F
| Embryology - 27 Apr 2024 |
|---|
| Google Translate - select your language from the list shown below (this will open a new external page) |
|
العربية | català | 中文 | 中國傳統的 | français | Deutsche | עִברִית | हिंदी | bahasa Indonesia | italiano | 日本語 | 한국어 | မြန်မာ | Pilipino | Polskie | português | ਪੰਜਾਬੀ ਦੇ | Română | русский | Español | Swahili | Svensk | ไทย | Türkçe | اردو | ייִדיש | Tiếng Việt These external translations are automated and may not be accurate. (More? About Translations) |
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
F
F-factor
- (fertility factor) A kind of episome in bacteria that can replicate either autonomously or in integrated form; can move from one bacterium to another during conjugation.
F1
- (Latin, filial = son) first filial generation or the initial progeny of a cross-breeding (hybrid). The genetic breeding out (recombination) is said to strengthen the progeny, hence "F1 hybrid vigour".
F2
- (Latin, filial = son) second filial generation The progeny of the F1 generation.
factor V Leiden
- A mutation which is a heritable thrombophilia (increased tendency of blood to clot, impaired natural anticoagulant or fibrinolytic pathways) present in 5 - 8% of Caucasian populations.
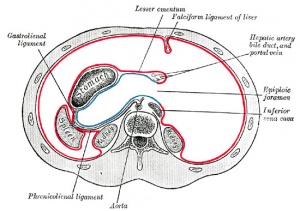
falciform ligament
- A sheet of parietal peritoneum between the two principal lobes of the liver, embryonically formed from the ventral mesogastrium. The ligamentum teres, the remnant of umbilical vein, lies within its folds.
fallopian tube
- (see uterine tube, uterine horn, oviducts) A pair of tubular structures designed to transport the oocyte (egg) from the ovary to the uterus body, named after Gabriel Fallopius (1523-1562), an anatomists and physician.
- (More? Uterus Development | Embryology History)
fallopian tube obstruction
- (tubal obstruction, tubal occlusion) An abnormal blockage of the uterine tube that can affect fertility. Blockage can have a number of causes including: a pathologic occlusion, spasm or plugging. The blockage can also be either unilateral (single tube) or bilateral (both tubes) and described anatomically as occurring in the proximal, the mid or the distal part of the tube.
- (More? Uterus Development)
Fabry disease
- (Fabry's disease, Anderson-Fabry disease, Alpha-galactosidase A deficiency, Angiokeratoma corporis diffusum, Ceramide trihexosidosis, Ruiter-Pompen-Wyers syndrome, Sweeley-Klionsky disease) Genetic disorder, a progressive X-linked inherited disorder of glycosphingolipid metabolism due to deficient or absent lysosomal α-galactosidase A activity. The reported annual incidence of 1 in 100,000 may underestimate the true prevalence of the disease.
FDA
- Acronym for the USA government organisation the Food and Drug Administration that has established the FDA drug classification system.
fecundability
- (Latin, fecundus = "fertile") See fecundity. Clinical term used in reference to the probability that conception will occur in a given population of couples during a specific time period.
- (More? menstrual cycle | fertilization)
fecundation
- (Latin, fecundus = "fertile") See fecundity. Term used to refer to the act of fertilisation.
- (More? Fertilization)
fecundity
- (Latin, fecundus = "fertile") Clinical term used in reference to the ability to reproduce. Fecundity can be altered by both genetic and environmental factors.
- (More? menstrual cycle | fertilization)
femur length
- (FL) An ultrasound measurement of femur length (FL) is used to determine fetal age and normal development (small/large/abnormal) parameters. The femur is the longest bone in the body and measurements and reflects the longitudinal growth of the fetus (approximately 14 weeks 1.5 cm - term 7.8 cm). It is one of the four typical ultrasound assessments of fetal size and age: Biparietal Diameter (BPD), Head Circumference (HC), Abdominal Circumference (AC), and Femur Length (FL).
