Timeline human development: Difference between revisions
(→Week 7) |
|||
| Line 811: | Line 811: | ||
[http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/genital.htm Genital] male and female external genital differences observable | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/genital.htm Genital] male and female external genital differences observable | ||
[ | [[Respiratory_System_Development|Respiratory]] Month 3-6 - lungs appear glandular, end month 6 alveolar cells type 2 appear and begin to secrete surfactant | ||
[http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/tongue.htm Tongue] Week 12 - first differentiated epithelial cells (Type II and III) | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/tongue.htm Tongue] Week 12 - first differentiated epithelial cells (Type II and III) | ||
| Line 841: | Line 841: | ||
[http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/endocrine7.htm Pituitary ] adenohypophysis fully differentiated | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/endocrine7.htm Pituitary ] adenohypophysis fully differentiated | ||
[ | [[Respiratory_System_Development|Respiratory]] Week 16 to 25 lung histology - canalicular | ||
[http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/skin.htm Skin]''' '''4 months - basal cell- proliferation generates folds in basement membrane; neural crest cells- (melanocytes) migrate into epithelium; embryonic connective tissue- differentiates into dermis, a loose ct layer over a dense ct layer. Beneath the dense ct layer is another loose ct layer that will form the subcutaneous layer. Ectoderm contributes to nails, hair follictles and glands. Nails form as thickening of ectoderm epidermis at the tips of fingers and toes. These form germinative cells of nail field. Cords of these cells extend into mesoderm forming epithelial columns. These form hair follocles, sebaceous and sweat glands. | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/skin.htm Skin]''' '''4 months - basal cell- proliferation generates folds in basement membrane; neural crest cells- (melanocytes) migrate into epithelium; embryonic connective tissue- differentiates into dermis, a loose ct layer over a dense ct layer. Beneath the dense ct layer is another loose ct layer that will form the subcutaneous layer. Ectoderm contributes to nails, hair follictles and glands. Nails form as thickening of ectoderm epidermis at the tips of fingers and toes. These form germinative cells of nail field. Cords of these cells extend into mesoderm forming epithelial columns. These form hair follocles, sebaceous and sweat glands. | ||
| Line 897: | Line 897: | ||
| <center>24</center> | | <center>24</center> | ||
| | | | ||
| [ | | [[Respiratory_System_Development|Respiratory]] Week 24 to 40 lung histology - terminal sac | ||
Earliest potential survival expected if born | Earliest potential survival expected if born | ||
| Line 906: | Line 906: | ||
| <center>25</center> | | <center>25</center> | ||
| | | | ||
| [ | | [[Respiratory_System_Development|Respiratory]] end month 6 alveolar cells type 2 appear and begin to secrete surfactant | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 21:01, 21 April 2010
Introduction
This page is organised to show week by week human development features and approximate timing of key events with more detailed information about specific events in different systems. For a less detailed timeline seeweek by week. The "weeks" refer to embryonic development and differ from clinical weeks (shown in brackets, from last menstrual period) and "stages" refer to Carnegie stages of development. Timing, dates and staging are "ideal" and there is significant variability in the general timing of events. PMID refers to the original Pubmed reference data source (links to be added). The timing is also based from fertilization, not gestational age from LMP (add 2 weeks). All links currently to original UNSW Embryology webpages.
