Trophoblast: Difference between revisions
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
* '''sCTB''' - subsyncytial cytotrophoblasts (this layer grows increasingly discontinuous in later trimesters) | * '''sCTB''' - subsyncytial cytotrophoblasts (this layer grows increasingly discontinuous in later trimesters) | ||
* '''EVT''' - extravillous cytotrophoblasts (anchor the villous tree in the decidua) | * '''EVT''' - extravillous cytotrophoblasts (anchor the villous tree in the decidua) | ||
==Syncitiotrophoblasts== | |||
==Cytotrophoblasts== | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
Revision as of 23:49, 12 October 2010
Introduction
(Greek, trophe = "nutrition" and -blast, a primordial cell) During early development the trophoblast cells have an important contribution to extraembryonic tissues (fetal placenta and membranes) and processes of early development (adplantation, implantation and endocrine support of pregnancy).
In humans, week 1 blastocyst formation the outer layer of cells (adjacent to the zona pellucida) form a flat squamous epithelial layer of cells, the trophoblast layer. Week 2 following blastocyst hatching the trophoblast layer is involved with initial adhesion to the uterine wall and subsequent implantation within the wall. During this period the trophoblast layer differentiates into two distinct layers (syncitiotrophoblast and cytotrophoblast).
- Links: Blastocyst | Implantation | Week 2 | Week 3 | Placenta Development
Some Recent Findings
|
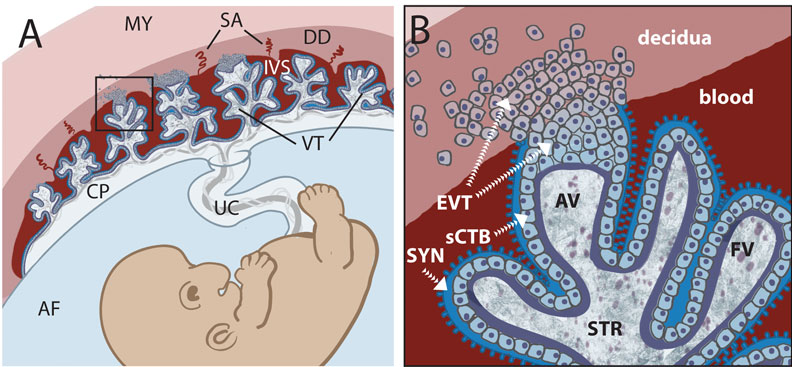
Trophoblast and Placental Villi
Early placental development cartoon showing trophoblast contribution to placental villi.[3]
Legend
- SYN - syncytiotrophoblasts
- sCTB - subsyncytial cytotrophoblasts (this layer grows increasingly discontinuous in later trimesters)
- EVT - extravillous cytotrophoblasts (anchor the villous tree in the decidua)
Syncitiotrophoblasts
Cytotrophoblasts
References
Reviews
Articles
<pubmed>19582159</pubmed>
Search PubMed
Search Pubmed: Trophoblast | syncitiotrophoblast | cytotrophoblast |
Embryo Week: Week 1 | Week 2 | Week 3 | Week 4 | Week 5 | Week 6 | Week 7 | Week 8 | Week 9
- Carnegie Stages: 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | About Stages | Timeline
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, May 18) Embryology Trophoblast. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Trophoblast
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G