- (More? Ultrasound | Limb | Bone | Fetal Development)
fenestra
- (Latin, fenestra = "window") A small pore approximately 60 to 70 nm diameter in vascular bed endothelium (renal glomerular, gastrointestinal, and endocrine gland capillaries, corneal capillaries) allowing exchange between blood and tissues, plural - fenestrae.
fenestra ovalis
- (Latin, fenestra = "window") (oval window) In the ear, the region that separates the tympanic cavity (middle ear) from the vestibule of the osseous labyrinth.
fenestra rotunda
- (Latin, fenestra = "window") (round window) In the ear, the region that separates the tympanic cavity (middle ear) from the scala tympani of the cochlea.
fermentation
- (Latin, fervere = "to boil") The anaerobic extraction of energy from organic compounds. The "boiling", or bubbling, is easily seen in the release of carbon dioxide from aerobic yeast during brewing processes.
fern test
- Clinical term for a relative (not conclusive) diagnostic test of rupture of membranes (ROM) or premature rupture of membranes (ROM prior to the onset of labor). Involves a microscopic evaluation of a collected specimen of fluid from the external cervical os or amniotic fluid fluid pooling in the posterior vaginal fornix.
- (More? PMID 8155212)
fertilisation
- (fertilization) The UK spelling for fertilization.
fertility rate
- A statisical term that refers to the total number of live births, regardless of age of mother, per 1,000 women of reproductive age, 15 to 44 years.
- (More? Embryology Statistics | Australian Statistics | Fertilization)
fertility treatment drugs
- A clinical term referring to a range of chemical therapeutics used to increase female fertility, for example: Clomid, Serophene, Pergonal, Metrodin, Profasi, Progesterol, Crinone (progesterone gel), Follistim FSH (follicule stimulating hormone), Gonadotropins HcG (human chorionic gonadotropin), Pergonal. Some of these are commercial and country-specific in availablity. This information is provided for educational purposes only.
- (More? Menstrual Cycle | Fertilization | In Vitro Fertilization)
fertilization
- (fertilisation) The process of penetration of the oocyte (egg) by the spermatozoa and the combining of their genetic material that initiates development of the embryo. The union of two haploid gametes to form the first diploid cell, the zygote.
- (More? Fertilization | Spermatozoa Development | Testis Development | Ovary Development | Lecture - Fertilization)
fertilization promoting peptide
- (FPP) Also called Glu2TRH which is a small tripeptide (3 amino acid; pGlu-Glu-Pro-NH2) present in human seminal plasma which stimulates spermatozoa capacitation. Peptide is a structural analogue to thyrotrophin-releasing hormone (TRH; pGlu-His-Pro-NH2).
- (More? Spermatozoa Development | Fertilization)
fetal breathing movements
- (FBM) Occur in the third trimester preparing both the skeletomuscular system and lungs mechanically for respiration.
fetal cardio-electrohysterographic coupling
- (FCEC) the influence of the uterine electrical activity on fetal heart rate, more apparent during the third trimester of pregnancy.
fetal death rate
- A statisical term refers to the number of fetal deaths with a stated or presumed gestation of 20 weeks or more divided by the sum of live births plus fetal deaths, per 1,000 live births plus fetal deaths. Late fetal death rate shifts the stated or presumed gestational age to 28 weeks.
fetal erythroblastosis
- (Haemolytic Disease of the Newborn) A clinical term describing an immune response between fetal and maternal blood groups; from fetus Rh+ / maternal Rh-. The leakage of blood from fetus, particularly at birth, causes maternal anti-Rh antibodies, which is then dangerous for a 2nd or future pregnancies.
