commercial affiliation.
- NIH Medline Plus Amniocentesis | Interactive Tutorial
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 27) Embryology Amniocentesis. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Amniocentesis
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
