2011 Lab 4
Cardiovascular and Placenta
Introduction
This laboratory will explore the development of the embryonic cardiovascular system, which includes the placental vascular system. We will look through cross-sections of the Carnegie stage 13 embryo and follow the flow of blood through the embryonic vasculature. In this lab, we will also examine placentation.
Objectives
- Understand development of early embryo heart and vascular system.
- Understand the early placentation events and the development of placental blood vessels.
- Brief understanding of prenatal diagnosis and cord stem cells.
Early circulation
The vascular system of the embryo is formed from blood islands that appear in the extraembryonic mesoderm of the yolk sac and the embryonic mesoderm (primarily splanchnic mesoderm). Both of these clusters fuse together and extend, forming a vast network.
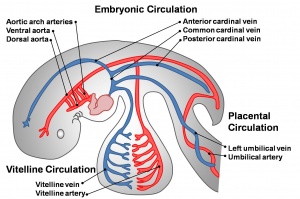
The early circulation has 3 components: Vitelline, Embryonic, Placental Each of these has its own system of arteries and veins.
- Vitelline - (not shown) the vitelline arteries branch off the dorsal aortas and enter the yolk sac, covering its entire surface. The vitelline veins return red blood cells from the capillary beds to the sinus venosus, posterior to the heart. The vitelline vessels eventually contribute to the portal system of the liver in the adult.
- Embryonic - blood from the dorsal aorta enters intersegmental arteries, including the arteries of the pharyngeal arches. The blood returns to the heart via the anterior and posterior cardinal veins.
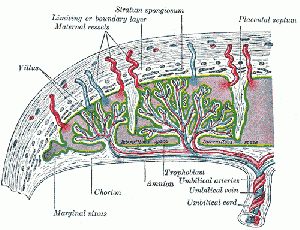
- Placental - the umbilical arteries receive blood from the aorta. This is carried to the chorionic villi, where exchange occurs with the mother. Waste products are disposed of, nutrients and oxygen are collected, and then the umbilical veins convey the blood to the sinus venosus.
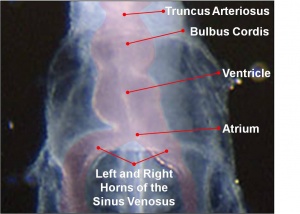
Heart - The heart develops from cardiogenic mesoderm, a region of splanchnic mesoderm lying above the buccopharyngeal membrane. Development begins in week 3 with the formation of a pair of heart tubes. These fuse and form a single tube in week 4, as a result of the embryonic folding processes that occur. As the heart grows, septation events occur, transforming it into a 4-chambered pump. Initially, the ventricles develop above the atria; however simultaneous growth and bending of the tube bring the structures into correct position. In humans, the heart begins to beat on day 22-23. (This will be covered in detail in a later Lab)
Cardiovascular Movies
| Heart Looping |
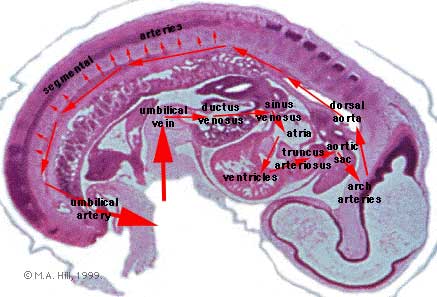
Stage 13 Embryo
Stage 13 3D CVS Reconstruction
About Stage 13 Embryo Sections - This image is from a serial section of a 6mm CRL pig embryo with some features of the Stage 14 embryo. This embryo is approximately equal to the day 42 human embryo. Use these serial images to identify internal features and relationships that exist within the embryo at this stage. Then compare these images with the later features of the Carnegie stage 22 human embryo.
| Stage 13 Serial unlabeled images | Embryo Stage 13 Serial labeled images |
Compare this mid-embryonic cardiovascular system with that existing at the end of embryonic development.
Stage 22 3D CVS Reconstruction
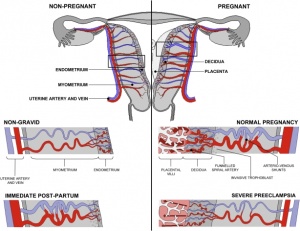
Placentation
Compare the features of a normal and gravid uterus.
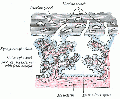
Chorionic Villi
- Compare the features of primary, secondary, tertiary and stemmed villi
Human Villi Timeline
The placental vill development data below is based upon a recent immunochemistry confocal laser scanning microscope (CLSM) study.[1] Note that the paper uses clinical gestational age (GA) from last menstrual period (LMP) and has been corrected for post-conception (fertilization) age, approximately 14 days later.
| Fertilization Age
(weeks) |
Gestational Age
(weeks) |
Vessel Lumen Diameter
(range in microns) |
Features |
| 3 to 4 | 5 and 6 | 10 - 15 |
|
| 5 to 6 | 7 and 8 | 10 - 26 |
|
| 7 to 8 | 9 and 10 | 60 - 75 two central vessels
26 - 34 capillary network |
|
| 9 to 10 | 11 and 12 | 70 - 90 two central vessels
26 - 34 capillary network |
|
CD31 - (PECAM-1, Platelet Endothelial Cell Adhesion Molecule) is a cluster of differentiation molecule found on endothelial and other blood cells.
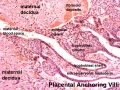
Histology
Virtual Slides: Placenta and Cord Histology | Virtual Slidebox of Histology
Chorionic villi sampling
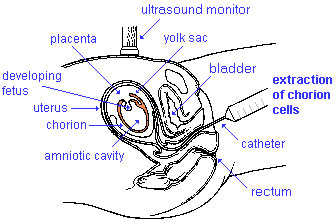
|
Modified from: Checking your baby's health before birth. State Health Publication Number (PA) 94-090 |
Ultrasound
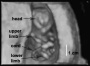
|

|
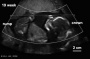
|
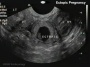
|
| 12 Week Fetus | 12 Week Heart Rate | 19 Week Fetus | Ectopic Pregnancy |
References
- ↑ <pubmed>17545656</pubmed>
External Links
External Links Notice - The dynamic nature of the internet may mean that some of these listed links may no longer function. If the link no longer works search the web with the link text or name. Links to any external commercial sites are provided for information purposes only and should never be considered an endorsement. UNSW Embryology is provided as an educational resource with no clinical information or commercial affiliation.
Course Content 2011
2011 Timetable: | Embryology Introduction | Fertilization | Cell Division/Fertilization | Week 1 and 2 Development | Week 3 Development | Week 1 to 3 | Mesoderm Development | Ectoderm, Early Neural, Neural Crest | Trilaminar Embryo to Early Embryo | Early Vascular Development | Placenta | Vascular and Placenta | Endoderm, Early Gastrointestinal | Respiratory Development | Endoderm and Respiratory | Head Development | Neural Crest Development | Head and Neural Crest | Musculoskeletal Development | Limb Development | Musculoskeletal | Renal Development | Genital | Kidney and Genital | Sensory | Stem Cells | Stem Cells | Endocrine Development | Endocrine | Heart | Integumentary Development | Heart and Integumentary | Fetal | Birth and Revision | Fetal
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2026, March 2) Embryology 2011 Lab 4. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/2011_Lab_4
- © Dr Mark Hill 2026, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G