ANAT2341 Lab 6 - Early Embryo
| Lab 6: Introduction | Trilaminar Embryo | Early Embryo | Late Embryo | Fetal | Postnatal | Abnormalities | Online Assessment |
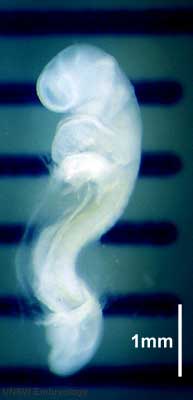
Week 4
During week 4 a number of features appear visible on the embryo surface:
- At the level of the body heart, liver, somite bulges and limb buds appear.
- At the level of the head sensory placodes and pharyngeal arches appear.
Carnegie Stage 12 to 14
Week 4
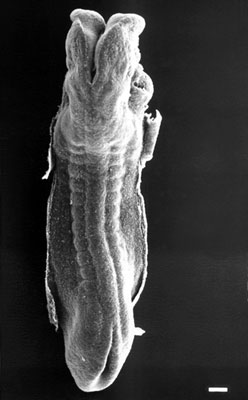
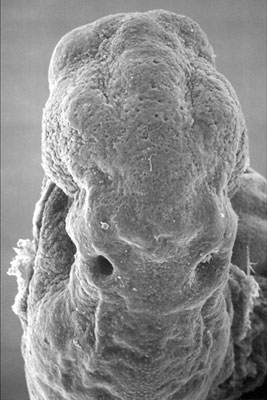
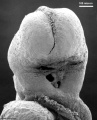
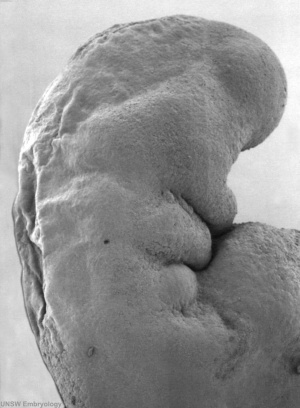
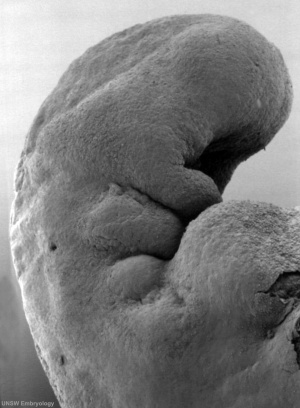
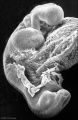
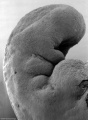
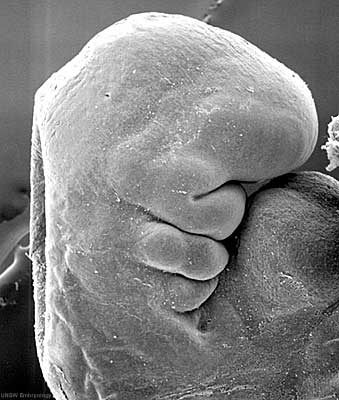
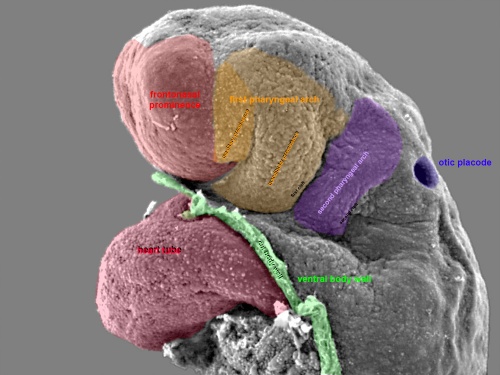
