HM Practical - Blood Vessel Histology
| Embryology - 6 Mar 2026 |
|---|
| Google Translate - select your language from the list shown below (this will open a new external page) |
|
العربية | català | 中文 | 中國傳統的 | français | Deutsche | עִברִית | हिंदी | bahasa Indonesia | italiano | 日本語 | 한국어 | မြန်မာ | Pilipino | Polskie | português | ਪੰਜਾਬੀ ਦੇ | Română | русский | Español | Swahili | Svensk | ไทย | Türkçe | اردو | ייִדיש | Tiếng Việt These external translations are automated and may not be accurate. (More? About Translations) |
Introduction
HMA Practical 3 for Monday July 23 and Wednesday July 25.
HMA Practical 3 Virtual Slides
This page provides histology support information for blood vessel structure.
Disclaimers
- does not form part of the actual practical class based upon the virtual slides.
- does not cover the pathology content.
- does not cover lymphatic vessels, they are covered in the SH lymphatic practical.
- HMA Links: Blood Vessel Histology | Cardiac Histology | Histology | Histology Stains | Blood Vessel Development | HMA Practical 3 Virtual Slides | HMA Practical 8 Virtual Slides
Aims
- To understand the microscopic appearance of normal blood vessels of different dimensions and to recognize changes in the arterial wall as seen in atherosclerosis.
Key concepts
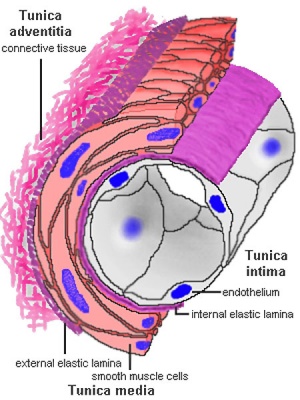
- Normal structure of large and medium blood vessels; tunica intima, tunica media & tunica adventitia and capillaries.
- Relation of blood vessel structure to function.
- Abnormalities of arteries in atherosclerosis.
Practical class activities
Note the features listed for the following virtual slides linked from: http://vslides.unsw.edu.au
- Aorta (elastic artery) - (2 virtual slides) Showing layers of the wall: tunica intima, tunica media and tunica adventitia. The media is extensive with multiple layers of smooth muscle mixed with elastic laminae, some of which are fenestrated. Vasa vasorum and nervi vasorum in the tunica adventitia; capillaries in adipose tissue surrounding the artery. (Note: capillaries are roughly 8 micrometers in diameter, enough to see 1 or 2 red blood cells inside the lumen).
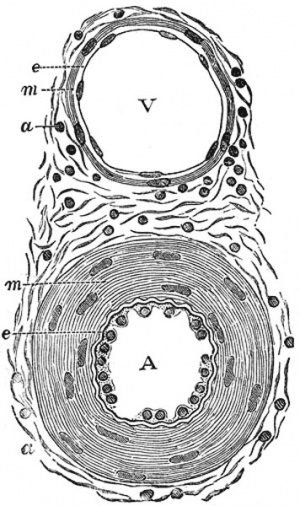
- Medium sized (muscular) artery and vein - (2 virtual slides) Distinct layers of wall of an artery: tunica intima, internal elastic lamina, tunica media (many layers of smooth muscle), external elastic lamina (multiple layers) extending into tunica adventitia; In the vein, the same 3 tunics can be seen but the tunica media is reduced, and the tunica adventitia is wider compared to the artery.
- Vena cava - Showing the 3 layers with an extensive tunica adventitia. Special features are the longitudinal smooth muscle bundles in the tunica adventitia.
- Atherosclerosis, artery - (Pathology is not covered on this histology support page) This section of a muscular artery from a 60-year-old male is very different from the normal vessels that you have just looked at. An adaptive tutorial is available to assist you to identify the features in this section.
Flow
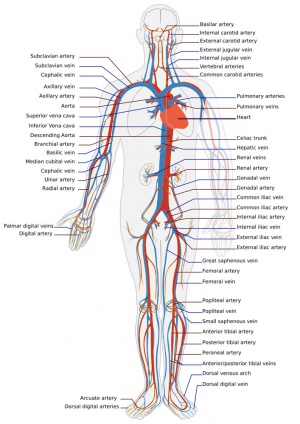
Starting at the Heart:
- Elastic arteries (conducting) - large arteries
- examples - aorta, brachiocephalic, common carotid, subclavian, vertebral, common iliac arteries.