UNSW Embryology Links
These links are to the original UNSW Embryology webpages: Timeline Human Development (simple) | Timeline Human Development (detailed) | Timeline Mouse Development
Week -2
(Clinical Week 1)
Week -1
(Clinical Week 2)
| Menstrual cycle | Event | |
| Proliferative Phase | ||
    Mid proliferative Mid proliferative
| ||
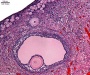
   Late Proliferative Late Proliferative
| ||
| Ovulation
Capacitation |
 |
Week 1
Week 1 (Clinical Week 3)
Week 2
Week 2 (Clinical Week 4)
| Event | ||
| Stage 6 | ||
Week 3
Week 3 (Clinical Week 5)
| Event | ||
| Stage 7 |   
| |
| Stage 8 | 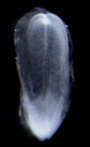 | |
| Stage 9 | 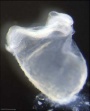 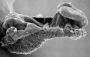 Musculoskeletal somitogenesis, first somites form and continue to be added in sequence caudally Musculoskeletal somitogenesis, first somites form and continue to be added in sequence caudally
Neural the three main divisions of the brain, which are not cerebral vesicles, can be distinguished while the neural groove is still completely open Neural Crest mesencephalic neural crest is visible PMID: 17848161 | |
| Heart cardiogenesis, week 3 begins as paired heart tubes. |
Week 4
Week 4 (Clinical Week 6)
| Event | ||
| Stage 10 |  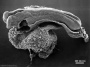 Neural Crest differentiation at spinal cord level from day 22 until day 26 Neural neural folds begin to fuse near the junction between brain and spinal cord, when Neural Crest cells are arising mainly from the neural ectoderm Neural Crest trigeminal, facial, and postotic ganglia components visible PMID: 17848161 Neural Crest migration of vagal level neural crest cells begins (7-10 somite stage) Brain rostral neural tube forms 3 primary brain vesicles (week 4) Respiratory Week 4 - laryngotracheal groove forms on floor foregut. | |
| Heart begins to beat in Humans by day 22-23, first functioning embryonic organ formed. | ||
| Stage 11 | 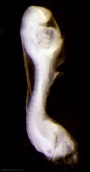
Thyroid thyroid median endodermal thickening in the floor of pharynx Neural rostral (or cephalic) neuropore closes within a few hours; closure is bidirectional, it takes place from the dorsal and terminal lips and may occur in two areas simultaneously. The two lips, however, behave differently. Optic ventricle appears | |
| Stage 12 |  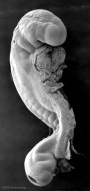
Pituitary Week 4 hypophysial pouch, Rathke's pouch, diverticulum from roof GIT - Liver septum transversum forming liver stroma and hepatic diverticulum forming hepatic trabeculae PMID: 9407542 Neural caudal neuropore takes a day to close (closure is approximately at future somitic pair 31/sacral vertebra 2) Neural secondary neurulation begins Neural Crest cardiac crest, neural crest from rhombomeres 6 and 7 that migrates to pharyngeal arch 3 and from there the truncus arteriosus PMID: 17848161 Neural Crest vagal neural crest enter the foregut (20-25 somite stage) | |
| Stage 13 | 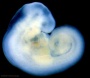 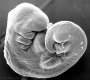 Neural the neural tube is normally completely closed, ventricular system now separated from amniotic fluid. Neural crest at spinal level is segregating, and spinal ganglia are in series with the somites. Spinal cord ventral roots beginning to develop. PMID: 3354839 Neural the neural tube is normally completely closed, ventricular system now separated from amniotic fluid. Neural crest at spinal level is segregating, and spinal ganglia are in series with the somites. Spinal cord ventral roots beginning to develop. PMID: 3354839
telencephalon cavity appears GIT - Liver epithelial cord proliferation enmeshing stromal capillaries PMID: 9407542 Sense - Smell Crest comes from the nasal platesPMID: 15604533 Skin 4 weeks - simple ectoderm epithelium over mesenchyme Skin 1-3 months ectoderm- germinative (basal) cell repeated division of generates stratified epithelium; mesoderm- differentiates into connective tissue and blood vessels |
Week 5
Week 5 (Clinical Week 7)
| Event | ||
| Pituitary Week 5 elongation, contacts infundibulum, diverticulum of diencephalon
Heart Week 5 septation starts, atrial and ventricular Respiratory Week 5 left and right lung buds push into the pericardioperitoneal canals (primordia of pleural cavity) Respiratory Week 5 to 17 lung histology - pseudoglandular Sense - Hearing Week 5 cochlear part of otic vesicle elongates (humans 2.5 turns) | ||
| Stage 14 | 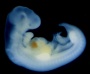  Ectoderm - sensory placodes, lens pit, otocyst, nasal placode, primary/secondary vesicles, fourth ventricle of brain Ectoderm - sensory placodes, lens pit, otocyst, nasal placode, primary/secondary vesicles, fourth ventricle of brain
