Developmental Signals - Retinoic acid
From Embryology
Notice - Mark Hill
Currently this page is only a template and will be updated (this notice removed when completed).Introduction
| Factor Links: AMH | hCG | BMP | sonic hedgehog | bHLH | HOX | FGF | FOX | Hippo | LIM | Nanog | NGF | Nodal | Notch | PAX | retinoic acid | SIX | Slit2/Robo1 | SOX | TBX | TGF-beta | VEGF | WNT | Category:Molecular |
Some Recent Findings
|
Recent References | References
Fetal Gonad
Immunohistochemical localisation of retinoid receptor expression in the human fetal gonad[2]
Neural
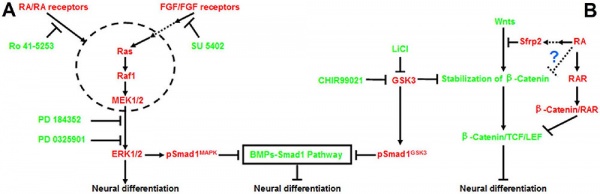
Model retinoic acid extracellular signal-regulated kinase and Wnt pathway interactions[3]
RA Is Not Required for Radial Expansion of the Embryonic Cortex
References
- ↑ <pubmed>23563268</pubmed>
- ↑ Childs AJ, Cowan G, Kinnell HL, Anderson RA, Saunders PTK (2011) Retinoic Acid Signalling and the Control of Meiotic Entry in the Human Fetal Gonad. PLoS ONE 6(6): e20249. PMID 21674038 | PLoS One
- ↑ <pubmed>19642999</pubmed>
Articles
<pubmed>21673209</pubmed>| Can Fam Physician
Search Pubmed
Search Bookshelf Retinoic acid
Search Pubmed Now: Retinoic acid
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, June 23) Embryology Developmental Signals - Retinoic acid. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Developmental_Signals_-_Retinoic_acid
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G