- thin wall compared to diameter.
- tunica media more elastic fibres, less smooth muscle.
- pressure reservoir.
- Muscular arteries (distributing) - medium sized arteries
- examples - axillary, brachial, radial, intercostal, splenic, mesenteric, femoral, popliteal, tibial.
- capable of greater vasoconstriction/vasodilation.
- adjust blood flow rate.
- Arterioles - small arteries deliver blood to capillaries.
- tunica interna, media (smooth muscle few elastic fibres), externa (elastic and collagen fibres)
- regulate blod flow into capillaries.
- Capillaries - smallest vessels.
- endothelium and basement membrane.
- main site of exchange (nutrients, waste).
- connect arterioles and venules.
- Venules - smallest veins.
- uniting capillaries drain into veins.
- further from capillary bed tunica media increases.
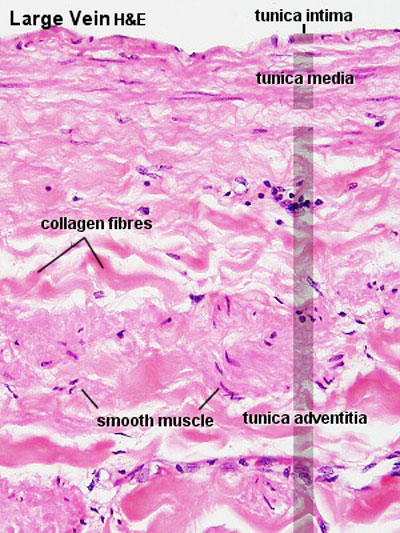
- Veins - same 3 coats as arteries.
- tunica interna and tunica media thinner than companion artery, tunica externa thicker.
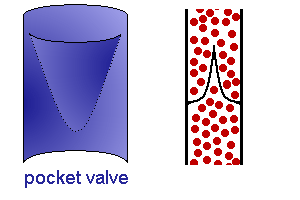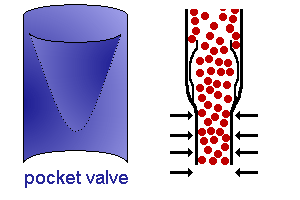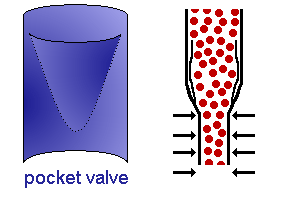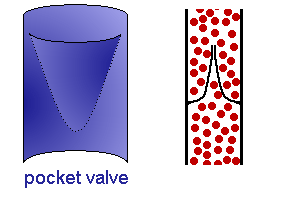
- many veins contain valves to prevent back flow.
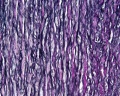
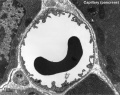
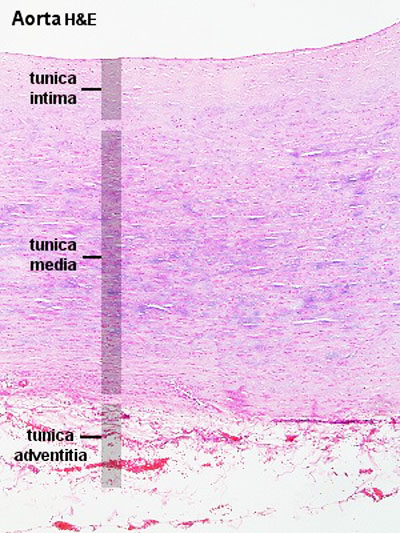
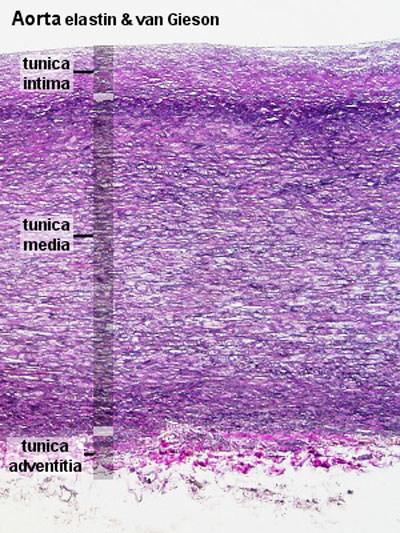
Aorta
tunica intima
- delimits the vessel wall towards the lumen of the vessel and comprises its endothelial lining (typically simple, squamous) and associated connective tissue.
