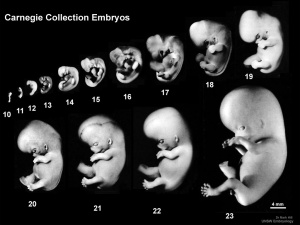
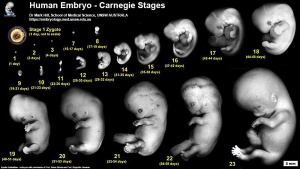
Human Embryo Collections
Introduction
While many universities hold collections of embryos from many species, very few have well-characterised collections of embryos showing human development. Many of those that are available are historic in nature, consist of histological sections, some with limited information about the embryo history.
There are groups now taking advantage of new imaging techniques to either re-evaluate these historic collections, or analysing new embryonic material. Some of these new databases are being made available online for research purposes.
Remember that this current site is for educational use only.
- Carnegie Stages: 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | About Stages | Timeline
Carnegie Collection
(Carnegie Institution, USA)
- Begun by Franklin Mall in the early 1900's.
- Many of these embryos were used in the historic papers in the Contributions to Embryology series - Carnegie Institution of Washington Series.
- Franklin Mall Links: Franklin Mall | 1891 26 Day Human Embryo | 1905 Blood-Vessels of the Brain | 1906 Human Ossification | 1910 Manual of Human Embryology 1 | 1912 Manual of Human Embryology 2 | 1911 Mall Human Embryo Collection | 1912 Heart Development | 1915 Tubal Pregnancy | 1916 Human Magma in Normal and Pathological Development | 1917 Frequency Human Abnormalities | 1917 Human Embryo Cyclopia | 1918 Embryo Age | 1918 Appreciation | 1934 Franklin Mall biography PDF | Mall photograph | Mall painting | Mall painting | Carnegie Stages | Carnegie Embryos | Carnegie Collection | Category:Franklin Mall | Contributions to Embryology Series
Kyoto Collection
(Kyoto University, Japan)
- Begun by Dr. Hideo Nishimura in 1961 and has over 44,000 human embryo specimens.
- Polydactyly in human embryos[1]
- 129 embryos with polydactyly in 36,380 human conceptuses obtained through induced abortion during the period from 1962 to 1974.
- Human embryo imaging with a super-parallel magnetic resonance (MR) microscope[2]
- Links: Kyoto Collection
Hamilton-Boyd Collection
(Cambridge University, UK)
- Collected by Professor JD Boyd, Professor of Anatomy at the University in the 1950s and 1960s.
- Held at the University of Cambridge.
- Professor Boyd wrote the monographs 'Human Embryology' (Hamilton, Boyd and Mossman) and 'The Human Placenta' (Boyd and Hamilton).
- Collection is only histological sections (no tissue blocks remain)
- Links: Boyd Collection
Blechschmidt Collection
(University of Goettingen, Germany)
- Erich Blechschmidt (1904–92) independently developed new methods of embryo reconstruction.
- Director of Göttingen University’s Anatomical Institute from 1942 until 1973.
- 200,000 serial sections of embryos and 64 models.
- Professor E. Blechschmidt embryological collection were assigned Carnegie Nos. 10315-10434 in 1972.
- Professor Blechschmidt's wish was to have his collection combined with the Carnegie Collection.
Central Laboratory for Human Embryology
(University of Washington, USA)
- begun August 1963.
- after 18years consists of 5,200 specimens.
- range from very young embryos to full-term fetus.
Ziegler Models
Not a collection as such, but a historic series of wax models made in the 1880s based upon the embryos of Prof. Wilhelm His, Leipzig. His had earlier prepared a series of freehand models. These models are still the basis of some teaching models used today.
The Carnegie Institute later in the early 1900's developed many additional models. (More? Carnegie Models)
Carnegie Stage Table
Weeks shown in the table below are embryonic post ovulation age, for clinical Gestational Age (GA) measured from last menstrual period, add 2 weeks.
(not to scale) |
||||
 |
fertilized oocyte, zygote, pronuclei | |||
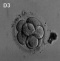 |
morula cell division with reduction in cytoplasmic volume, blastocyst formation of inner and outer cell mass | |||
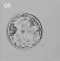 |
loss of zona pellucida, free blastocyst | |||
| attaching blastocyst | ||||
(week 2) |
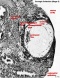 |
implantation | ||
 |
extraembryonic mesoderm, primitive streak, gastrulation | |||
| gastrulation, notochordal process | ||||
| primitive pit, notochordal canal | ||||
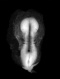 |
Somitogenesis Somite Number 1 - 3 neural folds, cardiac primordium, head fold | |||
| Somite Number 4 - 12 neural fold fuses | ||||
| Somite Number 13 - 20 rostral neuropore closes | ||||
| Somite Number 21 - 29 caudal neuropore closes | ||||
| Somite Number 30 leg buds, lens placode, pharyngeal arches | ||||
| lens pit, optic cup | ||||
| lens vesicle, nasal pit, hand plate | ||||
| nasal pits moved ventrally, auricular hillocks, foot plate | ||||
| finger rays | ||||
| ossification commences | ||||
| straightening of trunk | ||||
| upper limbs longer and bent at elbow | ||||
| hands and feet turned inward | ||||
| eyelids, external ears | ||||
| rounded head, body and limbs | ||||
The embryos shown in the table are from the Kyoto and Carnegie collection and other sources.
References
Reviews
<pubmed>14193295</pubmed>
Articles
<pubmed>19521537</pubmed> <pubmed>17183461</pubmed>| Int J Dev Biol. <pubmed>5681297</pubmed>
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, May 4) Embryology Human Embryo Collections. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Human_Embryo_Collections
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G