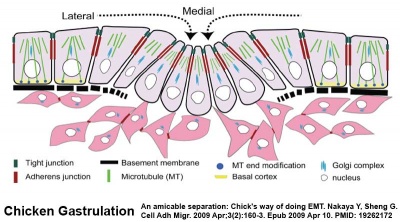
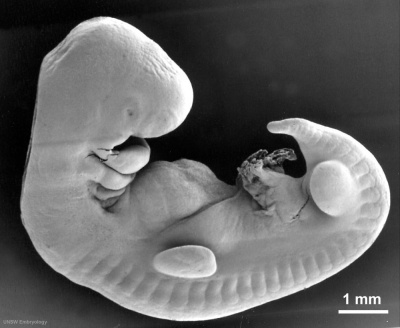
Lecture - Mesoderm Development
| Embryology - 27 Apr 2024 |
|---|
| Google Translate - select your language from the list shown below (this will open a new external page) |
|
العربية | català | 中文 | 中國傳統的 | français | Deutsche | עִברִית | हिंदी | bahasa Indonesia | italiano | 日本語 | 한국어 | မြန်မာ | Pilipino | Polskie | português | ਪੰਜਾਬੀ ਦੇ | Română | русский | Español | Swahili | Svensk | ไทย | Türkçe | اردو | ייִדיש | Tiếng Việt These external translations are automated and may not be accurate. (More? About Translations) |
Introduction
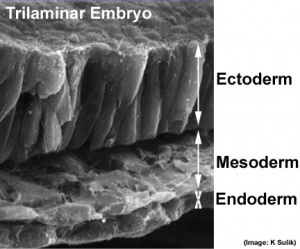
Having now reached week 3 in development we will now begin to look separately at the 3 transient germ layers (ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm) formed by the process of gastrulation. Beginning with the mesoderm layer, the middle embryonic connective tissue (mesenchyme) layer. Transient in terms of temporary structures that will become something else later in development.
Mesoderm initially forms a multilayered cellular layer separating ectoderm and endoderm, mesoderm also lies outside the embryo as extra-embryonic mesoderm (covered in placenta lecture). Embryonic mesoderm will form most of the adult connective tissues and muscle.
Towards the end of week 3 this layer begins to "partition" into different transient components based upon their location within the layer and the signals the cells are receiving. This partitioning process can be either in terms of cell differentiation or structural. This lecture will describe these initial regions and the tissues they will eventually form. Note that later lectures (muscle, skeleton, limb, integumentary and heart) will revisit these tissues later in development.
Objectives
|
These are mesoderm cells migrating from the primitive stria. |
Lecture Resources
| Movies | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| References | |
|---|---|
| Hill, M.A. (2020). UNSW Embryology (20th ed.) Retrieved April 27, 2024, from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au | |
| Moore, K.L., Persaud, T.V.N. & Torchia, M.G. (2015). The developing human: clinically oriented embryology (10th ed.). Philadelphia: Saunders. | The following chapter links only work with a UNSW connection. |
| Schoenwolf, G.C., Bleyl, S.B., Brauer, P.R., Francis-West, P.H. & Philippa H. (2015). Larsen's human embryology (5th ed.). New York; Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone. | The following chapter links only work with a UNSW connection. |
| Recent Research |
|---|
| Some recent papers that relate to mesoderm development.
<pubmed>27506116</pubmed> <pubmed>27385009</pubmed> <pubmed>27437584</pubmed> |
Take the Mesoderm Quiz.