Mesoderm - continued segmentation of paraxial mesoderm (somite pairs), heart prominence Head - 1st, 2nd and 3rd pharyngeal arch, forebrain, site of lens placode, site of otic placode, stomodeum Body - heart, liver, umbilical cord, mesonephric ridge visible externally as bulges. Limb - upper and lower limb buds growing Neural first appearance of the future cerebral hemispheres. Cerebellar plate differentiated to an intermediate layer, and future rhombic lip identifiable PMID: 3377191 GIT - Liver hepatic gland and its vascular channels enlarge, hematopoietic function appears PMID: 9407542 | |
| Stage 15 | 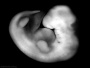
Neural cranial nerves (except olfactory and optic) are identifiable in more advanced embryos PMID: 3213956 | |
| Sense - Eye 35 to 37 days retinal pigment present |
Week 6
Week 6 (Clinical Week 8)
| Event | ||
| Pituitary Week 6 - connecting stalk between pouch and oral cavity degenerates
Parathyroid Week 6 - diverticulum elongate, hollow then solid, dorsal cell proliferation Thymus Week 6 - diverticulum elongate, hollow then solid, ventral cell proliferation Adrenal Week 6 - fetal cortex forms from mesothelium adjacent to dorsal mesentery, medulla neural crest cells from adjacent sympathetic ganglia Respire Week 6 - descent of heart and lungs into thorax. Pleuroperitoneal foramen closes Tongue Week 6 - descent of heart and lungs into thorax. Pleuroperitoneal foramen closes gustatory papilla, caudal midline near the foramen caecum (week 6 to 7 - nerve fibers approach the lingual epithelium) | ||
| Stage 16 | 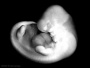 Neural first parasympathetic ganglia, submandibular and ciliary, are identifiable PMID: 2751117 Neural first parasympathetic ganglia, submandibular and ciliary, are identifiable PMID: 2751117
Limbs upper limb bud nerves median nerve, radial nerve and ulnar nerve entered into hand plate, myoblasts spindle shaped and oriented parallel to limb bud axis. Heart outflow tract elliptical configuration with four cushions, the two larger fusing at this stage. Semilunar valve leaflets form at the downstream end of the cushions Head lip and palate components of the upper lip, medial nasal prominence and maxillary process present, median palatine process appears. | |
| Stage 17 | 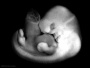
Neural telencephalon areas of the future archicortex, paleocortex, and neocortex, visible. Beginning of future choroid plexus PMID: 2802187 Sense - Smell olfactory nerve fibres enter the brain PMID: 15604533 Neural primordium of the epidural space appears first on the ventral part of the vertebral canal and develops rostro-caudally PMID: 15478101 | |
| Heart separation of common cardiac outflow (aortic arch and pulmonary aorta) |
Week 7
Week 7 (Clinical Week 9)
| Event | ||
| Pancreas Week 7 to 20 pancreatic hormones secretion increases, small amount maternal insulin
Respiratory Week 7 - enlargement of liver stops descent of heart and lungs | ||
| Stage 18 | 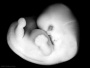
Limb bones form by endochondrial ossification and throughout embryo replacement of cartilage with bone (week 5-12). Sense - Smell vomeronasal fibres and nervus terminalis PMID: 15604533 GIT - Liver obturation due to epithelial proliferation, bile ducts became reorganized, continuity between liver cells and gut PMID: 9407542 Neural duramater appears PMID: 15478101 | |
|
GIT - Liver (stage 18 to 23) biliary ductules developed in periportal connective tissue produces ductal plates that receive biliary capillaries PMID: 9407542 | ||
| Stage 19 | 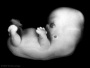 Neural accessory olivary nucleus appears PMID: 2268071 Neural accessory olivary nucleus appears PMID: 2268071
| |
Week 8
Week 8 (Clinical Week 10)
| Event | ||
| Stage 20 | 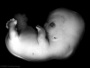
Head scalp vascular plexus visible Limb upper limbs begin to rotate ventrally Neural amygdaloid body has at least four individual nuclei PMID: 2268071 oculomotor nerve shows a dorsolateral and a ventromedial portion rhombic lip (rhombencephalon) formation of the cerebellum (intermediate layer) and of the cochlear nuclei cerebellum cell layer (future Purkinje cells) develops choroid plexuses of the fourth and lateral ventricles | |
| Gastrointestinal Tract anal membrane perforates | ||
| Stage 21 | 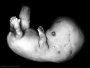
Neural cortical plate appears in the area of future insula PMID: 2252222 Limb upper and lower limbs rotate Intraembryonic Coelom pericardioperitoneal canals close | |