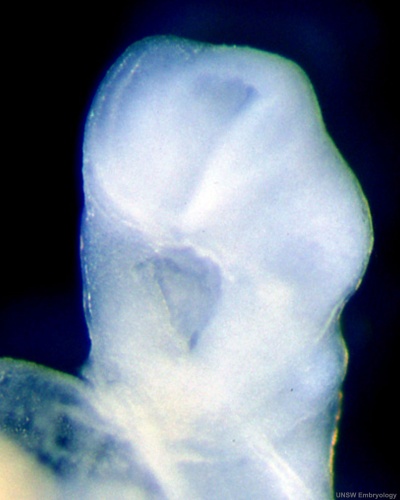
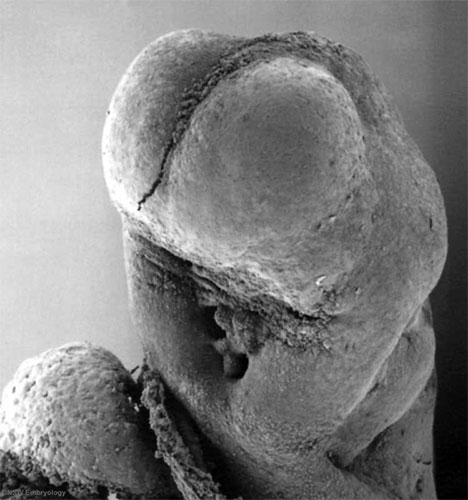
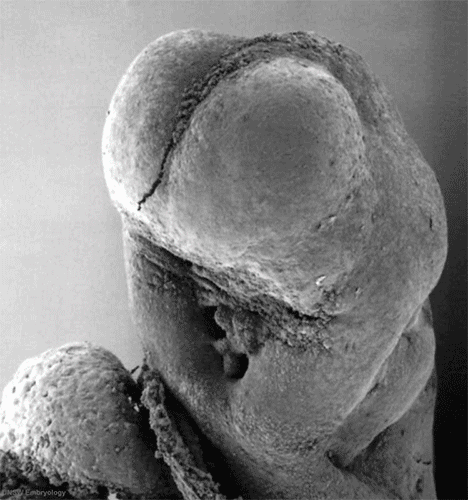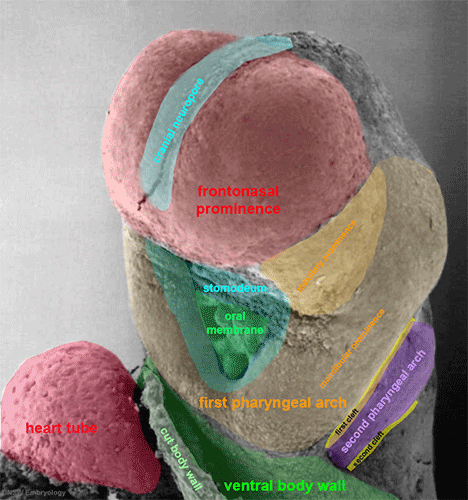
This is a scanning EM of the embryo superior dorsal view showing the paired otic placodes sinking into the surface at the level of the hindbrain between day 24 and day 25
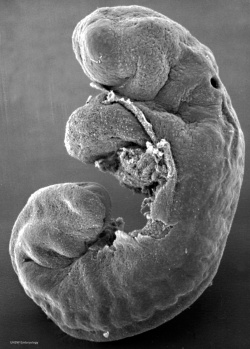
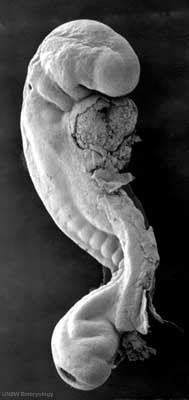
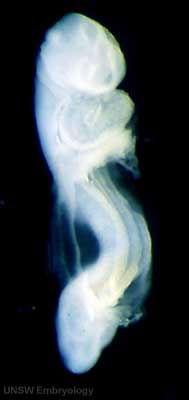
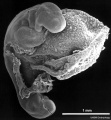
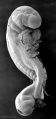
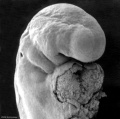
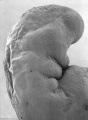
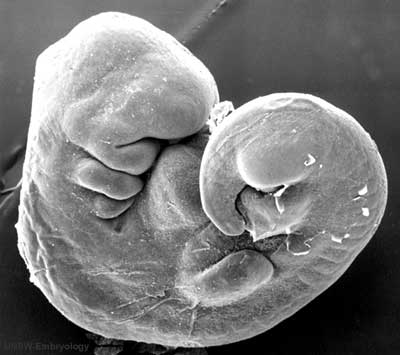
| Human Embryo (Stage 11) | |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Week 5
Sensory Placodes
Sensory placodes develop as small patches of ectodermal thickenings.
