Abnormal Development - Australian Statistics
Introduction
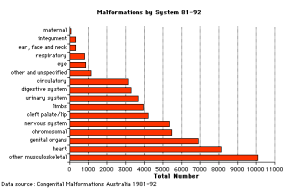
Data groupings and classification as Major or Minor Abnormalities are based on that used by the Australian Institute of Health and Welfare National Perinatal Statistics Unit, UNSW and published in Congenital Malformations Australia 1981-92.
For individual systems, data shown as a % of all Major Abnormalities based upon published statistics using the same groupings as CMA 81-92. Please note that some congenital diseases involve more than one system.
Reference: Original Data source for graphs from Congenital Malformations Australia 1981-1992, P. Lancaster and E. Pedisich, ISSN 1321-8352.
The classification groups for Major and Minor Abnormalities are also shown.
| Statistics Links: Introduction | Reports | World Population | World Fertility | World Infant Mortality | Maternal Mortality | Australia | Brazil | Canada | China | Germany | India | Indonesia | Europe | Myanmar | Netherlands | Spain | United Kingdom | Romania | Uganda | United States | BGD Tutorial - Applied Embryology and Teratology | National Perinatal Statistics Unit | AIHW | Category:Statistics | |
|
Some Recent Findings
Australian Birth Anomalies System
- "The national collation and reporting of birth anomalies data has been suspended in recent years due to concerns about data quality and comparability."
- Variability among states and territories in scope of birth anomalies data collections: sources of birth anomalies notifications and definitions and classifications used; method of data collection and available resources.
- Variability among the states and territories in the timing and method of the provision of birth anomalies data to the AIHW National Perinatal Statistics Unit (NPSU) for national collation and reporting.
- New Australian Birth Anomalies System should be data for birth anomalies detected up to 1 year of age
- including data on terminations of pregnancies with birth anomalies and regardless of gestational age (i.e. including less than 20 weeks gestation)
- System will initially be based on data from the states able to detect birth anomalies at least up to 1 year of age (NSW, VIC, WA and SA), further extending the period of detection in the future
The Australian Congenital Anomalies Monitoring System (ACAMS) supersedes the National Congenital Malformations and Birth Defects Data Collection (NCM&BD).
- Links: Australian Congenital Anomalies Monitoring System | Congenital Anomalies in Australia 2002-2003
Ten Most Frequently Reported Birth Anomalies
Based upon statistics from the Victorian Perinatal Data Collection Unit in Victoria (Australia) between 2003-2004.
|
Hypospadias (More? Development Animation - Genital Male External | Genital Abnormalities - Hypospadia) |

|
Obstructive Defects of the Renal Pelvis (obstructive defects of the renal pelvis, uteropelvic junction obstruction, pelvo-uterero junction obstruction) Term describing a developmental renal abnormality due to partial or complete blockage of the drainage of the kidney pelvis requiring surgical correction. The blockage can also have several causes including: unusual ureter twisting or bending, ureter compression by a blood vessel, malformations of the muscular wall. The blockage leads to an accumulation of urine in the affected region, with several potential effects: nephron damage from compression (hydronephrosis); decreased urine output leading to lack of amniotic fluid (oligohydramnios); respiratory development effects due to the lack of amniotic fluid.
(More? Renal System - Abnormalities | Renal System Development) |
|
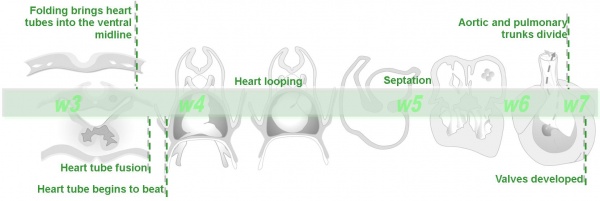
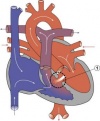
Ventricular Septal Defect (More? Cardiovascular Abnormalities - Ventricular Septal Defect)
Heart Development Timeline (see Basic Cardiac Embryology) |
|
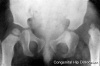
Congenital Dislocated Hip (More? Musculoskelal Abnormalities - Congenital Dislocation of the Hip (CDH))
(DHH, congenital dislocated hip, congenital hip dislocation, congenital hip dysplasia) Term describes a spectrum of musculoskeletal disorders of hip instability due either to the femoral head being able to move outside the acetabulum (luxation or dislocation), or abnormally within the acetabulum (subluxation or partial dislocation). This includes presentation following a normal examination of the hips in the newborn period (Ortolani and Barlow tests). When detected can be managed with splinting (Denis-Browne splint) allows the hip joint to develop normally and does not require surgery. If undetected and left untreated, the hip joint develops abnormally and surgical reduction is required. (More? Musculoskeletal System Development) |
|
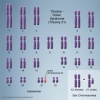
Trisomy 21 or Down syndrome - (More? Trisomy 21) |
|
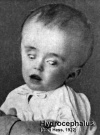
Hydrocephalus (More? Neural Abnormalities - Hydrocephalus | NINDS - Hydrocephalus Fact Sheet | Hydrocephalus Support Association | USA National Hydrocephalus Foundation) |
|
Cleft Palate (More? Development Animation - Palate 1 | Development Animation - Palate 2 | Cleft Palate) |
|
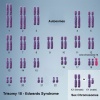
Trisomy 18 or Edward Syndrome - multiple abnormalities of the heart, diaphragm, lungs, kidneys, ureters and palate 86% discontinued (More? Trisomy 18) |
| Renal Agenesis/Dysgenesis - reduction in neonatal death and stillbirth since 1993 may be due to the more severe cases being identified in utero and being represented amongst the increased proportion of terminations (approximately 31%). (More? Renal Abnormalities - Renal Agenesis) | |
|
Cleft Lip and Palate - occur with another defect in 33.7% of cases. (More? Cleft Lip) |
NSW - Congenital Conditions Register
Scheduled congenital conditions (section 2) detected during pregnancy or in infants up to one year of age in NSW are required to be reported under the NSW Public Health Act 1991.
Scheduled congenital conditions include:
- All structural malformations. Examples include spina bifida, microcephaly, transposition of the great vessels, ventricular septal defects, pulmonary agenesis, polycystic lungs, duodenal atresia, exomphalos, hypospadias, cleft lip/palate, microphthalmia, limb reductions, polydactyly, birthmarks greater than 4 cms diameter, cystic hygroma and multisystem syndromes including at least one structural malformation.
- Chromosomal abnormalities. Examples include Down syndrome and unbalanced translocations.
- Four medical conditions: cystic fibrosis, phenylketonuria, congenital hypothyroidism and thalassaemia major.
Congenital conditions that are not notifiable include:
- Minor anomalies occurring in isolation (Examples of minor anomalies include skin tags, deviated nasal septum, tongue tie, benign heart murmurs, clicky non-dislocating hips, sacral dimples, positional talipes, abnormal palmar creases, dysmorphic features).
- Birth injuries.
- Congenital infections which do not result in a structural malformation.
- Tumours and cysts.
- Conditions arising from prematurity or asphyxiation.
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 27) Embryology Abnormal Development - Australian Statistics. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Abnormal_Development_-_Australian_Statistics
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G