Cardiac Embryology
| Embryology - 26 Feb 2026 |
|---|
| Google Translate - select your language from the list shown below (this will open a new external page) |
|
العربية | català | 中文 | 中國傳統的 | français | Deutsche | עִברִית | हिंदी | bahasa Indonesia | italiano | 日本語 | 한국어 | မြန်မာ | Pilipino | Polskie | português | ਪੰਜਾਬੀ ਦੇ | Română | русский | Español | Swahili | Svensk | ไทย | Türkçe | اردو | ייִדיש | Tiếng Việt These external translations are automated and may not be accurate. (More? About Translations) |
| Cardiac Embryology | Begin Basic | Begin Intermediate | Begin Advanced |
This website is an educational resource designed to teach human cardiac embryology and is a Medicine ILP project carried out by Phoebe Norville. Heart development represents an important area of both embryological and clinical studies, predominantly due to the high incidence of congenital heart disease in the community. Therefore this website aims to teach cardiac embryology to students of all ages with varying degrees of knowledge in the area. The module contains three different levels:
- Basic - begin here if you are new to heart embryology (high school level)
- Intermediate - begin here if you have some background in heart embryology (university level)
- Advanced - begin here after you have completed the earlier levels and have a good background in heart embryology (university level)
Your initial knowledge level determines your start level. Each level is then divided into a sequence of units/pages that roughly correspond to the sequence of heart development. The more detailed, the more pages; basic level has only 3 units, intermediate has 7 units, and the advanced module has 9 units. You can work through each level in sequence or jump to a more detailed level within each unit.
Each unit also has two sets of navigation panels and a timeline, to help work through the cardiac embryology modules.
| Top navigation panel
This panel allows you to easily move between pages within the same level or to jump to the beginning of a different level; green is the basic module, yellow the intermediate, and red the advanced. |
| ||||||||
| Bottom navigation panel
This panel allows you to easily move through the information sequentially as well as moving to the same content in a different level of complexity. |
|||||||||
| Timelines
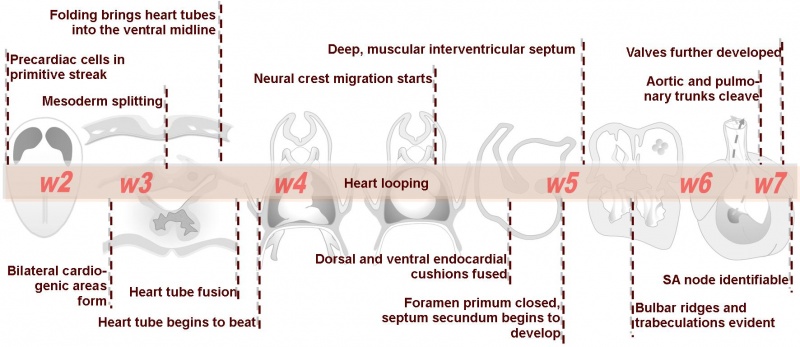
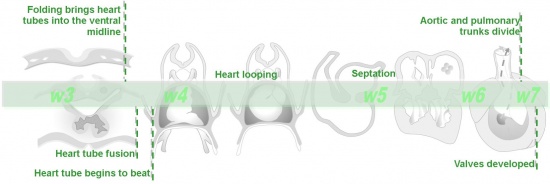
A timeline will appear at the top of each page to help you understand the order and context of the events occurring in cardiac embryology. |
Many of the concepts taught in embryology are best represented with animations or diagrams. Most of the pictures appear in the units as thumbnails. To see the images more clearly simply click on the picture which will take you to the original-sized version. To return to the module simply click the back button in your browser window.
Basic module
Intermediate module
Advanced module
| Cardiac Embryology | Begin Basic | Begin Intermediate | Begin Advanced |
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Aorta: The largest artery in the human body originating in the left ventricle. The aorta ascends, arches over the heart and then descends through the abdomen.
Atrioventricular canal: Junction between the primitive atrium and primitive ventricle in the embryo. This canal splits to later form two atrioventricular canals which consequently form the valves of the adult heart.
Caudal: Anatomical term referring to structures that are more towards the tail.
Cranial: Anatomical term referring to structures that are more towards the head.
Dorsal: Anatomical term referring to structures that are more towards the back.
Endocardial cushions: Swellings of migrated cells on the inner lining of the heart.
Foramen primum: Original space between the septum primum and the fused endocardial cushions as the septum primum grows towards the cushions.
Foramen secundum: Refers to the coalesced perforations in the septum primum after it has fused with the endocardial cushions.
Interventricular septum: Wall of muscular tissue growing from the base of the heart dividing the primitive ventricle into the left and right ventricles.
Lateral: Anatomical term referring to structures that are away from the midline.
Left atrium: Upper cavity in the left side of the heart. The left atrium forms from the division of the primitive atrium into left and right sides.
Left ventricle: Lower cavity on the left side of the heart. The left ventricle forms from the division of the primitive ventricle into left and right sides.
Medial: Anatomical term referring to structures towards the midline.
Outflow tract: Section of the heart tube where blood exits. The outflow tract forms the major arteries leaving the heart to supply blood to the lungs and rest of the body: the pulmonary artery and the aorta.
Pharynx: (Or throat) Forms the initial segment of the upper respiratory tract divided anatomically into three regions: nasopharynx, oropharynx, and laryngopharynx (hypopharynx). Anatomically extends from the base of the skull to the level of the sixth cervical vertebra.
Primitive atrium: Common cavity in the upper portion of the developing heart. Later divides to form the left and right atria.
Primitive ventricle: Common cavity in the lower portion of the developing heart. Later divides to form the left and right ventricles.
Pulmonary trunk: A vessel that arises from the right ventricle of the heart, extends upward, and divides into the right and left pulmonary arteries that transport deoxygenated blood to the lungs.
Right atrium: Upper cavity in the right side of the heart. The right atrium forms from the division of the primitive atrium into left and right sides.
Right ventricle: Lower cavity on the right side of the heart. The right ventricle forms from the division of the primitive ventricle into left and right sides.
Septum primum: Original structure growing from the roof of the heart towards the endocardial cushions dividing the primitive atrium.
Septum secundum: Second structure growing to the right of the septum primum dividing the primitive atrium.
Sinus venosus: An early developmental cardiovascular structure, thin walled cavity, forming the input to developing heart which has 3 venous inputs (vitelline vein, umbilical vein, common cardinal vein). Later in heart development this structure gets incorporated into the wall of the future right atrium.
Ventral: Anatomical term referring to structures that are more towards the front.
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2026, February 26) Embryology Cardiac Embryology. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Cardiac_Embryology
- © Dr Mark Hill 2026, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G