Developmental Signals - Nanog
| Embryology - 26 Feb 2026 |
|---|
| Google Translate - select your language from the list shown below (this will open a new external page) |
|
العربية | català | 中文 | 中國傳統的 | français | Deutsche | עִברִית | हिंदी | bahasa Indonesia | italiano | 日本語 | 한국어 | မြန်မာ | Pilipino | Polskie | português | ਪੰਜਾਬੀ ਦੇ | Română | русский | Español | Swahili | Svensk | ไทย | Türkçe | اردو | ייִדיש | Tiếng Việt These external translations are automated and may not be accurate. (More? About Translations) |
Introduction
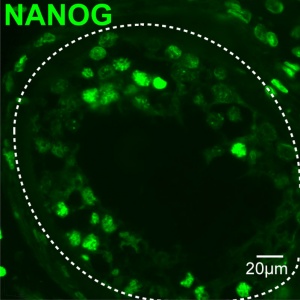
NANOG (Nanog) plays a central role in regulating self-renewal in pluripotent stem cells and tumor cells. Human NANOG is a transcription factor protein of 305 amino acids with a conserved homeodomain motif that is localized to the nucleus.
First identified in mouse ES cells in a 2003 study[2], the author (Chambers) named the factor after an Irish myth, Tír na nÓg ("Land of the Young") as it makes stem cells immortal.
| Factor Links: AMH | hCG | BMP | sonic hedgehog | bHLH | HOX | FGF | FOX | Hippo | LIM | Nanog | NGF | Nodal | Notch | PAX | retinoic acid | SIX | Slit2/Robo1 | SOX | TBX | TGF-beta | VEGF | WNT | Category:Molecular |
Some Recent Findings
|
| More recent papers |
|---|
|
This table allows an automated computer search of the external PubMed database using the listed "Search term" text link.
More? References | Discussion Page | Journal Searches | 2019 References | 2020 References Search term: Nanog |
| Older papers |
|---|
Human NANOG Family
Nanog belongs to the NKL subclass homeoboxes and pseudogenes.
| Table - Human Nanog Family - pseudogenes | ||||
| Approved Symbol |
Approved Name | Previous Symbols | Chromosome | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NANOG | Nanog homeobox | FLJ12581, FLJ40451 | 12p13.31 | |
| NANOG P1 | Nanog homeobox pseudogene 1 | NANOG2 | 12p13.31 | |
| NANOG P2 | Nanog homeobox pseudogene 2 | NANOGP4 | 2q36.1 | |
| NANOG P3 | Nanog homeobox pseudogene 3 | 6p12.1 | ||
| NANOG P4 | Nanog homeobox pseudogene 4 | NANOGP2 | 7p14.3 | |
| NANOG P5 | Nanog homeobox pseudogene 5 | 9q31.1 | ||
| NANOG P6 | Nanog homeobox pseudogene 6 | 10q24.2 | ||
| NANOG P7 | Nanog homeobox pseudogene 7 | NANOGP3 | 14q32.12 | |
| NANOG P8 | Nanog homeobox retrogene P8 | 15q14 | ||
| NANOG P9 | Nanog homeobox pseudogene 9 | Xq12 | ||
| NANOG P10 | Nanog homeobox pseudogene 10 | Xp11.3 | ||
| NANOG P11 | Nanog homeobox pseudogene 11 | 6q25.2 | ||
| Links: Developmental Signals - Nanog | OMIM | HGNC | Tbx Family | ||||
| Human NANOG Family | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Classification
Functions
Required for embryonic stem cell self-renewal.
Blastocyst - Inner Cell Mass
In the early mouse embryo, Nano expression appears to be related to maintain of pluripotency in the blastocyst inner cell mass epiblast layer.[5]
Nanog expression pattern four phases:
- cleavage stages - very low levels
- morula stage - increased stochastically, no correlation with future cell fates.
- blastocyst stage (after 32-cell stage) - inner cell mass expression was up-regulated.
- blastocyst stage onwards - primitive endoderm repressed in an FGF signalling-dependent manner.