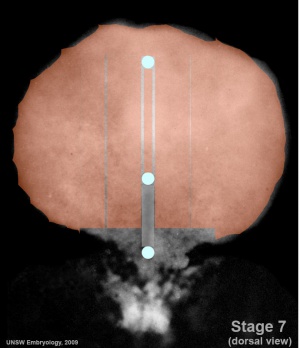
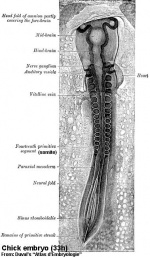
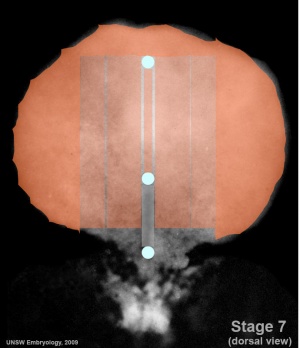
Notochord (Axial mesoderm)
- Embryo Stage 7 (dorsal)
Mesoderm
- generated from epiblast cells migrating through the primitive streak
- epiblast cells expressing fibroblast growth factor (FGF2)
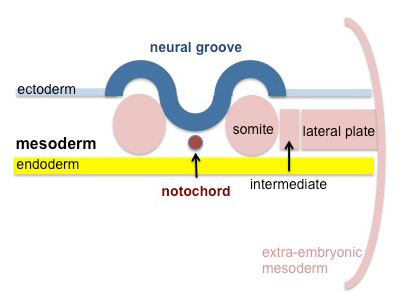
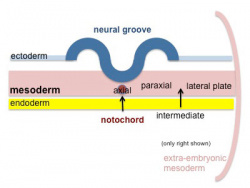
- forms a layer between ectoderm and endoderm with notochord down midline
- present before neural tube formation
- divides initially into 3 components
- Embryo Stage 7 (dorsal)
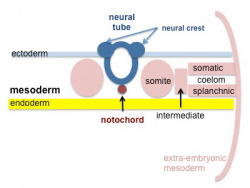
- Paraxial mesoderm - somites - musculoskeletal structures
- Intermediate mesoderm - urogenital (kidney and genital)
- Lateral plate mesoderm - body wall, body cavities, cardiovascular and GIT structures
Mesoderm Development
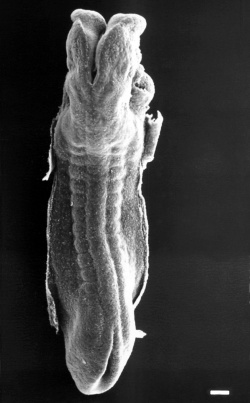
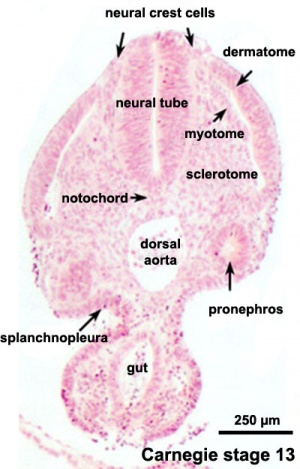
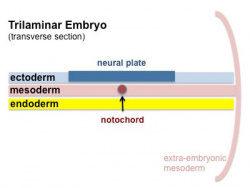
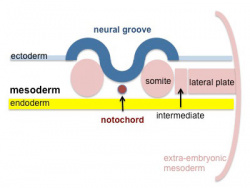
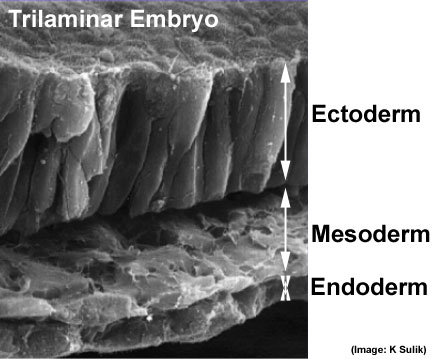
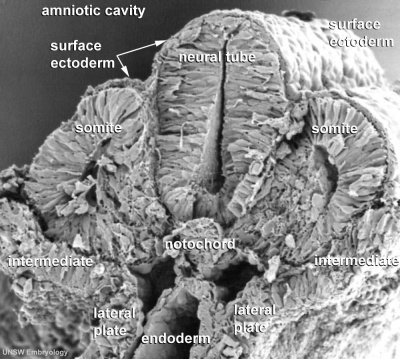
The four images below beginning at week 3 show cross-sections of the trilaminar embryo and the sequence of mesoderm development.
|
|
|
|
Mesoderm Overview
|
|
| Week 3
Trilaminar embryo Compare this week 3 trilaminar embryo with the week 4 embryo.
