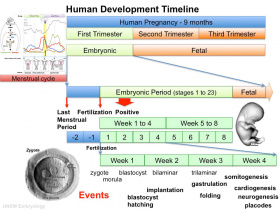
Timeline human development
| Embryology - 27 Apr 2024 |
|---|
| Google Translate - select your language from the list shown below (this will open a new external page) |
|
العربية | català | 中文 | 中國傳統的 | français | Deutsche | עִברִית | हिंदी | bahasa Indonesia | italiano | 日本語 | 한국어 | မြန်မာ | Pilipino | Polskie | português | ਪੰਜਾਬੀ ਦੇ | Română | русский | Español | Swahili | Svensk | ไทย | Türkçe | اردو | ייִדיש | Tiếng Việt These external translations are automated and may not be accurate. (More? About Translations) |
Introduction
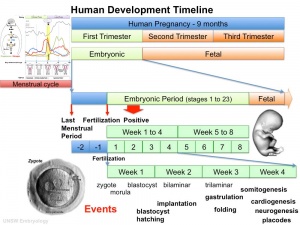
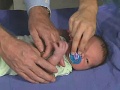
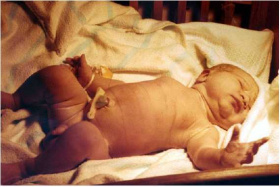
| From a single cell | to a newborn infant | in 9 months. |
|---|---|---|
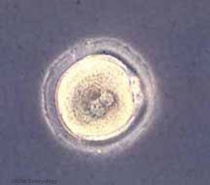
|
|
|
This page is organised to show week by week human development features and approximate timing of key events with more detailed information about specific events in different systems. For a less detailed timeline see week by week.
- "Weeks" refer to embryonic development from fertilization.
- Clinical weeks (shown in brackets) or Gestational Age GA) is from the first day of the Last Menstrual Period (LMP).
- "Stages" refer to the Carnegie stages of development.
- "Timing" refers to days from fertilization or post conception age (PC), not the clinical or gestational age (GA) calculated from LMP (add 2 weeks).
- Dates and staging are also "ideal", and there is significant biological variability in the general timing of events.
- Week 1 to Week 8 (GA 10)are considered the embryonic period of development.
- Week 9 to week 37 (GA 11-39) or birth are considered the fetal period of development.
- First month (4 weeks) after birth is the neonatal period of development.
Each developmental feature is linked to online content with more detailed information and resources such as images and movies. The superscript numbers are the original source references. There are similar "timelines" for other species shown below.
Human Systems
Alphabetical: bone timeline | eye neural crest timeline | heart abnormality timeline | hearing EAM timeline | muscle timeline | ovary timeline | placental villi timeline | shoulder timeline | smell timeline | spleen timeline | ventricular timeline
Second Trimester
(GA Clinical Week 14) Second Trimester
Third Trimester
Postnatal
| Event | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| vision - eye globe growth plateaus after 42 weeks of gestation[1] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| testis | spermatozoa - about 2 months of age, primordial germ cells (gonocytes) are replaced by adult dark (Ad) and pale (Ap) spermatogonia forming the spermatogonial stem cell (SSC) population that at puberty will commence differentiation into spermatozoa. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| neural Hearing (6 months to 5 years) thalamocortical afferents to the deeper cortical layers mature and are the first source of input to the auditory cortex[2]
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adrenal - Year 3 zona reticularis present.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| neural hearing - (5 to 12 years) commissural and association axons in the superficial cortical layers allows communication between subdivisions of the auditory cortex[2] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| puberty - Female | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| puberty - Male | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
- ↑ Paquette LB, Jackson HA, Tavaré CJ, Miller DA & Panigrahy A. (2009). In utero eye development documented by fetal MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol , 30, 1787-91. PMID: 19541779 DOI.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Moore JK. (2002). Maturation of human auditory cortex: implications for speech perception. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol Suppl , 189, 7-10. PMID: 12018354
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 27) Embryology Timeline human development. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Timeline_human_development
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G