- (More? Placenta Development | Blood Development | March of Dimes)
fetal fibronectin
- (fFN) An extracellular matrix glycoprotein produced by fetal cells. Fetal fibronectin appears to act as an adhesive between the interface of the chorion and the decidua (fetal membrane and uterine lining). As a prenatal diagnostic test, a positive fetal fibronectin test result can indicate a higher risk of preterm delivery, but may also has false positive results.
- (More? Prenatal Diagnosis | Birth)
fetal frontomaxillary facial angle
Fetal Growth Restriction
- (FGR, Intrauterine Growth Retardation) A term used to describe poor fatal growth, less than 90% of the average weight for same gestational age. Suggested causes include placental abnormalities and the prenatal environment.
fetal head position
- See fetal head station.
fetal head station
- (fetal head positions, stations of presentation) Birth term referring the relationship between the presenting part of the fetus and the maternal pelvis ischial spines. These spines are normally the narrowest part of the pelvis. A numerical centimetre system is used with presenting parts above the spines as decreasing negative values (-5 to -1), even with the spines as zero (0) and below the spines as increasing positive values (+1 to +5).
- (More? Birth | Medline Plus - Delivery presentations)
fetal length
- The measurement of crown to rump length of the developing fetus. The greatest growth in length occurs in the middle second trimester, of human development. There are a number of other growth parameters that can be measured, commonly determined by ultrasound, during the fetal period.
- (More? Fetal Development | Ultrasound)
Fetal Origins Hypothesis
- (Developmental Origins of Health and Disease, fetal programming hypothesis, Barker Hypothesis) Originally called the Barker Hypothesis, which began as statistical analysis carried out by Barker in the UK, of low birth weight data (early 1900's) and proposes in utero influences cause permanent changes in embryo/fetus, low birth weight, predisposition to chronic disease in adult life. Currently also known as Developmental Origins of Health and Disease (DOHaD).
fetal period
- (foetal period) In humans, the development week 9 to 36 is the fetal stage (second and third trimester) and during this time organs formed in the embryonic period continue to develop and the fetus grows in size and weight. The first 8 weeks of development is considered the embryonic period and is divided into 23 Carnegie stages based upon developmental milestones. Note when searching an alternate spelling "foetal".
- (More? Fetal Development)
fetal macrosomia
- A clinical description for a fetus that is too large, condition increases steadily with advancing gestational age and defined by a variety of birthweights. In pregnant women anywhere between 2 - 15% have birth weights of greater than 4000 grams (4 Kg, 8 lb 13 oz) and can be associated with diabetes.
- (More? Fetal Development | Birth)
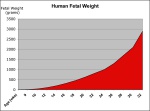
fetal weight
- The measurement of the weight of the developing fetus. The measurement is obtained by ultrasound calculation or clinically estimated by palpatation. The greatest addition of fetal weight occurs during and towards the end of the third trimester.
- (More? Fetal Development)
fetal varicella syndrome
- (FVS) A viral infection by varicella zoster virus (chickenpox) virus following a maternal infection that is transmitted transplacentally to the fetus.
- (More? Varicella Zoster Virus | Viral Infection)
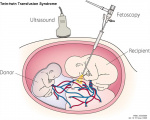
fetoscopic laser photocoagulation
- A clinical technique used in correcting twin–twin transfusion syndrome where intrauterine blood transfusion from one twin (donor) to another twin (recipient) where there is an imbalance of blood flow from the donor twin to the recipient twin. The technique ablates placental vascular anastomoses between the twins.
- (More? twin–twin transfusion syndrome | twinning)
fetotoxicant
- A chemical that adversely affects the developing fetus, resulting in low birth weight, symptoms of poisoning at birth or stillbirth (fetus dies before it is born). Note when searching an alternate spelling "foetal".
fetus
- (foetus) In mammals, term describes the period of development following the embryonic period. In humans, the development week 9 to 36 is the fetal stage (second and third trimester). (see fetal period above). This term is also used non-scientifically to describe the human conceptus at both embryonic and fetal stages of development.