| Stage 22 | 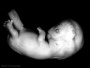 Neural neocortical fibres project to epithalamus, to dorsal thalamus, and to mesencephalon PMID: 2252222 Neural neocortical fibres project to epithalamus, to dorsal thalamus, and to mesencephalon PMID: 2252222
Limb fingers and toes lengthen Sense - Smell Stage 22 to early fetal period - migratory streams of neurons from the subventricular zone of the olfactory bulb towards the future claustrum PMID: 15604533 | |
| Genital 8 Weeks Testis - mesenchyme, interstitial cells (of Leydig) secrete testosterone, androstenedione
Genital 8 to 12 Weeks - hCG stimulates testosterone production Tongue Week 8 - nerves penetrate epitheilai basal lamina and synapse with undifferentiated, elongated, epithelial cells (taste bud progenitor cell) | ||
| Stage 23 | 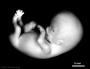 [1]Stage 23 defines the end of the embryonic (organogenesis) period [1]Stage 23 defines the end of the embryonic (organogenesis) period
Mesoderm heart prominence, ossification continues Head nose, eye, external acoustic meatus, eyelids, external ears, rounded head Body - straightening of trunk, heart, liver, umbilical cord, intestines herniated at umbilicus Limb upper limbs longer and bent at elbow, hands and feet turned inward, foot with separated digits, wrist, hand with separated digits Extraembryonic Coelom chorionic cavity is now lost by fusion with the expanding amniotic cavity Neural rhombencephalon, pyramidal decussation present, nuclei and tracts similar to those present in the newborn cerebellum present as only a plate connected to midbrain and hindbrain through fibre bundles PMID: 2244584 Axial Skeleton vertebral column 33 or 34 cartilaginous vertebrae (20-33 mm in total length), vertebral pedicles, articular and transverse processes identifiable (no spinous processes) PMID: 7216919 | |
| Week 8 | GIT - Stomach - Week 8 - Gastrin containing cells in stomach antrum. Somatostatin cells in both the antrum and the fundus. |
Week 9
(Clinical Week 11)
| Event | ||
| Fetal Period | 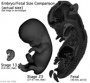
Sense - Hearing Week 9 - mesenchyme surrounding membranous labrynth (otic capsule) chondrifies Sense - Smell Embryonic/Fetal transition - localized incomplete lamination of the olfactory bulb PMID: 15604533 | |
| Week 9 - CRL 43 mm, femur length 6 mm
9 weeks CRL 50 mm - genitalia in both sexes look identical PMID: 17875485 uterus - paramesonephric ducts come into apposition with the urorectal septum and begin to fuse |
Week 10
(Clinical Week 12)
| Event | ||

Gastrointestinal Tract Week 10 intestines in abdomen Pituitary growth hormone and ACTH detectable Pancreas Week 10 glucagon (alpha) differentiate first, somatostatin (delta), insulin (beta) cells differentiate, insulin secretion begins Tongue Week 10 shallow grooves above the taste bud primordium GIT - Stomach - Week 10 - Glucagon containing cells in stomach fundus. | ||
| Week 10 - CRL 55 mm, femur length 9 mm, biparietal diameter 17 mm |
Week 11
(Clinical Week 13)
| Event | ||

Thyroid colloid appearance in thyroid follicles, iodine and thyroid hormone (TH) synthesis GIT - Stomach - Week 11 - Serotonin containing cells in both the antrum and the fundus. | ||
| Week 11 - CRL 68 mm, femur length 12 mm, biparietal diameter 20 mm |
Second Trimester
(Clinical Week 14)
| Event | ||
| Clinical second trimester |  Week 12 - CRL 85 mm, femur length 15 mm, biparietal diameter 25 mm Week 12 - CRL 85 mm, femur length 15 mm, biparietal diameter 25 mm
Sense - Hearing Week 12-16 - Capsule adjacent to membranous labrynth undegoes vacuolization to form a cavity (perilymphatic space) around membranous labrynth and fills with perilymph Genital male and female external genital differences observable Respiratory Month 3-6 - lungs appear glandular, end month 6 alveolar cells type 2 appear and begin to secrete surfactant Tongue Week 12 - first differentiated epithelial cells (Type II and III) female genital canal (80 days) formed with absorption of the median septum | |
| Tongue Week 12 to 13 - maximum synapses between cells and afferent nerve fibers
| ||
| Tongue Week 14 to 15 - taste pores develop, mucous | ||
| Pancreas glucagon detectable in fetal plasma | ||
| 14 cm | 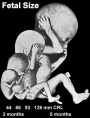 Sense - Hearing Week 16-24 - Centres of ossification appear in remaining cartilage of otic capsule form petrous portion of temporal bone. Continues to ossify to form mastoid process of temporal bone. Sense - Hearing Week 16-24 - Centres of ossification appear in remaining cartilage of otic capsule form petrous portion of temporal bone. Continues to ossify to form mastoid process of temporal bone.
