Ultrasound: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 73: | Line 73: | ||
'''Search PubMed:''' [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?db=pubmed&cmd=search&term=Ultrasound_prenatal_diagnosis Ultrasound prenatal diagnosis] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?db=pubmed&cmd=search&term=Ultrasound Ultrasound] | '''Search PubMed:''' [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?db=pubmed&cmd=search&term=Ultrasound_prenatal_diagnosis Ultrasound prenatal diagnosis] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?db=pubmed&cmd=search&term=Ultrasound Ultrasound] | ||
{{Template:Prenatal Diagnosis terms}} | |||
==Terms== | |||
'''Femur length''' - (FL) is used to determine fetal age and normal development (small/large/abnormal) parameters. The femur is the longest bone in the body and measurements and reflects the longitudinal growth of the [[F#fetus|fetus]] (approximately 14 weeks 1.5 cm - term 7.8 cm). It is one of the four typical [[U#ultrasound|ultrasound]] assessments of fetal size and age: [[B#biparietal_diameter|Biparietal Diameter]] (BPD), [[H#head_circumference|Head Circumference]] (HC), [[A#abdominal_circumference|Abdominal Circumference]] (AC), and Femur Length (FL). | |||
{{Template:Glossary}} | {{Template:Glossary}} | ||
{{Template:Footer}} | {{Template:Footer}} | ||
Revision as of 18:59, 24 May 2010
Introduction
This page links to all ultrasound movies of live normal human embryos. Ultrasound imaging began in the 1950's but it was only with the application of computer analysis beginning in the 1980's that more detailed images could be generated.
Parents now commonly see ultrasound movies or images in the first trimester and clinically this is a non-invasive prenatal diagnostic tool for detection of abnormalities as well as a method of staging (ageing) and checking growth. There are several different standards available[1] for calculating age based upon several measurements, including embryo or fetal crown rump length (CRL).[2]
Ultrasound can also be used in combination with other techniques to locate both embryo and placenta for other prenatal tests (More? prenatal diagnosis).
The ultrasound technique can be used at any stage during pregnancy for embryo and placenta monitoring. The ultrasound movies can be viewed in two ways. Firstly, click the image or text link opens a new page with both the movie and a more detailed text description of features. Secondly, clicking on the quicktime link will open the movie alone on a new page. At the bottom of this current page is further ultrasound information and links to internet ultrasound sites.
Abnormal developmental ultrasound and features are listed on a separate page (More? abnormal ultrasound) all content is for educational use only.
Special thanks to Dr Andrew McLennan, Foetal Medicine Unit, Royal North Shore Hospital for the original video materials.
Some Recent Findings
Comparison between ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging in assessment of fetal cytomegalovirus infection. Picone O, Simon I, Benachi A, Brunelle F, Sonigo P. Prenat Diagn. 2008 Jun 13. PMID: 18551722
- "MRI can provide important additional information with regard to abnormal gyration, cerebellar hypoplasia, or abnormal signal in white matter. It is certainly useful in the assessment of fetuses with extracerebral features without brain abnormalities detected with ultrasounds. If the fetal ultrasound is strictly normal in an infected fetus, MRI may not detect brain anomalies; however, it seems difficult to not perform this noninvasive procedure."
Prenatal diagnosis of vasa previa through color Doppler and three-dimensional power Doppler ultrasonography. A case report. Araujo Júnior E, Filho HA, Pires CR, Zanforlin Filho SM, Moron AF. Clin Exp Obstet Gynecol. 2006;33(2):122-4. PMID: 16903253
- "Vasa previa occurs in pregnancy when one of the membrane vessels extends down to the level of the internal cervical os, ahead of the fetal presenting part and unsupported by the placenta tissue or umbilical cord. The rupture of the vessels might happen spontaneously or artificially and frequently results in fetal exsanguination and demise. Ultrasound prenatal diagnosis is highly important as it allows the identification of patients at risk, thus an elective cesarean can be performed before rupture the membranes. We report a case of vasa previa diagnosed through color Doppler mode in the 30th week of gestation, emphasizing the contribution of three-dimensional power Doppler to the adequate mapping of aberrant vessels, which greatly contributed to the success of the perinatal result."
Ultrasound Movies
UNSW Embryology Ultrasound Movies
The links below are to currently external pages containing ultrasound movies and direct links to the Quicktime movies.
- 7 week human embryo | Movie 1.3 Mb
- 7 week human twin embryos | Movie 1.0 Mb
- 8 week human embryo | Movie 1.8 Mb
- 12 week human fetus | Movie 800 Kb
- 12 week human fetal heart rate | Movie 848 Kb
- 12 week human 4D
3D Ultrasound
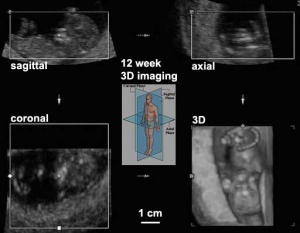
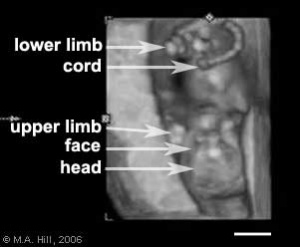
Three dimensional (3D) ultrasound scan images are generated from a series of images in 3 different planes. The image shows a 12 week fetal ultrasound images in the sagittal, axial and coronal planes that are used by the computer to generate the final 3D image in the lower right. Computers are able to generate these images in realtime, therefore in addition to static pictures, realtime 4D movies can be generated.