- Links: Morula | Blastocyst | Mouse Development | FGF
Spermatogenesis
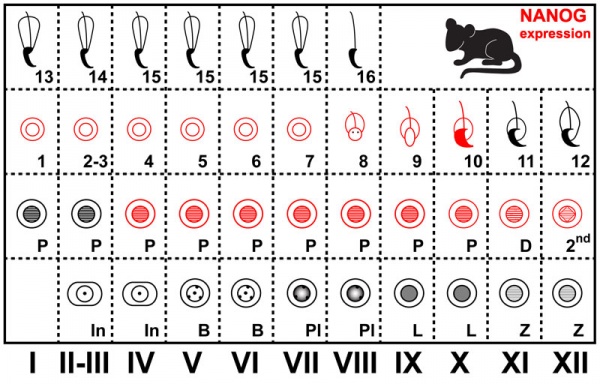
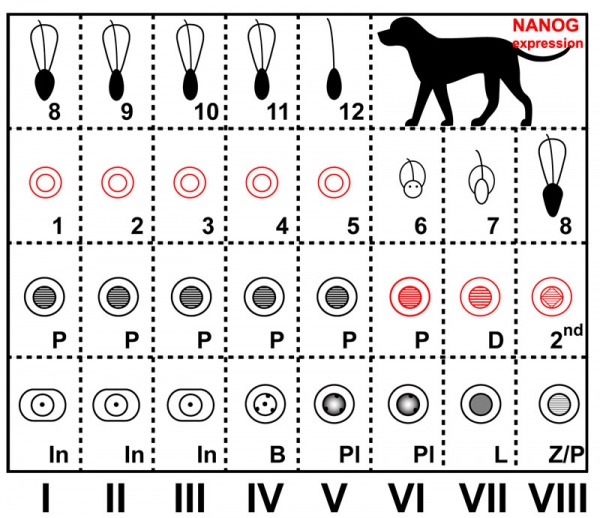
The cartoons below show nanog expression in mouse and dog during spermatogenesis.[1]
Signaling Pathway
![Two-level process for the induction of stem cell differentiation[7]](/embryology/images/d/da/Stem_cell_nanog_model.png)
|
| Two-level process for the induction of stem cell differentiation[7] |
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Kuijk EW, de Gier J, Lopes SM, Chambers I, van Pelt AM, Colenbrander B & Roelen BA. (2010). A distinct expression pattern in mammalian testes indicates a conserved role for NANOG in spermatogenesis. PLoS ONE , 5, e10987. PMID: 20539761 DOI.
- ↑ Chambers I, Colby D, Robertson M, Nichols J, Lee S, Tweedie S & Smith A. (2003). Functional expression cloning of Nanog, a pluripotency sustaining factor in embryonic stem cells. Cell , 113, 643-55. PMID: 12787505 DOI.
- ↑ Zhang M, Leitch HG, Tang WWC, Festuccia N, Hall-Ponsele E, Nichols J, Surani MA, Smith A & Chambers I. (2018). Esrrb Complementation Rescues Development of Nanog-Null Germ Cells. Cell Rep , 22, 332-339. PMID: 29320730 DOI.
- ↑ Gagnon JA, Obbad K & Schier AF. (2018). The primary role of zebrafishnanogis in extra-embryonic tissue. Development , 145, . PMID: 29180571 DOI.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Komatsu K & Fujimori T. (2015). Multiple phases in regulation of Nanog expression during pre-implantation development. Dev. Growth Differ. , 57, 648-56. PMID: 26660234 DOI.
- ↑ Moretto-Zita M, Jin H, Shen Z, Zhao T, Briggs SP & Xu Y. (2010). Phosphorylation stabilizes Nanog by promoting its interaction with Pin1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. , 107, 13312-7. PMID: 20622153 DOI.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Glauche I, Herberg M & Roeder I. (2010). Nanog variability and pluripotency regulation of embryonic stem cells--insights from a mathematical model analysis. PLoS ONE , 5, e11238. PMID: 20574542 DOI.
Reviews
Blinka S & Rao S. (2017). Nanog Expression in Embryonic Stem Cells - An Ideal Model System to Dissect Enhancer Function. Bioessays , 39, . PMID: 28977693 DOI.
Marucci L. (2017). Nanog Dynamics in Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells: Results from Systems Biology Approaches. Stem Cells Int , 2017, 7160419. PMID: 28684962 DOI.
Zhang W, Sui Y, Ni J & Yang T. (2016). Insights into theNanoggene: A propeller for stemness in primitive stem cells. Int. J. Biol. Sci. , 12, 1372-1381. PMID: 27877089 DOI.
Search Pubmed
Search Pubmed Now: Nanog
Search OMIM Nanog
External Links
External Links Notice - The dynamic nature of the internet may mean that some of these listed links may no longer function. If the link no longer works search the web with the link text or name. Links to any external commercial sites are provided for information purposes only and should never be considered an endorsement. UNSW Embryology is provided as an educational resource with no clinical information or commercial affiliation.
- Entrez Gene - NANOG Nanog homeobox - Homo sapiens
- OMIM - NANOG
- HGNC - NKL subclass homeoboxes
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2026, February 26) Embryology Developmental Signals - Nanog. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Developmental_Signals_-_Nanog
- © Dr Mark Hill 2026, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G