The placodes are laterally paired and contribute key components to sensory structures of the ear, eye and nose.
Named by the sensory system and components they will form: otic placode, optic (lens) placode and nasal placode.
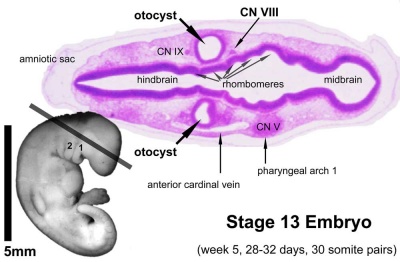
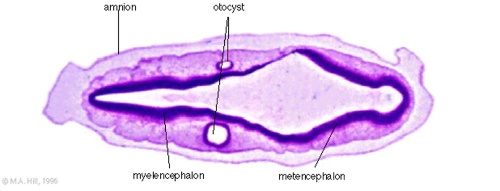
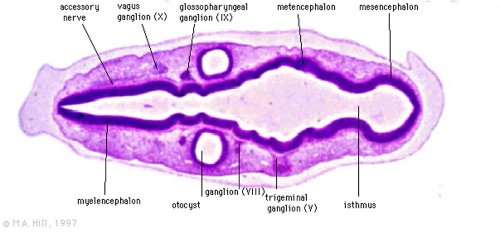
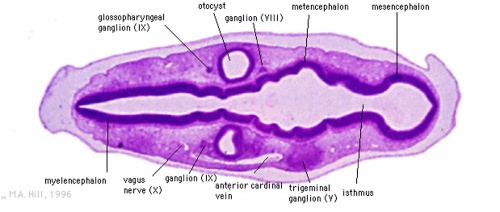
Stage 13
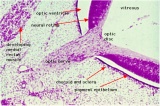
Identify the structure and position of the otic vesicle (otocyst) relative to other head structures.
Stage 13 Movie - Overview of Head, Pharyngeal Arches and Pharynx
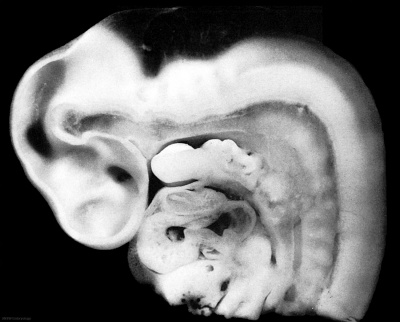
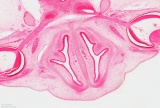
Stage 15
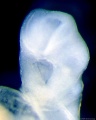
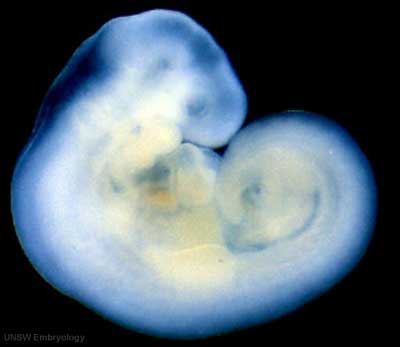
Later week 5 development showing a sagittal section upper half of human embryo.
