File:HillH202 Stage 17 bf04.jpg
From Embryology
Size of this preview: 600 × 600 pixels. Other resolution: 1,000 × 1,000 pixels.
Original file (1,000 × 1,000 pixels, file size: 138 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
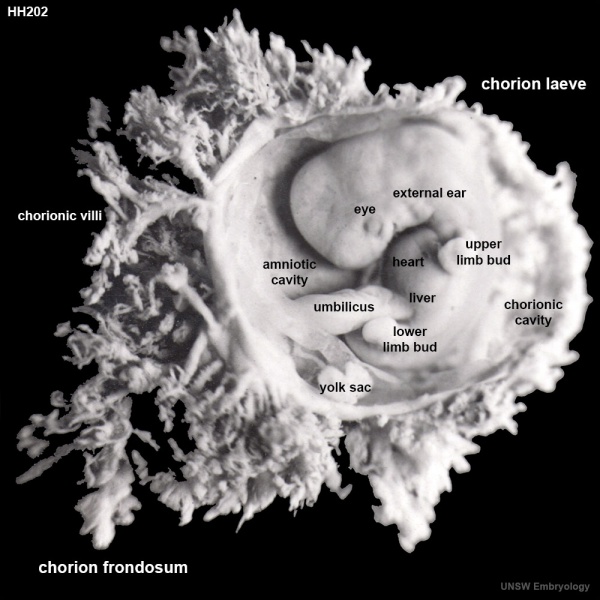
Human Embryo (Carnegie stage 17)
HillH202 embryo CRL 12.5mm
Chorionic sac has been open to observe the developing embryo and extra-embryonic coeloms (cavities).
- chorion laeve - (laeve = smooth) The smooth chorion found on conceptus away from maternal blood supply (towards uterine epithelium and cavity) with very few villi present.
- chorion frondosum - (frondosum = leafy) The chorion found on conceptus oriented towards maternal blood supply where the majority of villi form and proliferate, will contribute the fetal component of the future placenta.
- chorionic villi - Plural of villus, which is a thin projection from a surface. The term in development is used to describe the individual functional units together of the fetal placenta. Placenta Development
- chorionic cavity - The fluid-filled extraembryonic coelom (cavity) formed initially from trophoblast and extraembryonic mesoderm that forms placenta. chorion and amnion are made by the somatopleure. The chorion becomes incorporated into placental development. The avian and reptilian chorion lies beside the egg shell and allows gas exchange. In humans, this cavity is lost during week 8 when the amniotic cavity expands and fuses with the chorion.
- amniotic cavity - The fluid-filled (amniotic fluid) extraembryonic coelom (cavity) formed initially by epiblast and then lined by ectoderm and surrounding extraembryonic mesoderm. In humans, it forms the innermost fetal membrane, produces amniotic fluid expanding to eventually fuse with the chorionic membrane during week 8 of development. This fluid-filled sac initially lies above the trilaminar embryo disc and with embryonic disc folding this sac is drawn ventrally to enclose (cover) the entire embryo, then fetus. The presence of this membrane led to the description of reptiles, bird, and mammals as "amniotes".
- yolk sac - An extraembryonic membrane which is endoderm origin and covered with extraembryonic mesoderm. Yolk sac lies outside the embryo connected initially by a yolk stalk to the midgut with which it is continuous with. The endodermal lining is continuous with the endoderm of the gastrointestinal tract. The extra-embryonic mesoderm differentiates to form both blood and blood vessels of the vitelline system. In reptiles and birds, the yolk sac has a function associated with nutrition. In mammals the yolk sac acts as a source of primordial germ cells and blood cells. Note that in early development (week 2) a structure called the "primitive yolk sac" forms from hypoblast, this is an entirely different structure.
- HH202 Links: Image 1 | Image 2 | Image 3 | labeled Image 3 | Animation small | Animation large | Carnegie Stage 17 | Hill Collection
| Week: | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| Carnegie stage: | 1 2 3 4 | 5 6 | 7 8 9 | 10 11 12 13 | 14 15 | 16 17 | 18 19 | 20 21 22 23 |
Image source: The images from the Hill Collection (part of the Embryological Collection) are reproduced with the permission of the Museum für Naturkunde, Leibniz Institute for Research on Evolution and Biodiversity. Images are for educational purposes only and must not be reproduced electronically or in writing without permission from the Museum für Naturkunde Berlin.
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 17:52, 22 March 2014 |  | 1,000 × 1,000 (138 KB) | Z8600021 (talk | contribs) | ==Human Embryo (Carnegie stage 17)== HillH202 embryo CRL 12.5mm Chorionic sac has been open to observe the developing embryo and yolk sac. {{HillH202 links}} |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
There are no pages that use this file.