- (More? Fetal Development)
fetus in fetu
- (FIF) An extremely rare abnormality (incidence is 1 in 500,000 live births, less than 150 cases reported in the world) where a malformed monozygotic twin (non-dominant twin) is found inside the body of a living child or sometimes in an adult (dominant twin). The most commonly reported site is in the retroperitoneum (80%) and can also occur within the skull, oropharynx, sacrum or genitourinary tract of the host twin.
FFPE
- Histology and clinical pathology acronym for Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded specimens. This is a routine fixation and embedding technique for tissues and pathology specimens for analysis and storage.
- (More? Histology)
FGR
- Acronym for Fetal Growth Restriction a term used to describe poor fetal growth and is also known as Intrauterine Growth Retardation.
fibrillin
- A connective tissue protein encoded in humans by (FBN1) gene which is associated with Marfan's syndrome (ICD10 - Q87.4 Marfan's syndrome)
- (More? (ICD10 - Q87.4 Marfan's syndrome)
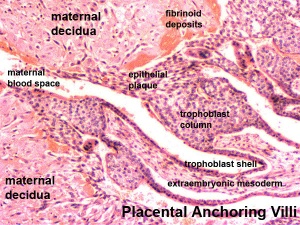
fibrinoid layer
- (Nitabuch's layer) A layer formed at maternal/fetal interface during placentation and is thought to act to prevent excessively deep conceptus implantation. Fibrin-type fibrinoid (maternal blood-clot product) and matrix-type fibrinoid (secreted by invasive extravillous trophoblast cells).
- (More? Placenta Development)
fibroadenomas
- Term describing in relation to the breast, a lump, both smooth and firm, made up of fibrous and glandular tissue. These are generally not cancerous and are more common in younger women and may become tender in the days before a period or grow bigger during pregnancy.
fibroid embolization
- The treatment method for uterine fibroids (non-cancerous tumor that can develop within the wall of the uterus) involving stopping or blocking the blood flow to the tumor.
- (More? Menstrual Cycle | Uterus Development | Medline Plus)
fibrinolysin
- Part of the prostate secretion, a secreted enzyme that liquefies the semen.
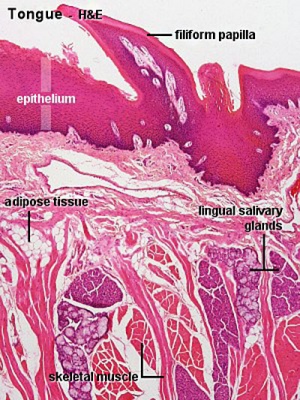
filiform papillae
- Tongue surface specialisation forming the rough surface to aid in the manipulation and processing of foods. These are the smallest and most numerous of the three types of papillae (filiform, fungiform and circumvallate).
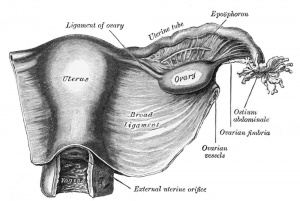
fimbriae
- (Latin, fimbria = a fringe) The finger-like projections at the ovarian end of uterine tube. At ovulation they sit over the ovary to aid egg movement into the uterine tube.
- (More? Week 1)
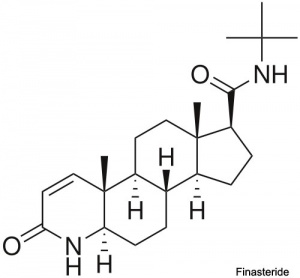
Finasteride
- A chemical used to prevent male pattern baldness and enlargement of prostate glands. An anti-androgen (blocks synthesis of dihydrotestosterone) and therefore a potential endocrine disruptor, exposed pregnant women can impact on male fetus genetial development.