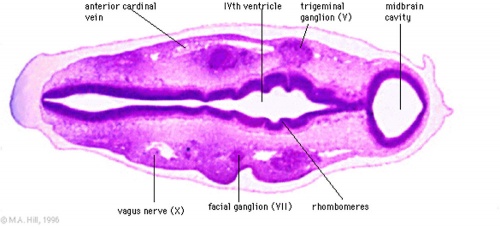
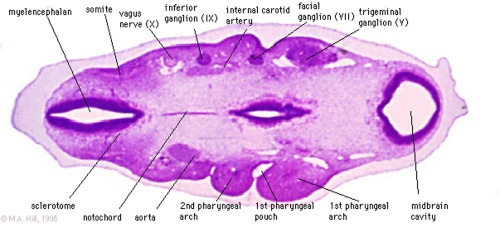
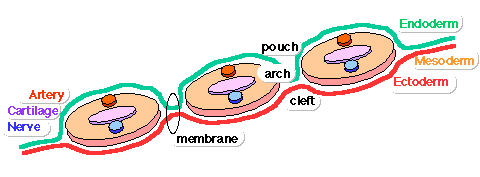
Pharyngeal Arches
Stage 13 Pharyngeal Arches
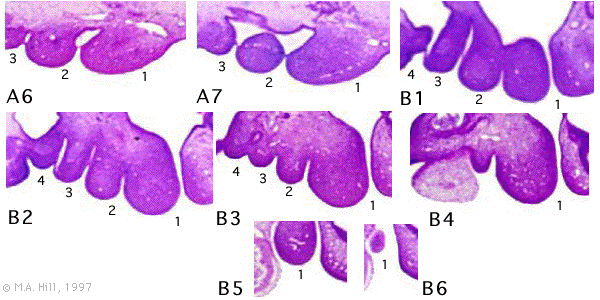
Section Images: A6L A7L B1L B2L B3L B4L B5L B6L
Look through the above cross-sections of the stage 13 embryo observing and identifying structures of the face and ear visible at this stage.
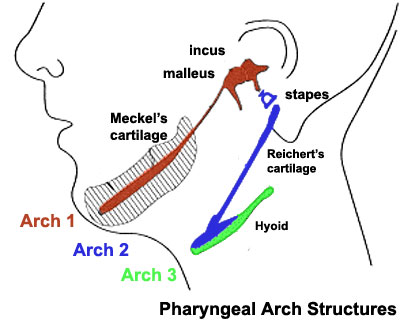
Structures derived from Arches
| Pharyngeal Arch | Nerve | Artery | Neural Crest (Skeletal Structures) |
Muscles | Ligaments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (maxillary/mandibular) |
trigeminal (CN V) | maxillary artery (terminal branches) | mandible, maxilla, malleus, incus | muscles of mastication, mylohyoid, tensor tympanic, ant. belly digastric | ant lig of malleus, sphenomandibular ligament |
| 2 (hyoid) |
facial (CN VII) | stapedial (embryonic) corticotympanic (adult) |
stapes, styloid process, lesser cornu of hyoid, upper part of body of hyoid bone | muscles of facial expression, stapedius, stylohyoid, post. belly digastric | stylohyoid ligament |
| 3 | glossopharyngeal (CN IX) | common carotid, internal carotid arteries | greater cornu of hyoid, lower part of body of hyoid bone | stylopharyngeus | |
| 4 | vagus (CN X) superior laryngeal branch | part of aortic arch (left), part right subclavian artery (right) | thyroid, cricoid, arytenoid, corniculate and cuneform cartilages | crycothyroid, soft palate levator veli palatini (not tensor veli palatini) | |
| 6 | vagus (CN X) recurrent laryngeal branch | part of left pulmonary artery (left), part of right pulmonary artery (right) | thyroid, cricoid, arytenoid, corniculate and cuneform cartilages | larynx intrinsic muscles (not cricothyroid muscle) |
Additional Information
| Additional Information - Content shown under this heading is not part of the material covered in this class. It is provided for those students who would like to know about some concepts or current research in topics related to the current class page. |
Other Sensory Systems
The links below are to additional information providing background about each of the sensory systems. Only hearing is covered in today's class.
|
|
|
|
| Vision Links: vision | lens | retina | placode | extraocular muscle | cornea | eyelid | lacrima gland | vision abnormalities | Student project 1 | Student project 2 | Category:Vision | sensory | ||
|
| Smell Links: Introduction | placode | Rhinencephalon | head | respiratory | Student project | taste | sensory | Category:Smell | ||
|
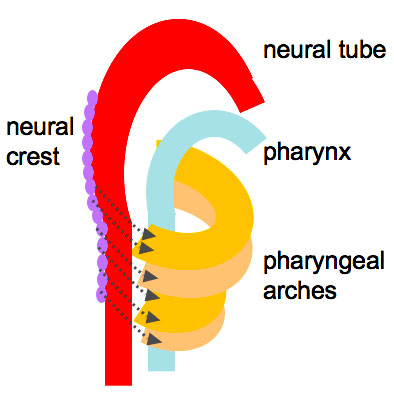
Neural Crest
During this period neural crest cells migrate into the pharyngeal arches and other head locations, and have an important contribution to many different head structures. Neural crest cells at other levels contribute to body many structures. There are also many developmental abnormalities associated with abnormal neural crest development and/or migration. This topic is beyond the scope of the current class.