- Endothelium - simple squamous epithelium, cells organised longitudinally, joined by tight and gap junctions.
- Internal elastic lamina (layer, membrane) not obvious due to may elastic layers.
- the tunica intima of elastic arteries is thicker than in other arteries.
tunica media
- layer of circumferential smooth muscle and variable amounts of connective tissue.
- A second layer of elastic fibers, the external elastic lamina, is located beneath the smooth muscle.
- Components
- Elastin - fenestrated sheets or lamellae between muscle layers.
- Smooth Muscle Cells - arranged in layers.
- Collagen fibre and ground substance.
tunica adventitia
- mainly of connective tissue fibres.
- The tunica adventitia blends with the connective tissue surrounding the vessel, and the definition of the outer limit of the tunica adventitia is therefore somewhat arbitrary.
- Thin - collagen fibres, elastic fibres (not lamellae), fibroblasts, macrophages.
- vasa vasorum - (Latin, "vessels of the vessels") the network of small blood vessels that supply large blood vessels.
Labeled
|
|
| Aorta overview | Aorta elastin |
Unlabeled
Arteries
- elastic arteries - the tunica intima of elastic arteries is thicker than in other arteries.
- muscular arteries
- arterioles - smaller vessels with a diameter below 0.1 - 0.5 mm. Endothelial cells are smaller than in larger arteries, and the nucleus and surrounding cytoplasm may 'bulge' slightly into the lumen of the arteriole. Endothelium rests on a internal elastic lamina, which may also be incomplete. The tunica media consists of 1-3 concentric layers of smooth muscle cells. Difficult to identify an external elastic lamina or to distinguish the tunica adventitia from the connective tissue surrounding the vessel. Smooth muscle regulates tissue blood flow and arterioles receive both sympathetic and parasympathetic innervation.
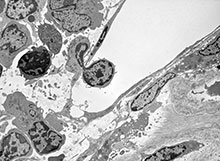
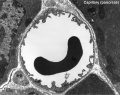
- capillary - arise from the final branches of arterioles, lined by a endothelial cells, each cell forms the wall around the entire circumference of a segment of the capillary. The lumen only allows 1-2 red blood cells to fit side by side in the capillary. Three main types of capillaries (continuous, fenestrated and discontinuous) can be distinguished based on features of their endothelium.
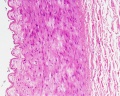
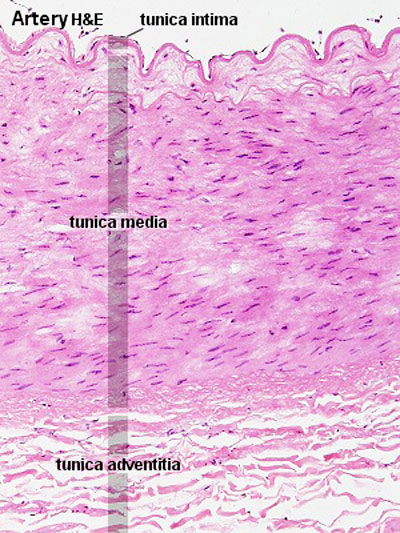
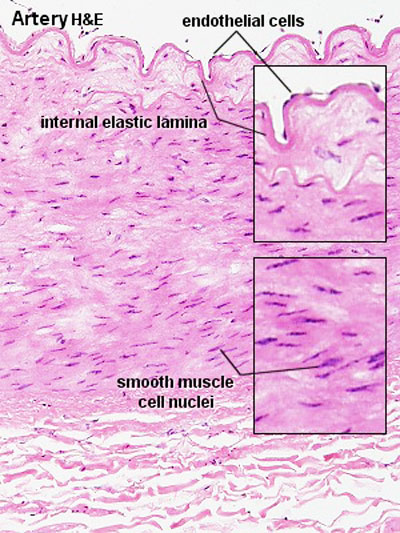
Muscular Arteries
- Medium sized (muscular) artery and vein - (2 virtual slides)
- Distinct layers of wall of an artery: tunica intima, internal elastic lamina, tunica media (many layers of smooth muscle), external elastic lamina (multiple layers) extending into tunica adventitia;
- Neurovascular bundle
- In the vein, the same 3 tunics can be seen but the tunica media is reduced, and the tunica adventitia is wider compared to the artery.
- nervi vasorum - (nervi vascularorum) vascular nerves that innervate both arteries and veins and control vessel vasodilation and vasoconstriction.
