Week 2: Difference between revisions
| Line 67: | Line 67: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
== Implantation == | |||
The second week of human development is concerned with the process of implantation and the differentiation of the blastocyst into early embryonic and placental forming structures. | |||
* implantation commences about '''day 6 to 7''' | |||
* '''Adplantation''' - begins with initial adhesion to the uterine epithelium | |||
** blastocyst then slows in motility, "rolls" on surface, aligns with the inner cell mass closest to the epithelium and stops | |||
* '''Implantation''' - migration of the blastocyst into the uterine epithelium, process complete by about '''day 9''' | |||
* '''coagulation plug''' - left where the blastocyst has entered the uterine wall '''day 12''' | |||
'''Normal Implantation Sites''' - in uterine wall superior, posterior, lateral | |||
==Week 2 Abnormalities== | ==Week 2 Abnormalities== | ||
===Abnormal Implantation=== | |||
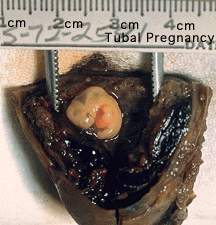
[[Image:Tubal pregnancy.gif|thumb|Ectopic tubal pregnancy]] | |||
[http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/week2_2.htm Ectopic Pregnancy] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Movies/usoundab/Ectopic1.htm Movie - Ectopic pregnancy ultrasound] | |||
Abnormal implantation sites or Ectopic Pregnancy occurs if implantation is in uterine tube or outside the uterus. | |||
* sites - external surface of uterus, ovary, bowel, gastrointestinal tract, mesentry, peritoneal wall | |||
* If not spontaneous then, embryo has to be removed surgically | |||
'''Tubal pregnancy''' - 94% of ectopic pregnancies | |||
* if uterine epithelium is damaged (scarring, pelvic inflammatory disease) | |||
* if zona pellucida is lost too early, allows premature tubal implantation | |||
* embryo may develop through early stages, can erode through the uterine horn and reattach within the peritoneal cavity | |||
===Monoygotic Twinning=== | ===Monoygotic Twinning=== | ||
| Line 190: | Line 211: | ||
Table based upon: Twinning. Hall JG. <ref><pubmed>12957099</pubmed></ref> | Table based upon: Twinning. Hall JG. <ref><pubmed>12957099</pubmed></ref> | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 14:48, 22 July 2010
Introduction
Key events of human development during the second week (week 2) following fertilization or Clinical week 4 (LMP).
- Week 2 Links: Lecture - Week 1 and 2 | Implantation
- Embryo Week: Week 1 | Week 2 | Week 3 | Week 4 | Week 5 | Week 6 | Week 7 | Week 8 | Week 9
Timeline
| Event | ||
| Stage 6 | ||
Week 2 and 3 Movies
| Implantation | Mesoderm | Chorionic Cavity | Amniotic Cavity | Week 3 |
Implantation
The second week of human development is concerned with the process of implantation and the differentiation of the blastocyst into early embryonic and placental forming structures.
- implantation commences about day 6 to 7
- Adplantation - begins with initial adhesion to the uterine epithelium
- blastocyst then slows in motility, "rolls" on surface, aligns with the inner cell mass closest to the epithelium and stops
- Implantation - migration of the blastocyst into the uterine epithelium, process complete by about day 9
- coagulation plug - left where the blastocyst has entered the uterine wall day 12
Normal Implantation Sites - in uterine wall superior, posterior, lateral
Week 2 Abnormalities
Abnormal Implantation
Ectopic Pregnancy | Movie - Ectopic pregnancy ultrasound
Abnormal implantation sites or Ectopic Pregnancy occurs if implantation is in uterine tube or outside the uterus.
- sites - external surface of uterus, ovary, bowel, gastrointestinal tract, mesentry, peritoneal wall
- If not spontaneous then, embryo has to be removed surgically
Tubal pregnancy - 94% of ectopic pregnancies
- if uterine epithelium is damaged (scarring, pelvic inflammatory disease)
- if zona pellucida is lost too early, allows premature tubal implantation
- embryo may develop through early stages, can erode through the uterine horn and reattach within the peritoneal cavity
Monoygotic Twinning
Monozygotic twins (identical) produced from a single fertilization event (one fertilised egg and a single spermatazoa, form a single zygote), these twins therefore share the same genetic makeup. Occurs in approximately 3-5 per 1000 pregnancies, more commonly with aged mothers. The later the twinning event, the less common are initially separate placental membranes and finally resulting in conjoined twins.
Table based upon: Twinning. Hall JG. [1]
References
- ↑ <pubmed>12957099</pubmed>
Embryo Week: Week 1 | Week 2 | Week 3 | Week 4 | Week 5 | Week 6 | Week 7 | Week 8 | Week 9
- Carnegie Stages: 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | About Stages | Timeline
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, June 3) Embryology Week 2. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Week_2
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G