(Note - 2 these images are not to scale) |
Week 4
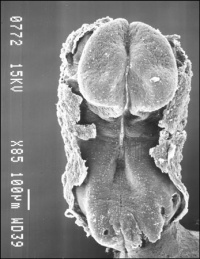
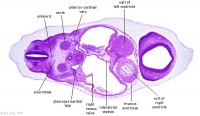
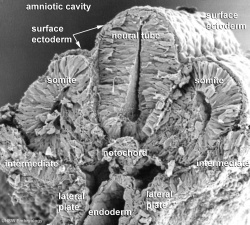
Scanning electron micrograph of a cross-section of a human embryo at week 4 (stage 11). Note the mesoderm structures now present and their relative position and size within the embryo. Compare the mesoderm structures to those formed by ectoderm (neural tube and epidermis) and endoderm (epithelia of developing gastrointestinal tract). |
| Human Embryo Week 4 (Carnegie stage 10) - transverse section | |
|---|---|
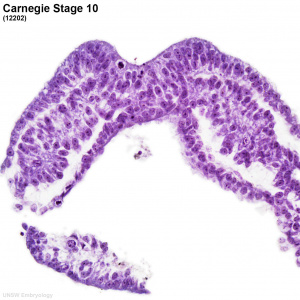
|
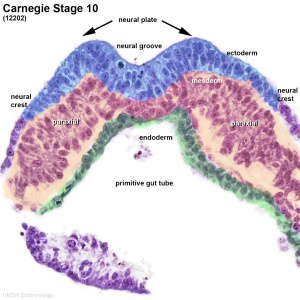
|
Paraxial Mesoderm
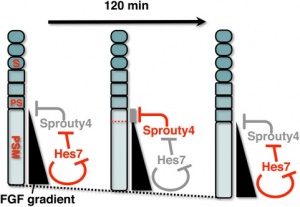
Model for Sprouty4 and FGF in mouse mesoderm segmentation
Somite Formation
|
|
|
Somite Specification
- Different segmental level somites have to generate different segmental body structures?
- somite has to form different tissues?
- Somite Differentiation
- Compartmentalization accompanied by altered patterns of expression of Pax genes within the somite
- rostro-caudal axis appears regulated by Pax/Hox expression, family of DNA binding transcription factors
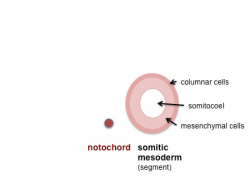
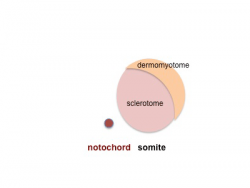
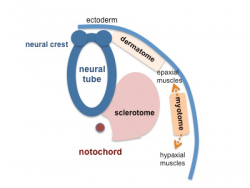
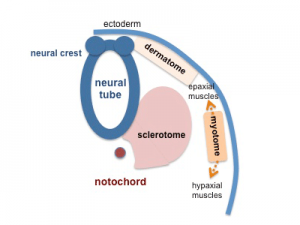
Somite initially forms 2 main components
- ventromedial- sclerotome forms vertebral body and intervertebral disc
- dorsolateral - dermomyotome forms dermis and skeletal muscle
Sclerotome
- sclerotome later becomes subdivided
- rostral and caudal halves separated laterally by von Ebner's fissure
- half somites contribute to a single vertebral level body
- other half intervertebral disc
- therefore final vertebral segmentation ‚"shifts"
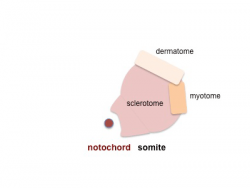
Dermomyotome
- later divides into dorsal dermatome and ventral myotome
- This topic of muscle and skeleton development will be covered in 2 later lectures Musculoskeletal Development and Limb Development)
- lateral myotome edge migrates at level of limbs
- upper limb first then lower
- mixes with somatic mesoderm
- dermotome continues to contribute cells to myotome
