Stem Cells - Placental Cord Blood
| Embryology - 27 Apr 2024 |
|---|
| Google Translate - select your language from the list shown below (this will open a new external page) |
|
العربية | català | 中文 | 中國傳統的 | français | Deutsche | עִברִית | हिंदी | bahasa Indonesia | italiano | 日本語 | 한국어 | မြန်မာ | Pilipino | Polskie | português | ਪੰਜਾਬੀ ਦੇ | Română | русский | Español | Swahili | Svensk | ไทย | Türkçe | اردو | ייִדיש | Tiếng Việt These external translations are automated and may not be accurate. (More? About Translations) |
Introduction
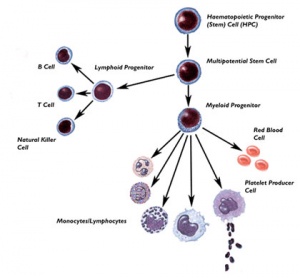
Placenta and placental cord blood (umbilical cord blood, UCB) contains stem cells that can be harvested at birth (More? Placenta Development). The total amout of blood that can be collected is about 90 ml, from which stem cells can be collected, typed and stored in Cord Blood Banks. Both public and private Cord Blood Banks have arisen in this area. These cells provide a resource for bone marrow replacement therapy in many diseases, bone marrow transplantation was originally the only treatment available for many otherwise fatal diseases. Recently, cord blood transplantation has developed as a new alternative therapy for some of these same diseases.
Placental cord blood is a rich souce of haematopoietic stem cells for transplantation. Cord blood can collected at birth, with no impact on the mother or neonate, and stured in cord blood banks for later use.
BBC (UK) A brief article on Cord Blood stem cells and their therapeutic potential.
A useful guide (online PDF document) to stem cells was produced in a report by the National Institute of Health (NIH, USA, May 2000) Stem Cells: A Primer (PDF 1.89 MB) and more recently NIH has established a Stem Cell information page.
Note that placental cord Wharton's jelly can be also used to derive mesenchymal stem cells. These stem cells have been trans-differentiated into more advanced stages of germ cells by a simple two-step induction protocol using retinoic acid and Sertoli cell-conditioned medium. [1]
Some Recent Findings
|
| More recent papers |
|---|
|
This table allows an automated computer search of the external PubMed database using the listed "Search term" text link.
More? References | Discussion Page | Journal Searches | 2019 References | 2020 References Search term: Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell | Cord Stem Cell | cord blood banking |
| Older papers |
|---|
| These papers originally appeared in the Some Recent Findings table, but as that list grew in length have now been shuffled down to this collapsible table.
See also the Discussion Page for other references listed by year and References on this current page.
|
Cord Blood Registries
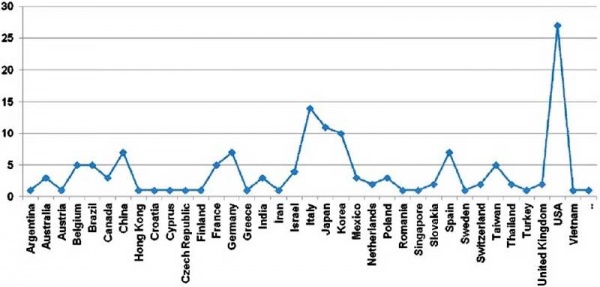
Placental cord blood banks (2009)[9]
Cord blood collection statistics began in 1994 and have been increasing ever since. In January 2007, there were 254,000 cord blood units collected in worldwide registries.
CBU Cord Blood Units
NVC Net Volume Collected of CBU Volume of the unit in milliliters; see note below.
TNC Total Nucleated Cells count of CBU The rounded number of nucleated cells in the units of 10 million.
CD34P Collected number of CD34+ cells of CBU Cell count after volume reduction; numeric value with decimal point in units of 1 million.
MONONUC Collected number of mononuclear cells of CBU The rounded number of mononuclear cells in the units of 10 million.