- Links: Neural Crest Development
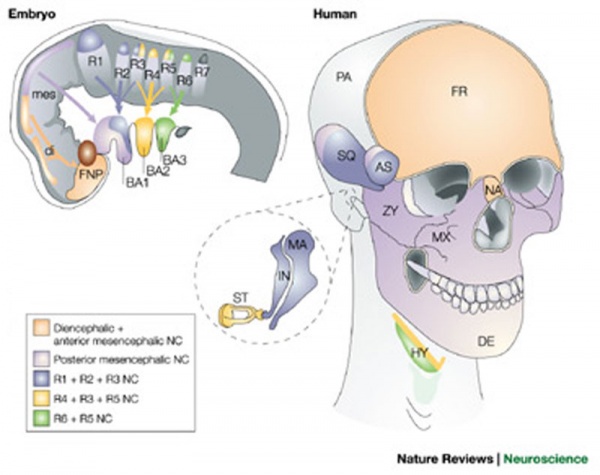
|
Cranial neural crest contribution to skeletal structures
There has been controversy about the neural crest embryonic contribution to the parietal region. A recent transcriptional analysis of second trimester human cranial compartments[1] suggests that "a gene expression signature of neural crest origin still exists in frontal and metopic compartments while gene expression of parietal and sagittal compartments is more similar to mesoderm." |
|
|
See also this 2014 Review:
Epigenetic regulation in neural crest development. [3]
- "The neural crest is a migratory and multipotent cell population that plays a crucial role in many aspects of embryonic development. In all vertebrate embryos, these cells emerge from the dorsal neural tube then migrate long distances to different regions of the body, where they contribute to formation of many cell types and structures. These include much of the peripheral nervous system, craniofacial skeleton, smooth muscle, and pigmentation of the skin. The best-studied regulatory events guiding neural crest development are mediated by transcription factors and signaling molecules. In recent years, however, growing evidence supports an important role for epigenetic regulation as an additional mechanism for controlling the timing and level of gene expression at different stages of neural crest development. Here, we summarize the process of neural crest formation, with focus on the role of epigenetic regulation in neural crest specification, migration, and differentiation as well as in neural crest related birth defects and diseases."
Human cranial compartments different embryonic origins[1]
- Our data suggest that in the second trimester of human foetal development, a gene expression signature of neural crest origin still exists in frontal and metopic compartments while gene expression of parietal and sagittal compartments is more similar to mesoderm."
Placodes
The links below are to additional information providing background about each of the sensory systems.
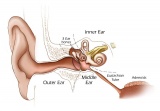
| Hearing Links: Introduction | inner ear | middle ear | outer ear | balance | placode | hearing neural | Science Lecture | Lecture Movie | Medicine Lecture | Stage 22 | hearing abnormalities | hearing test | sensory | Student project Categories: Hearing | Outer Ear | Middle Ear | Inner Ear | Balance | ||
|
| Vision Links: vision | lens | retina | placode | extraocular muscle | cornea | eyelid | lacrima gland | vision abnormalities | Student project 1 | Student project 2 | Category:Vision | sensory | ||
|
| Smell Links: Introduction | placode | Rhinencephalon | head | respiratory | Student project | taste | sensory | Category:Smell | ||
|
- Taste Links: Introduction
Reference
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 <pubmed>26188427</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>14523380</pubmed>| Nat Rev Neurosci.
- ↑ <pubmed>25446277</pubmed>
| Lab 6: Introduction | Trilaminar Embryo | Early Embryo | Late Embryo | Fetal | Postnatal | Abnormalities | Online Assessment |
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 18) Embryology ANAT2341 Lab 6 - Early Embryo. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/ANAT2341_Lab_6_-_Early_Embryo
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G