Somitogenesis
Introduction
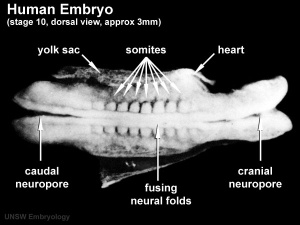
The term used to describe the process of segmentation of the paraxial mesoderm within the trilaminar embryo body to form pairs of somites, or balls of mesoderm. In humans, the first somite pair appears at day 20 and adds caudally at 1 somite pair/90 minutes until on average 44 pairs eventually form.
A somite is added either side of the notochord (axial mesoderm) to form a somite pair. The segmentation does not occur in the head region, and begins cranially (head end) and extends caudally (tailward) adding a somite pair at regular time intervals. The process is sequential and therefore used to stage the age of many different species embryos based upon the number visible somite pairs.
Some Recent Findings
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Mar 8;108(10):4018-23. Epub 2011 Feb 22. FGF4 and FGF8 comprise the wavefront activity that controls somitogenesis. Naiche LA, Holder N, Lewandoski M.
Genetics of Vertebrate Development Section, National Cancer Institute, Frederick, MD 21701. Abstract Somites form along the embryonic axis by sequential segmentation from the presomitic mesoderm (PSM) and differentiate into the segmented vertebral column as well as other unsegmented tissues. Somites are thought to form via the intersection of two activities known as the clock and the wavefront. Previous work has suggested that fibroblast growth factor (FGF) activity may be the wavefront signal, which maintains the PSM in an undifferentiated state. However, it is unclear which (if any) of the FGFs expressed in the PSM comprise this activity, as removal of any one gene is insufficient to disrupt early somitogenesis. Here we show that when both Fgf4 and Fgf8 are deleted in the PSM, expression of most PSM genes is absent, including cycling genes, WNT pathway genes, and markers of undifferentiated PSM. Significantly, markers of nascent somite cell fate expand throughout the PSM, demonstrating the premature differentiation of this entire tissue, a highly unusual phenotype indicative of the loss of wavefront activity. When WNT signaling is restored in mutants, PSM progenitor markers are partially restored but premature differentiation of the PSM still occurs, demonstrating that FGF signaling operates independently of WNT signaling. This study provides genetic evidence that FGFs are the wavefront signal and identifies the specific FGF ligands that encode this activity. Furthermore, these data show that FGF action maintains WNT signaling, and that both signaling pathways are required in parallel to maintain PSM progenitor tissue.
PMID: 21368122
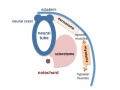
Paraxial Mesoderm to Somite
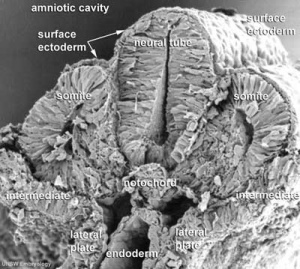
Mesoderm means the "middle layer" and it is from this layer that nearly all the bodies connective tissues are derived. In early mesoderm development a number of transient structures will form and then be lost as tissue structure is patterned and organised. Humans are vertebrates, with a "backbone", and the first mesoderm structure we will see form after the notochord will be somites.
Coelom, meaning "cavity", and major fluid-filled cavities can be seen to form both within the embryo (intraembryonic coelom) and outside the embryo (extraembryonic coelom). The intraembryonic coelom is the single primitive cavity that lies within the mesoderm layer that will eventually form the 3 major anatomical body cavities (pericardial, pleural, peritoneal).
Somite initially forms 2 main components
- ventromedial- sclerotome forms vertebral body and intervertebral disc
- dorsolateral - dermomyotome forms dermis and skeletal muscle
Embryo Week: Week 1 | Week 2 | Week 3 | Week 4 | Week 5 | Week 6 | Week 7 | Week 8 | Week 9
- Carnegie Stages: 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | About Stages | Timeline
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, May 6) Embryology Somitogenesis. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Somitogenesis
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G