Cardiovascular System - Hypoplastic Left Heart: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
|-bgcolor="F5FAFF" | |-bgcolor="F5FAFF" | ||
| | | | ||
* '''Are There Head Volume Alterations at 11 to 14 Weeks in Fetuses with Congenital Heart Defects? A First Trimester Case Series'''<ref name=PMID27308099><pubmed> | * '''Are There Head Volume Alterations at 11 to 14 Weeks in Fetuses with Congenital Heart Defects? A First Trimester Case Series'''<ref name=PMID27308099><pubmed>PMID 27308099</pubmed></ref> "This study aims to assess head volume (HV) alterations at 11 to 14 weeks in fetuses with congenital heart defects (CHD). Methods A retrospective case-control study on 100 normal and 26 CHD fetuses was conducted. ...Despite the small sample size, our case series suggests that alterations in HV may potentially be apparent as early as 11 to 14 weeks in CHD fetuses, particularly those with HLH. Larger prospective studies are needed to validate our findings." | ||
|} | |} | ||
{| class="wikitable mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" | {| class="wikitable mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" | ||
Revision as of 15:56, 22 June 2016
| Embryology - 2 May 2024 |
|---|
| Google Translate - select your language from the list shown below (this will open a new external page) |
|
العربية | català | 中文 | 中國傳統的 | français | Deutsche | עִברִית | हिंदी | bahasa Indonesia | italiano | 日本語 | 한국어 | မြန်မာ | Pilipino | Polskie | português | ਪੰਜਾਬੀ ਦੇ | Română | русский | Español | Swahili | Svensk | ไทย | Türkçe | اردو | ייִדיש | Tiếng Việt These external translations are automated and may not be accurate. (More? About Translations) |
Introduction
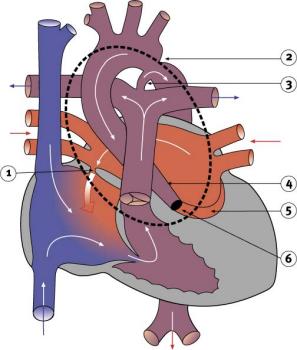
Characterized by hypoplasia (underdevelopment or absence) of the left ventricle obstructive valvular and vascular lesion of the left side of the heart.
ICD-10 Q23.4 Hypoplastic left heart syndrome Atresia, or marked hypoplasia of aortic orifice or valve, with hypoplasia of ascending aorta and defective develop-ment of left ventricle (with mitral valve stenosis or atresia).
Some Recent Findings
|
| More recent papers |
|---|
|
This table allows an automated computer search of the external PubMed database using the listed "Search term" text link.
More? References | Discussion Page | Journal Searches | 2019 References | 2020 References Search term: Hypoplastic Left Heart <pubmed limit=5>Hypoplastic Left Heart</pubmed> |
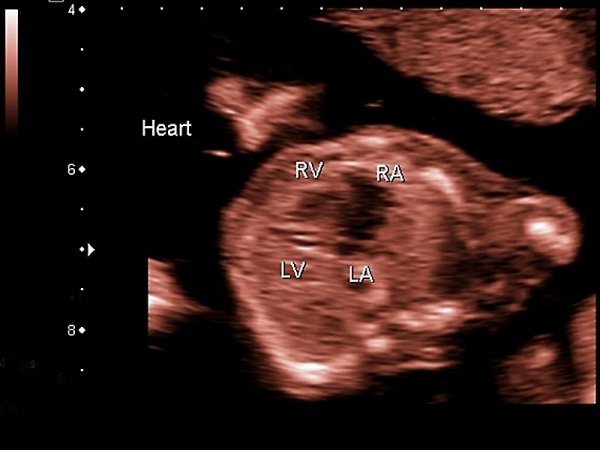
Ultrasound
- Links: Ultrasound
History
Treatment
International Classification of Diseases
The International Classification of Diseases (ICD) World Health Organization's classification used worldwide as the standard diagnostic tool for epidemiology, health management and clinical purposes. This includes the analysis of the general health situation of population groups. It is used to monitor the incidence and prevalence of diseases and other health problems. Within this classification "congenital malformations, deformations and chromosomal abnormalities" are (Q00-Q99) but excludes "inborn errors of metabolism" (E70-E90).
Congenital malformations of the circulatory system (Q20-Q28)
- ICD-10 Code: Q21.1 Atrial septal defect
Q21 Congenital malformations of cardiac septa
Cardiovascular Abnormalities
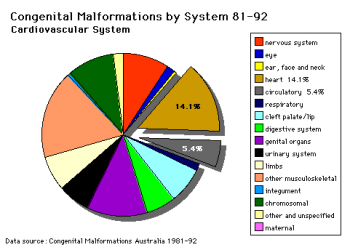
Heart defects and preterm birth are the most common causes of neonatal and infant death. The long-term development of the heart combined with extensive remodelling and post-natal changes in circulation lead to an abundance of abnormalities associated with this system.
A UK study literature showed that preterm infants have more than twice as many cardiovascular malformations (5.1 / 1000 term infants and 12.5 / 1000 preterm infants) as do infants born at term and that 16% of all infants with cardiovascular malformations are preterm. (0.4% of live births occur at greater than 28 weeks of gestation, 0.9% at 28 to 31 weeks, and 6% at 32 to 36 weeks. Overall, 7.3% of live-born infants are preterm)[2]
"Baltimore-Washington Infant Study data on live-born cases and controls (1981-1989) was reanalyzed for potential environmental and genetic risk-factor associations in complete atrioventricular septal defects AVSD (n = 213), with separate comparisons to the atrial (n = 75) and the ventricular (n = 32) forms of partial AVSD. ...Maternal diabetes constituted a potentially preventable risk factor for the most severe, complete form of AVSD." [3]
In addition, there are in several congenital abnormalities that exist in adults (bicuspid aortic valve, mitral valve prolapse, and partial anomalous pulmonary venous connection) which may not be clinically recognized.
References
Reviews
<pubmed></pubmed> <pubmed></pubmed> <pubmed></pubmed>
Articles
<pubmed></pubmed> <pubmed></pubmed> <pubmed></pubmed> <pubmed></pubmed>
Search Pubmed
Search Pubmed: Search PubMed
External Links
External Links Notice - The dynamic nature of the internet may mean that some of these listed links may no longer function. If the link no longer works search the web with the link text or name. Links to any external commercial sites are provided for information purposes only and should never be considered an endorsement. UNSW Embryology is provided as an educational resource with no clinical information or commercial affiliation.
- OMIM Atrial Septal Defect
- Medline Plus
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, May 2) Embryology Cardiovascular System - Hypoplastic Left Heart. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Cardiovascular_System_-_Hypoplastic_Left_Heart
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G