Ultrasound Research
Ultrasound imaging began in the 1950's but it was only with the application of computer analysis beginning in the 1980's that more detailed images could be generated. The increasing quality of ultrasonic equipment and computing allows today realtime 3D scans and calculations of fetal measurements as well as doppler measurement of heart rates.
In medical research there have been recent developments that allow spatial high resolution down to 30 microns in real-time. (More? commercial site Visualsonics | Dev Biology scans)
Other Imaging Techniques
There are a range of other imaging techniques to study development and used in developmental research.
Other developmental research imaging techniques include:
- magnetic resonance imaging
- computed tomography
- high frequency ultrasound or High Intensity Focused Ultrasound (HIFU)
- positron emission tomography (PET)
- single photon emission computed tomography
- optical bioluminescence
- fluorescence
References
- ↑ Ultrasonic fetal measurements: new Australian standards for the new millennium. Westerway SC, Davison A, Cowell S. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 2000 Aug;40(3):297-302. PMID: 11065037
- ↑ A comparison of first trimester measurements for prediction of delivery date. Chalouhi GE, Bernard JP, Benoist G, Nasr B, Ville Y, Salomon LJ. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2010 Mar 30. PMID: 20350241
Search PubMed: Ultrasound prenatal diagnosis | Ultrasound
- ART - Assisted Reproductive Technology a general term to describe all the clinical techniques used to aid fertility.
- blastomere biopsy - An ART preimplantation genetic diagnosis technique carried out at cleavage stage (day 3), excluding poor quality embryos, detects chromosomal abnormalities of both maternal and paternal origin. May not detect cellular mosaicism in the embryo.
- blastocyst biopsy - An ART preimplantation genetic diagnosis technique carried out at blastocyst stage (day 4-5), removes several trophoblast (trophoderm) cells, detects chromosomal abnormalities of both maternal and paternal origin and may detect cellular mosaicism.
- cell-free fetal deoxyribonucleic acid - (cfDNA) refers to fetal DNA circulating and isolated from the plasma portion of maternal blood. Can be performed from GA 10 weeks as a first-tier test or as a second-tier test, with women with increased probability on combined first trimester screening offered cfDNA or diagnostic testing.
- false negative rate - The proportion of pregnancies that will test negative given that the congenital anomaly is present.
- false positive rate - The proportion of pregnancies that will test positive given that the congenital anomaly is absent.
- free β human chorionic gonadotrophin - beta-hCG subunit of hCG used as a diagnostic marker for: early detection of pregnancy, Trisomy 21, spontaneous abortion, ectopic pregnancy, hydatidiform mole or choriocarcinoma.
- multiples of the median - (MoM) A multiple of the median is a measure of how far an individual test result deviates from the median and is used to report the results of medical screening tests, particularly where the results of the individual tests are highly variable.
- negative predictive value - The probability that a congenital anomaly is absent given that the prenatal screening test is negative.
- Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing - (NIPT) could refer to ultrasound or other imaging techniques, but more frequently used to describe analysis of cell-free fetal DNA circulating in maternal blood.
- polar body biopsy - (PB biopsy) An ART preimplantation genetic diagnosis technique that removes either the first or second polar body from the zygote. As these are generated by oocyte meiosis they detects chromosomal abnormalities only on the female genetics.
- positive predictive value - The probability that a congenital anomaly is present given that the prenatal screening test is positive.
- pre-implantation genetic diagnosis - (PGD, pre-implantation genetic screening) a diagnostic procedure for embryos produced through Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART, in vitro fertilisation, IVF) for genetic diseases that would generate developmental abnormalities or serious postnatal diseases.
- prenatal screening sensitivity - (detection rate) The probability of testing positive on a prenatal screening test if the congenital anomaly is present.
- prenatal screening specificity - The probability of testing negative on a prenatal screening test if the congenital anomaly is absent.
- quadruple test (maternal serum testing of a-fetoprotein Template:AFP, free B-hCG or total hCG, unconjugated estriol, and inhibin A) is a fetal chromosomal anomaly test usually carried out later in pregnancy (GA 14 to 20 weeks).
- single nucleotide polymorphisms - (SNPs) the variation in a single DNA nucleotide that occurs at a specific position in the genome.
- triple test - (maternal serum testing of a-fetoprotein Template:AFP, free B-hCG or total hCG, and unconjugated estriol) is a fetal chromosomal anomaly test usually carried out later in pregnancy (GA 14 to 20 weeks).
| Other Terms Lists |
|---|
| Terms Lists: ART | Birth | Bone | Cardiovascular | Cell Division | Endocrine | Gastrointestinal | Genital | Genetic | Head | Hearing | Heart | Immune | Integumentary | Neonatal | Neural | Oocyte | Palate | Placenta | Radiation | Renal | Respiratory | Spermatozoa | Statistics | Tooth | Ultrasound | Vision | Historic | Drugs | Glossary |
Terms
Femur length - (FL) is used to determine fetal age and normal development (small/large/abnormal) parameters. The femur is the longest bone in the body and measurements and reflects the longitudinal growth of the fetus (approximately 14 weeks 1.5 cm - term 7.8 cm). It is one of the four typical ultrasound assessments of fetal size and age: Biparietal Diameter (BPD), Head Circumference (HC), Abdominal Circumference (AC), and Femur Length (FL).
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, May 2) Embryology Ultrasound. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Ultrasound
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G