- (More? Endocrine System - Abnormalities)
first polar body
- The small cytoplasmic exclusion body formed when the oocyte (egg) completes meiosis 1 at ovulation. This exclusion body contains the excess DNA from the first reductive division (the second and third polar bodies are formed from meiosis 2 at fertilization). These polar bodies do not contribute to the genetic complement of the zygote, embryo or fetus. Recent research in some species suggest that the space formed by the peripheral polar body (between the oocyte and the zona pellucia) can influence site of sperm fertilization.
first trimester
- Clinical term used to describe and divide human pregnancy period (9 months) into three equal parts of approximately three calendar months. The first trimester corresponds approximately to embryonic development (week 1 to 8) of organogenesis and early fetal. The second and third trimester correspond to the fetal period of growth in size (second trimester) and weight (third trimester), as well as continued differentiation of existing organs and tissues.
- (More? Embryonic Development | Fetal Development)
FISH
- Acronym for Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization, a molecular biology imaging technique used in studying cell genetic make up and gene expression. Used also as a prenatal diagnostic technique.
- (More? Molecular Development | Prenatal Diagnosis)
fistula
- An abnormal communication between 2 structures (organs, vessels, cavities) that do not normally connect.
FL
- Acronym for Femur Length, longest bone in the body, used in clinical ultrasound measurements and reflects growth of the fetus.
- (More? Ultrasound)
flagella
FLASH
- Acronym for FLICE associated huge protein, a cytoplasmic component of the apoptosis signaling pathway which also translocates to nuclear Cajal bodies.
flexion
- Anatomical term describing a body movement by skeletal muscle contraction to bend and decrease the angle between two skeletal parts. For example, flexing the biceps, bends the elbow moving the two upper limb parts together. The opposite movement is extension.
flexure
- Anatomical term describing a curve, turn, fold, or bend in a tubular organ. For example in the gastrointestinal tract or early neural tube development (cranial flexure, pontine flexure and cervical flexure).
floating chorionic villi
- Term used to describe the placental microanatomy structure of chorionic villi that are not attached to the maternal decidua and float in the maternal blood-filled space (lacunae). Structurally the same as anchoring chorionic villi conceptus side that are attached to the maternal decidua.These villi go through the same stages of development: primary, secondary and tertiary villi.
floor plate
- The term used to describe the thin ventral region of the early neural tube. This region also lies closest to the notochord and is involved in sonic hedgehog signaling. The neural tube forms the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord). The opposite side of the early neural tube forms the roof plate and the lateral parts are divided into two thicker regions, the alar plate and basal plate.
Flt1
- Gene acronym for fms-like tyrosine kinase 1, one of the membrane receptors for vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). A soluble form of the receptor (sFlt1) inhibits VEGF signaling in the vasculature by competing with full-length Flt1 for binding to VEGF.
fluorescence in situ hybridization
- (FISH) A molecular biology imaging technique used in studying cell genetic make up and gene expression. Used also as a prenatal diagnostic technique.
- (More? Molecular Development | Prenatal Diagnosis | PMID 20809319)
fluoroquinolones
- (ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin, levofloxacin) A class of synthetic broad-spectrum antibiotics contraindicated for use during pregnancy, except when no other option is available. Used clinically for a variety of infections, including sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). The antibiotic acts by preventing bacterial DNA replication.
fms-like tyrosine kinase 1
- (Flt1) One of the membrane receptors for vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). A soluble form of the receptor (sFlt1) inhibits VEGF signaling in the vasculature by competing with full-length Flt1 for binding to VEGF.
foetal
- Often considered the British spelling, US spelling is actually more correct, "fetus" correctly derives from the Latin fetus see alternate spelling fetal period above.