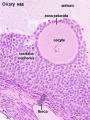
Pituitary adenohypophysis fully differentiated Respiratory Week 16 to 25 lung histology - canalicular Skin 4 months - basal cell- proliferation generates folds in basement membrane; neural crest cells- (melanocytes) migrate into epithelium; embryonic connective tissue- differentiates into dermis, a loose ct layer over a dense ct layer. Beneath the dense ct layer is another loose ct layer that will form the subcutaneous layer. Ectoderm contributes to nails, hair follictles and glands. Nails form as thickening of ectoderm epidermis at the tips of fingers and toes. These form germinative cells of nail field. Cords of these cells extend into mesoderm forming epithelial columns. These form hair follocles, sebaceous and sweat glands. primary follicles begin to form in the ovary and are characterized by an oocyte glandular urethra forms and skin folds present | |
| Tongue Week 18 - substance P detected in dermal papillae, not in taste bud primordia
Skin vernix caseosa covers skin Spleen -SMA-positive reticulum cells increase in number and begin to form a reticular framework. PMID: 1925578 | ||
| Pituitary week 20 to 24 growth hormone levels peak, then decline
Skin lanugo, skin hair Skin 5 months - Hair growth initiated at base of cord, lateral outgrowths form associated sebaceous glands; Other cords elongate and coil to form sweat glands; Cords in mammary region branch as they elongate to form mammary glands. | ||
 Neural brain cortical sulcation - sylvian fissure, interhemispheric fissure, callosal sulcus, parietooccipital fissure, and hippocampic fissures present(PMID:11158907 Neural brain cortical sulcation - sylvian fissure, interhemispheric fissure, callosal sulcus, parietooccipital fissure, and hippocampic fissures present(PMID:11158907
Spleen - antigenic reticular framework diversity, T and B lymphocytes segregated in the framework PMID: 1925578 | ||
| Respiratory Week 24 to 40 lung histology - terminal sac
Earliest potential survival expected if born ovarian follicles can consist of growing oocytes surrounded by several layers of granulosa cells | ||
| Respiratory end month 6 alveolar cells type 2 appear and begin to secrete surfactant |
Third Trimester
(Clinical Week 28)
| Event | ||
| Clinical third trimester |  Sense - Hearing 3rd Trimester - vibration acoustically of maternal abdominal wall induces startle respone in fetus. Sense - Hearing 3rd Trimester - vibration acoustically of maternal abdominal wall induces startle respone in fetus.
| |
| Respire Month 7 - respiratory bronchioles proliferate and end in alveolar ducts and sacs | ||
|
Genital male gonad (testes) descending | ||
| Neural brain cortical sulcation - primary sulci present PMID:11158907 | ||
| Neural brain cortical sulcation - insular, cingular, and occipital secondary sulci present PMID:11158907 | ||
| ||
| Birth | File:Birthsm.gif Clinical Week 40
Heart pressure difference closes foramen ovale leaving a fossa ovalis Thyroid TSH levels increase, thyroxine (T3) and T4 levels increase to 24 h, then 5-7 days postnatal decline to normal levels Adrenal - zona glomerulosa, zona fasiculata present
|
Postnatal
| Event | ||
| Hearing - (6 months to 5 years) thalamocortical afferents to the deeper cortical layers mature and are the first source of input to the auditory cortex PMID: 12018354 | ||
| Adrenal - Year 3 zona reticularis present | ||
| Hearing - (5 to 12 years) commissural and association axons in the superficial cortical layers allows communication between subdivisions of the auditory cortex PMID: 12018354 | ||
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, May 4) Embryology Timeline human development. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Timeline_human_development
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G