Myotome
- Myotome component of Somite
- epaxial myotome (dorsomedial quarter) forms the dorsal epimere (erector spinae)
- hypaxial myotome (dorsolateral quarter) forms the ventral hypomere, 3 primary muscle layers which are different at neck, thorax and abdomen
Muscle
- Myoblast determining transcription factor MyoD is first expressed in the dorsomedial quadrant of the still epithelial somite whose cells are not yet definitely committed
- basic Helix Loop Helix
- from myotome
Muscle Development Abnormalities
- Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
- Embryonic muscle development normal and changes occur postnatally
- X-linked dystrophy, large gene encoding cytoskeletal protein - Dystrophin
- progressive wasting of muscle, die late teens
- Becker Muscular Dystrophy, milder form, adult onset
Intermediate Mesoderm
|
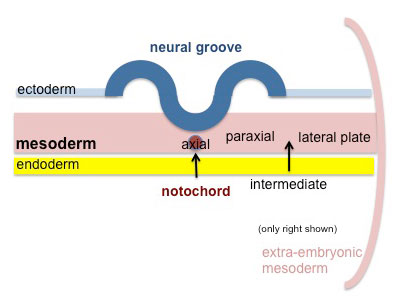
|
Lateral Plate Development
- lying at the surrounding edge of he embryonic disc
- a cavity begins in this week to form within the mesoderm itself
Intraembryonic Coelom
Somatic Mesoderm
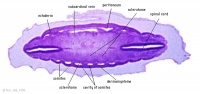
The intraembryonic coelom divides the lateral plate into 2 portions
|
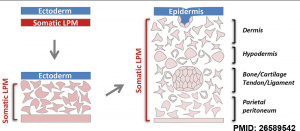
Lateral plate somatic mesoderm[1] |
Splanchnic Mesoderm
|
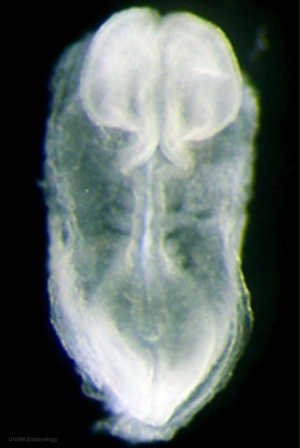
|
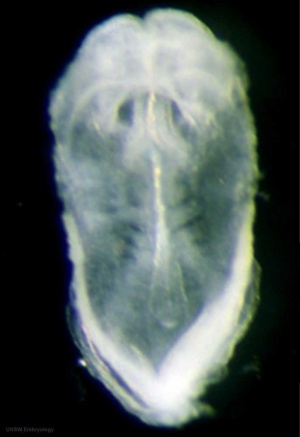
|
- Carnegie Stages: 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | About Stages | Timeline
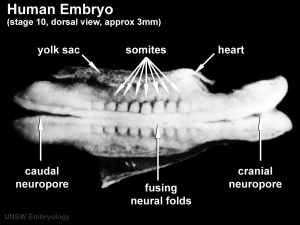
Somitogenesis
(not to scale) |
||||
| gastrulation, notochordal process | ||||
| primitive pit, notochordal canal | ||||
 |
Somite Number 1 - 3 neural folds, cardiac primordium, head fold | |||
| Somite Number 4 - 12 neural fold fuses | ||||
| Somite Number 13 - 20 rostral neuropore closes | ||||
| Somite Number 21 - 29 caudal neuropore closes | ||||
| Somite Number 30 leg buds, lens placode, pharyngeal arches | ||||
Stage 14
- Links: Somitogenesis
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 27) Embryology Lecture - Mesoderm Development. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Lecture_-_Mesoderm_Development
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G