- (More? Fetal Development)
Fog2
- Acronym for Friend of Gata 2, a transcription factor required for diaphragm and lung development.
folate
- See folic acid
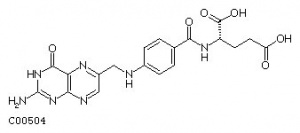
folic acid
- (Latin, folium = leaf) (= Folate, Pteroylglutamic acid) A water soluble vitamin, found in many fruits (particularly oranges, berries and bananas), leafy green vegetables, cereals and legumes, which can prevent neural tube defects (NTDs). The cellular roles of folate include: DNA synthesis, amino acid metabolism and methylation of genes, proteins and lipids via S-adenosylmethionine-mediated one-carbon transfer reactions.
follicle
- (Latin, folliculus = little bag, dim. of Latin follis) Term used in the structure of the ovary, in skin associated hair and within the thyroid gland. The functional unit within the ovary that includes the developing oocyte (egg) and the surrounding layers of cells that support that oocyte. Some cells within the follicle are released along with the ooctye at ovulation, while other cells are involved with female sex hormone secretion into the maternal bloodstream. The hair follicle is a specialized skin structure that forms the associated hair extending from the skin surface. In the endocrine thyroid gland the thyroid follicle is the histological unit structure of the thyroid gland.
follicle atresia
- The degeneration of the developing ovarian follicle, which can occur at any stage of follicular development. Many developing follicles undergo this process in each menstrual cycle.
- (More? Oocyte Development | Menstrual Cycle | Ovary Development)
follicle stimulating hormone
- (FSH, gonadotropin) A glycoprotein hormone secreted by anterior pituitary (adenohypophysis gonadotrophs, a subgroup of basophilic cells) and acts on gametogenesis and other systems in both males and females. In females, FSH acts on the ovary to stimulate follicle development. Negative feedback by inhibin from the developing follicle decreases FSH secretion. In males, acts on the testis Sertoli cells to increase androgen-binding protein (ABP) that binds androgens and has a role in spermatogenesis. FSH-defficiency in females results in infertile (block in folliculogenesis prior to antral follicle formation) and in males does not affect fertility (have small testes but are fertile). FSH protein has a molecular weight 30 kDa and a 3-4 hour half-life in circulation. Gonadotrophins have been used clinically in humans for the treatment of infertility. Other glycoproetin hormones include luteinizing hormone (LH), thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), and chorionic gonadotropin.
- (More? FSH | pituitary | menstrual cycle | ovary | testis | oocyte | In Vitro Fertilization | PMID 9020850)
follicular basal lamina
- The basal lamina beneath the membrana granulosa (granulosa cell) layer of the developing follicles of the ovary. It separates the stratum granulosa from the thecal layers. Thought to be synthesized by granulosa cells, but may also have a contribution from the thecal layer.
- (More? Oocyte Development)
follicular waves
- An ovarian follicle development term referring to their growth in coordinated groups or waves, in humans this occurs either 2 to 3 times between ovulations. These waves have previously been described in several other mono-ovulatory species, such as the horse (equine) and cow (bovine).
- (More? Ovary Development)
folliculin
- (FLCN) A tumor-suppressor protein with unknown functions (see PNAS paper). Germ line mutations in the gene lead to Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome, characterized by benign tumors of the hair follicle, lung cysts, and renal neoplasia.
- (More? - folliculin | Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome | PMID 17028174)
follicular fluid
- (liquor folliculi) The fluid found in the antral follicle (secondary follicle) antrum or fluid-filled space that develops within the ovary. The fluid is secreted by cells in the wall of the follicle. This fluid is released along with the oocyte at ovulation.
folliculogenesis
- The term used to describe the process of follicle development within the ovary. The follicle is the structure developing within the ovary that includes the oocyte (egg) and surrounding support cells.
- (More? Oocyte Development | Menstrual Cycle | Ovary Development)
fontanel
- (fontanelle) A fibrous region between flat bones of developing skull. This region has a role in birth allowing the cranial vault to flex and postnatally allow the skull to enlarge. In humans, there are six fontanels; an obvious anterior (bregmatic) and posterior (occipital) fontanels, as well the less noticeable lateral fontanels (two mastoid fontanels and two sphenoidal fontanels). A month or two after birth, the posterior and lateral fontanelles are lost, the anterior is not completely closed until about the 18 months.