Diseases
The list of diseases that were transplanted with cord blood include the following: Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia, Acute Myeloblastic Leukaemia, Adrenoleukodystrophy, Blackfan-Diamond, Cancer-miscellaneous, Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia, Chronic Lymphocytic leukaemia, Fanconi's Anaemia, Genetic disorders - miscellaneous, Hurler's Syndrome, Immune deficiency-Miscellaneous, Krabbe's disease, Lymphomas, Myelodysplastic Syndrome, Mucolipopolysaccharide deficiency, Osteopetrosis, Syndrome Severe Aplastic Anaemia, Severe Combined Immunodeficiency Disease, Storage disorders, Thalassaemia, Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome (From: The Sydney Cord Blood Bank)
Australia
Australia has three cord blood banks (CBBs) located in Brisbane (Queensland), Sydney (New South Wales) and Melbourne (Victoria). AusCord is the Australian national network of umbilical cord blood banks and cord blood collection centres.
Links: Australian Bone Marrow Donor Registry | The Sydney Cord Blood Bank (SCBB) | Melbourne - BMDI Cord Blood Bank | Queensland Cord Blood Bank | PDF - AusCord Brochure
United States
On August 9, 2001, at 9:00 p.m. EDT, the President announced his decision to allow Federal funds to be used for research on existing human embryonic stem cell lines as long as prior to his announcement (1) the derivation process (which commences with the removal of the inner cell mass from the blastocyst) had already been initiated and (2) the embryo from which the stem cell line was derived no longer had the possibility of development as a human being.
In addition, the President established the following criteria that must be met:
- The stem cells must have been derived from an embryo that was created for reproductive purposes;
- The embryo was no longer needed for these purposes;
- Informed consent must have been obtained for the donation of the embryo;
- No financial inducements were provided for donation of the embryo.
In order to facilitate research using human embryonic stem cells, the NIH is creating a Human Embryonic Stem Cell Registry that will list the human embryonic stem cell lines -- at varying stages of development -- that meet the eligibility criteria. Listed below are entities that have developed stem cell lines that meet the President's criteria and are therefore eligible for federal funding. Please click on the name of the laboratory or company for contact information.
Dartmouth ethics professor discusses promise and pitfalls of stem cell research (2005)
NIH Clinical Trials (May 2004) Launches Study of Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation for Severe, Treatment-Resistant Lupus (NIAMS, May 13,2004)
A clinical therapeutic trial in the USA for hematopoietic stem cells in an autoimmune disease.
"A five-year study to see whether a therapy using transplantation of hematopoietic stem cells, blood stem cells found in bone marrow, can produce long-term remission for patients with severe, treatment-resistant systemic lupus erythematosus (or lupus), a rheumatic autoimmune disease that can affect the body's major organs. The study will include a basic research component to examine the roles of B and T cells, white blood cells in the immune system, in triggering lupus symptoms."
Read more of the NIH Press Release
Note that a May search of NIH Clinical Trials with "stem cell" found 302 study results.
Repeat search: NIH Clinical Trials with "stem cell"
A recent paper has also identified SP cells in ovarian cancer which have properties similar to stem cells.[10]
References
- ↑ Dissanayake D, Patel H & Wijesinghe PS. (2018). Differentiation of human male germ cells from Wharton's jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Clin Exp Reprod Med , 45, 75-81. PMID: 29984207 DOI.
- ↑ Murdoch B, Marcon AR & Caulfield T. (2020). The law and problematic marketing by private umbilical cord blood banks. BMC Med Ethics , 21, 52. PMID: 32611408 DOI.
- ↑ . (2019). ACOG Committee Opinion No. 771: Umbilical Cord Blood Banking. Obstet Gynecol , 133, e249-e253. PMID: 30801478 DOI.
- ↑ Strong A, Gračner T, Chen P & Kapinos K. (2018). On the Value of the Umbilical Cord Blood Supply. Value Health , 21, 1077-1082. PMID: 30224112 DOI.
- ↑ Arrojo IP, Lamas Mdel C, Verdugo LP, Alfaro PR, Pena RR, Gordo FS, Maldonado PG & Gémar GG. (2012). Trends in cord blood banking. Blood Transfus , 10, 95-100. PMID: 22153685 DOI.
- ↑ Kocaefe C, Balci D, Hayta BB & Can A. (2010). Reprogramming of human umbilical cord stromal mesenchymal stem cells for myogenic differentiation and muscle repair. Stem Cell Rev , 6, 512-22. PMID: 20665127 DOI.
