Week 1: Difference between revisions
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
[[File:Human-oocyte to blastocyst.jpg|thumb|Human-oocyte to blastocyst]] | |||
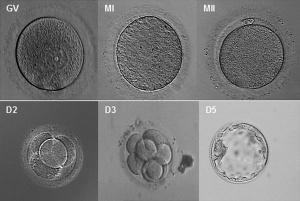
Key Events of Human Development during the first week (week 1) following fertilization or Clinical week 3 (LMP). | Key Events of Human Development during the first week (week 1) following fertilization or Clinical week 3 (LMP). | ||
| Line 8: | Line 9: | ||
:'''Week 1 Links:''' [[2009_Lecture_2|Lecture - Fertilization]] | [[2009_Lecture_3|Lecture - Week 1 and 2]] | [[Oocyte]] | [[Spermatozoa]] | [[Fertilization]] | :'''Week 1 Links:''' [[2009_Lecture_2|Lecture - Fertilization]] | [[2009_Lecture_3|Lecture - Week 1 and 2]] | [[Oocyte]] | [[Spermatozoa]] | [[Fertilization]] | ||
:{{Template:Week}} | :{{Template:Week}} | ||
==Reading== | ==Reading== | ||
Revision as of 14:43, 22 July 2010
Introduction
Key Events of Human Development during the first week (week 1) following fertilization or Clinical week 3 (LMP).
The first week of human development begins with fertilization of the egg by sperm forming the zygote, followed by early cell division forming the blastocyst. These notes also cover events before fertilization formation of both the egg and sperm, gametogenesis.
Initially, there is a halving of choromosomal content in the gametes, which is restored by fertilization, allowing genetic recombination to occur. This is then followed by a series of cell divisions without cytoplasmic growth. During this first week the egg, then zygote, then the blastula is moving along the uterine horn into the uterus for implantation in the uterine wall. Implantation also begins in this first week, but will be covered in Week 2 notes, as the implantation process is completed by the end of the second week.
- Week 1 Links: Lecture - Fertilization | Lecture - Week 1 and 2 | Oocyte | Spermatozoa | Fertilization
- Embryo Week: Week 1 | Week 2 | Week 3 | Week 4 | Week 5 | Week 6 | Week 7 | Week 8 | Week 9
Reading
- Human Embryology (2nd ed.) Larson Chapter 1 pp1-32
- The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology (6th ed.) Moore and Persaud
- Before we Are Born (5th ed.) Moore and Persaud Chapter 2 pp14-33
- Essentials of Human Embryology Larson Chapter 1 pp1-16
- Human Embryology Fitzgerald and Fitzgerald Chapter 2 pp8-14
Timeline
| Event | ||
| Secretory PhaseStage 1 | 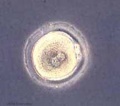 Fertilization, Secretory Phase Fertilization, Secretory Phase
| |
| Stage 2 | 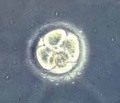 | |
| Stage 3 |  Blastocyst Hatching (zona pellucida lost) Blastocyst Hatching (zona pellucida lost)
| |

Blastocyst (free floating) | ||
| Stage 4 | Adplantation | |
| Stage 5 | File:2ndwk.jpg |
Week 1 Movies
| Ovulation | Fertilization | Pronuclear Fusion | Week 1 | Ovulation in the rabbit | Fertilization in the mouse |
Week 1 Abnormalities
Dizygotic Twinning
Dizygotic twins (fraternal, non-identical) arise from separate fertilization events involving two separate oocyte (egg, ova) and spermatozoa (sperm).
Monoygotic Twinning
Monozygotic twins (identical) produced from a single fertilization event (one fertilised egg and a single spermatazoa, form a single zygote), these twins therefore share the same genetic makeup. Occurs in approximately 3-5 per 1000 pregnancies, more commonly with aged mothers. The later the twinning event, the less common are initially separate placental membranes and finally resulting in conjoined twins.
Table based upon: Twinning. Hall JG. [1]
References
- ↑ <pubmed>12957099</pubmed>
Embryo Week: Week 1 | Week 2 | Week 3 | Week 4 | Week 5 | Week 6 | Week 7 | Week 8 | Week 9
- Carnegie Stages: 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | About Stages | Timeline
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, May 4) Embryology Week 1. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Week_1
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G