- (More? Skull Development)
4 (four) dimensional ultrasound
- (4D) A diagnostic ultrasound term used to describe the collection of three dimensional (3D) ultrasound images over time. These images can be assembled and played as a detailed movie.
- (More? Ultrasound)
forebrain
- (prosencephalon) The common term used to describe the most anterior neural tube primary brain vesicle (there are 3 primary brain vesicles) that will form the two secondary brain vesicles , telencephalon and diaencephalon. These generate in the adult brain the cerebral hemispheres (neocortex, basal nuclei, palaeocortex, archicortex) and thalmus, hypothalmus and other nuclei respectively. The prosencephalon lumen (cavity of the neural tube) will form the lateral ventricle and third ventricle.
- Three primary brain vesicles: forebrain ( prosencephalon) - midbrain (mesencephalon) - hindbrain (rhombencephalon)
- (More? ectoderm | Neural System Development)
foregut
- The first of the three part/division (foregut - midgut - hindgut) of the early forming gastrointestinal tract. The foregut runs from the buccopharyngeal membrane to the midgut and forms all the tract (esophagus and stomach) from the oral cavity to beneath the stomach. In addition, a ventral bifurcation of the foregut will also form the respiratory tract epithelium. These anatomical divisions also correspond to their 3 main vascular supply divisions of foregut coeliac artery, midgut superior mesenteric artery and hindgut inferior mesenteric artery.
- (More? Lecture - Gastrointestinal Development | Lecture - Respiratory Development | Stomach Development | Gastrointestinal Tract Development | Respiratory Development)
Forkhead Box F1
- (Foxf1) A member of the forkhead gene family, a group of transcription factors originally identified in drosophila and have a role in development of the gall bladder and other tissues. The'forkhead' domain is a conserved 100 amino acid sequence.
- (More? Gall Bladder Development | OMIM FORKHEAD BOX F1; FOXF1)
fourth ventricle
- (4th ventricle) A cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) filled space formed from neural tube lumen (cavity), located within the rhombencephalon from the primary brain vesicle, commonly called the hindbrain. This fluid-filled space is readily visible through the thin surface epithelium of the young embryo as a "V" shaped space, later thickening of the dermis means the space is not visible from the surface.
Fraser syndrome
- (cryptophthalmos-syndactyly syndrome) An autosomal recessive congenital malformation syndrome characterized by cryptophthalmos, syndactyly, and urogenital defects (bicornuate uterus, imperforate anus, anal stenosis or renal malformations).
fraternal twins
- (dizygotic twins, non-identical) Twins resulting from two fertilization events, involving two separate oocyte (egg, ova) and spermatozoa (sperm). The other form of twinning, monozygotic twins, results from a single fertilization event.
frontomaxillary facial angle
- (FMF, fetal frontomaxillary facial angle) A first trimester (11-13 weeks GA) or second trimester head ultrasound measurement that has been suggested to be useful as an indicator, along with nuchal translucency, for trisomy 21. The angle in aneuploid trisomy 21 fetuses is wider than that in euploid normal fetuses. Euploid fatal angle also decreases linearly with growth measured by crown rump length (CRL); CRL 45 mm average 83.5 degrees to CRL 84 mm 76.4 degrees.
- (More? Trisomy 21 | Ultrasound | PMID 18512854 | PMID 20127748)
frontonasal prominence
- (FNP) The major embryonic region that contributes to face development. Anatomically in the embryo a large anterior midline structure that fuses with the two maxillary processes of the first pharyngeal arch. The other two regions are formed by the mandibular processes of the first pharyngeal arch. The FNP also contributes the philtrum (infranasal depression) of the upper lip.
- (More? Lecture - Head Development)
freemartin
- Bovine term for a imperfect sterile female calf due to a disorder of sexual development. Occurs with the twin of a male calf whose hormones (testosterone, AMH) affected the twin female genital development.