- ↑ Garbuzova-Davis S, Sanberg CD, Kuzmin-Nichols N, Willing AE, Gemma C, Bickford PC, Miller C, Rossi R & Sanberg PR. (2008). Human umbilical cord blood treatment in a mouse model of ALS: optimization of cell dose. PLoS ONE , 3, e2494. PMID: 18575617 DOI.
- ↑ Brunstein CG, Baker KS & Wagner JE. (2007). Umbilical cord blood transplantation for myeloid malignancies. Curr. Opin. Hematol. , 14, 162-9. PMID: 17255794 DOI.
- ↑ McKenna D & Sheth J. (2011). Umbilical cord blood: current status & promise for the future. Indian J. Med. Res. , 134, 261-9. PMID: 21985808
- ↑ Moore KA & Lemischka IR. (2006). Stem cells and their niches. Science , 311, 1880-5. PMID: 16574858 DOI.
Journals
- Cell Stem Cell is the official affiliated journal of the International Society for Stem Cell Research (ISSCR).
- Stem Cells welcomes original articles and concise reviews describing basic laboratory investigations of stem cells and the translation of their clinical aspects of characterization and manipulation from the bench to patient care. The journal covers all aspects of stem cells: embryonic stem cells; tissue-specific stem cells; cancer stem cells; the stem cell niche; stem cell genomics and proteomics; and translational and clinical researc
Reviews
Sanchez-Ramos J. (2006). Stem cells from umbilical cord blood. Semin. Reprod. Med. , 24, 358-69. PMID: 17123231 DOI.
O'Brien TA, Tiedemann K & Vowels MR. (2006). No longer a biological waste product: umbilical cord blood. Med. J. Aust. , 184, 407-10. PMID: 16618241
Brunstein CG & Wagner JE. (2006). Umbilical cord blood transplantation and banking. Annu. Rev. Med. , 57, 403-17. PMID: 16409157 DOI.
Saulnier N, Di Campli C, Zocco MA, Di Gioacchino G, Novi M & Gasbarrini A. (2005). From stem cell to solid organ. Bone marrow, peripheral blood or umbilical cord blood as favorable source?. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci , 9, 315-24. PMID: 16479735
Articles
Garbuzova-Davis S, Sanberg CD, Kuzmin-Nichols N, Willing AE, Gemma C, Bickford PC, Miller C, Rossi R & Sanberg PR. (2008). Human umbilical cord blood treatment in a mouse model of ALS: optimization of cell dose. PLoS ONE , 3, e2494. PMID: 18575617 DOI.
Brunstein CG, Baker KS & Wagner JE. (2007). Umbilical cord blood transplantation for myeloid malignancies. Curr. Opin. Hematol. , 14, 162-9. PMID: 17255794 DOI.
Rubinstein P. (2006). Why cord blood?. Hum. Immunol. , 67, 398-404. PMID: 16728260 DOI.
Search PubMed
July 2010 "cord stem cell" All (9884) Review (1260) Free Full Text (2357)
Search PubMed Now: cord stem cell | cord blood bank
External Links
External Links Notice - The dynamic nature of the internet may mean that some of these listed links may no longer function. If the link no longer works search the web with the link text or name. Links to any external commercial sites are provided for information purposes only and should never be considered an endorsement. UNSW Embryology is provided as an educational resource with no clinical information or commercial affiliation.
- Sydney Cord Blood Bank (SCBB) | How to Search Cord Blood (Sydney Children's Hospital, Sydney, NSW)
- Murdoch Childrens Research Institute BMDI Cord Blood Bank (The Royal Children's Hospital, Parkville, Victoria)
- Bone Marrow Donors Worldwide (BMDW) | Number of donors/CBU's per registry in BMDW
- WHO Nomenclature for Factors of the HLA System
- International Society for Stem Cell Research (ISSCR) is an independent, nonprofit organization formed in 2002 to foster the exchange of information on stem cell research.
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 27) Embryology Stem Cells - Placental Cord Blood. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Stem_Cells_-_Placental_Cord_Blood
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G