- The toluidine blue stains nucleic acids blue and polysaccharides purple and also increases the sharpness of histology slide images.
|
|
| Artery overview | Artery detail |

|
|
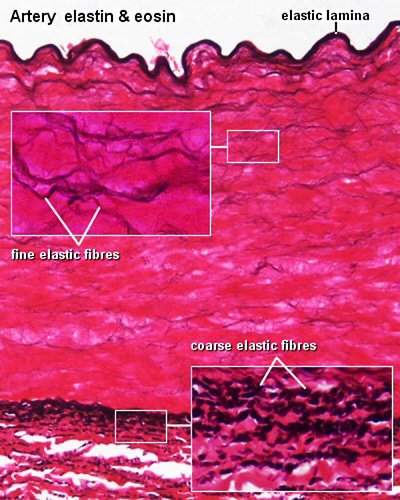
| Artery elastin | Artery elastin detail |
Unlabeled
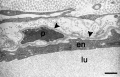
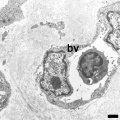
Capillaries
Electron Micrographs
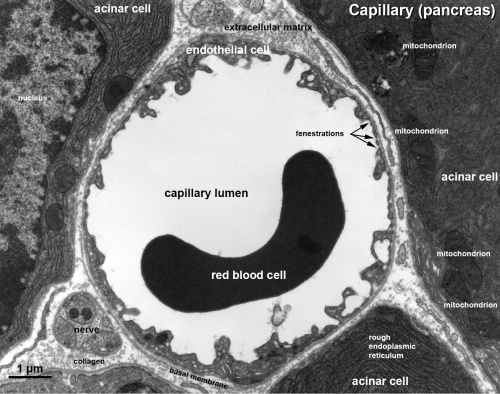
|
|
Vena cava
Vein
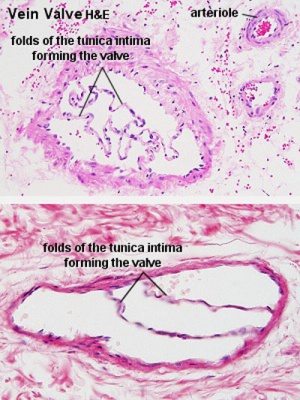
Small to medium-sized veins are characterised by the presence of valves.
Venule with endothelium (simple squamous epithelium) lining. (Stain - Haematoxylin Eosin)
Note the obvious difference between this small venule and a capillary is the increased lumen size.
Terms
- artifact - changes and distortions introduced to the normal tissue structure by the histological processing. Common artifacts include: folds (gives the tissue a darker appearance), tears (rips in the tissue can be seen in epithelia), shrinkage when tissues loose mainly liquid through histological processing, and cuts often used in tissue preparation.
- elastic fibres - coloured light yellow in fresh tissues, special stains required to show in tissue sections. Composed of the protein elastin, can be stretched and return to original length.
- elastic laminae - layer of elastic tissue in a blood vessel wall.
- external elastic lamina - elastic tissue layer that lies within the tunica media of blood vessels.
- internal elastic lamina - (internal elastic lamella) elastic tissue layer that forms the outermost part of the tunica intima of blood vessels.
- nervi vasorum - (nervi vascularorum) vascular nerves that innervate both arteries and veins and control vessel vasodilation and vasoconstriction.
- pericyte - (Rouget cells, mural cells) a contractile cell located around endothelial cells of capillaries, venules and larger lymphatic vessels. Role in regulating blood flow, phagocytosis, and signalling.
- tunica - (Latin, "tunic") refers to a coat or coating surrounding a blood vessel.
- tunica adventitia - (adventitia, tunica externa) the outermost layer of a blood vessel surrounding the tunica media. Anchors blood vessel to surrounding tissue and consists of many collagen fibres.
- tunica intima - (intima) innermost layer in both arteries and veins.
- tunica media - (media) middle layer in both arteries and veins.
- vasa vasorum - (Latin, "vessels of the vessels") the network of small blood vessels that supply large blood vessels.
- vena cava - the largest veins in the body, formed by the superior vena cava (SVC) and inferior vena cava (IVC).
Search Pubmed: Atherosclerosis |
Atherosclerosis images
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2026, March 6) Embryology HM Practical - Blood Vessel Histology. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/HM_Practical_-_Blood_Vessel_Histology
- © Dr Mark Hill 2026, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G