- (More? testosterone | AMH | cow | twinning | YouTube)
frenulum
- (Latin, frenulum = little bridle") Anatomical term for a small fold of integument (skin) or mucous membrane that limits the movements of an organ or part. Adult anatomy locations where a frenulum can be found include the tongue, penis, clitoris and lip.
- (More? Tongue Development)
Fryns syndrome
- A generally neonatal lethal abnormality showing autosomal recessive inheritance, with currently no identified gene. Associated abnormalities include: diaphragm defects (hernia, eventration, hypoplasia or agenesis); characteristic facial appearance (coarse facies, ocular hypertelorism, broad and flat nasal bridge, thick nasal tip, long philtrum, low-set and poorly formed ears, tented upper lip, macrostomia, micrognathia); distal digital hypoplasia (nails, terminal phalanges); pulmonary hypoplasia; and associated anomalies (polyhydramnios, cloudy corneas and/or microphthalmia, orofacial clefting, renal dysplasia/renal cortical cysts. Additional malformations have be seen in brain, cardiovascular system, gastrointestinal system and genitalia.
- (More? GeneReviews | PMID 20301632)
FUCCI
- Acronym for Fluorescence Ubiquitination Cell Cycle Indicator a molecular tool for identifying the stage in the cell cycle. In G0/G1 cells express a red fluorescent protein and S/G2/M cells express a green fluorescent protein.
- (More? Tooth Development Movie)
fundal height
- Clinical measurement of distance from the top of the pubic bone to the top of the uterus (fundus). Used during pregnancy as a general guide to fetal growth rate, the fundal height (cm) is n approximately equal to the the gestational age (GA) in weeks.
- (More? Fetal Development)
fundamental frequency
- (natural frequency) Related to hearing and speech and is the lowest audio frequency in a harmonic series. For the female voice this is about 225 Hz.
fundus
- (Latin, fundus = "bottom") A general term meaning the bottom or base of an organ. Term also describes the top part of the uterus body lying between the two uterine tubes and also a common implantation site.
- (More? Uterus Development | Implantation)
fungal spore
- An inactive and hardy form of fungi forming part of the reproductive life cycle of fungi, that can survive in a metabolically dormant state for many years and can also withstand high temperatures, radiation, and toxic chemicals.
fungiform papillae
- Tongue surface specialisation named by their resemblance to a mushroom with narrow at their attachment to the tongue, but broad and rounded at their free extremities, and covered with secondary papillæ. They are large in size, deep red color, and found mainly at the sides and apex, but also scattered irregularly and sparingly over the dorsum. The three types of papillae from numerous to few are: filiform, fungiform and circumvallate.
- (More? Image - fungiform papillae | Tongue Development)
fusiform
- (Latin, fusus = "spindle-shaped") widest near the middle and tapering in toward both ends, (back in the days of smoking) often described as "cigar-shaped". For example, used to describe the shape of the early developing stomach or the shape of smooth muscle cells.
fusome
- An organelle formed in association with germline cyst formation in many insect germ cells, well characterised in the fly model, drosophila. Consists of membrane skeletal proteins and membranous vesicles.
Glossary Comments
Use this page to access brief definitions of specific embryology terms. Additional information can be accessed from links listed at the end of each definition. Glossary from the UNSW Embryology program compiled and written by Dr Mark Hill. Reference material used in preparing this glossary list includes: texts listed on page 1 "Reading" of each notes section, Department of Anatomy Publications, WWW resources from NCBI, NIH, OMIM, NHMRC (Australia), AMA (USA), Office of Rare Diseases (USA), PubMed Medline Dictionaries, MSDS, Merck Manual home edn. and WHO ART terminology (2009).
These notes are for Educational Purposes Only Please email Dr Mark Hill if you wish to make a comment about this current project.
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 27) Embryology F. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/F
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G