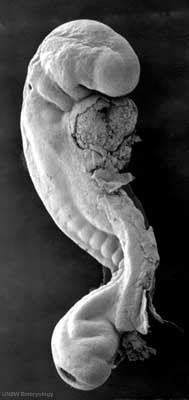
Scanning Electron Microscopy
Introduction
The Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) was a development of the electron microscope. Unlike a light microscope, using light, the electron microscope uses a focussed beam of electrons to image materials. The first version of this technology was the transmission electron microscope (TEM).
- On this current site the acronym "SEM" is used to denote a Scanning Electron Micrograph, the image produced by this form of microscopy.
There are a series of beautiful SEM images made available by Prof Kathy Sulik of the early developing human embryo between week 3 to 5 (Carnegie stage 7 to 14) available: 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13 and 14.
Template:Stage 11 BF images - Menu list of human embryo Carnegie stage 11 bright field images.
Template:Stage 12 SEM images - Menu list of human embryo Carnegie stage 12 scanning EM images.
- Links: Carnegie stage 11 SEM images | Carnegie stage 12 SEM images | Carnegie stage 14 SEM images | Category:Scanning EM
Microscopy Timeline
- 1665 - Robert Hooke publishes Micrographia, a collection of biological micrographs.
- 1674 - Anton van Leeuwenhoek improved simple microscope for biological specimens.
- 1833 - Brown published a microscopic observation of orchids, describing the cell nucleus.
- 1898 - Golgi first saw and described the Golgi apparatus by staining cells with silver nitrate.
- 1931 - Ernst Ruska first transmission electron microscope, (TEM).
- 1934 - Frits Zernike describes phase contrast microscopy.
- 1957 - Marvin Minsky patents principle of confocal imaging.
- 1953 - Frits Zernike receives the Nobel Prize in Physics for invention of the phase contrast microscope.
- 1955 - George Nomarski theoretical basis of Differential interference contrast microscopy.
- 1981 - Gerd Binnig and Heinrich Rohrer develop the canning Tunneling Microscope (STM).
- 1981 - Daniel Axelrod develop Total Internal Reflection Fluorescence Microscope (TIRFM).
- 1981 - Allen and Inoué perfected video-enhanced-contrast light microscopy.
- 1986 - Ernst Ruska, Gerd Binnig and Heinrich Rohrer receive the Nobel Prize in Physics for invention of the electron microscope (ER) and scanning tunneling microscope (GB and HR).
- 2000 - Hell and collaborators develop Stimulated Emission Depletion Microscopy (STED).
- 2008 - Freudiger and Wei Min develop Stimulated Raman Scattering Microscopy (SRS)
- Carnegie Stages: 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | About Stages | Timeline
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, May 2) Embryology Scanning Electron Microscopy. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Scanning_Electron_Microscopy
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G