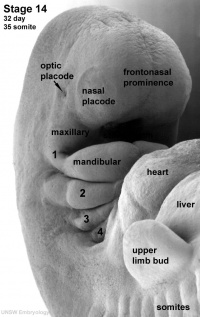
Sensory System Development
| Embryology - 9 Mar 2026 |
|---|
| Google Translate - select your language from the list shown below (this will open a new external page) |
|
العربية | català | 中文 | 中國傳統的 | français | Deutsche | עִברִית | हिंदी | bahasa Indonesia | italiano | 日本語 | 한국어 | မြန်မာ | Pilipino | Polskie | português | ਪੰਜਾਬੀ ਦੇ | Română | русский | Español | Swahili | Svensk | ไทย | Türkçe | اردو | ייִדיש | Tiếng Việt These external translations are automated and may not be accurate. (More? About Translations) |
Introduction
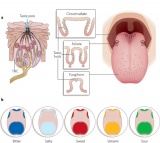
This current page is a "landing page" for your study of sensory development (hearing and balance, sight, smell, taste) through the development of the specialized sense organs (ear, eye, nose and tongue). Note that other species have a range of additional sensory systems (magnetoreception).
Portions of the eye, nose and ear appear very early in development each as a specialized surface ectoderm region (placode) on the embryo. These regions must be connected to the central nervous system by neural pathways that originate as extensions from the developing brain.
This section of notes will not specifically cover development of the central nervous system component of these sensory systems, the sensorimotor cortex[1], nor the sensory components of the skin (More? neural | integumentary | neural crest).
- Use the specific sensory start page shown below to explore each system development.
|
|
|
|
|
All Sensory System Pages
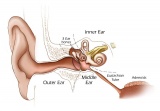
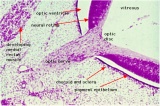
| Vision Links: vision | lens | retina | placode | extraocular muscle | cornea | eyelid | lacrima gland | vision abnormalities | Student project 1 | Student project 2 | Category:Vision | sensory | ||
|
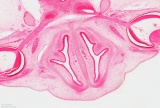
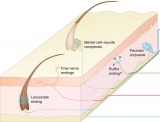
| Smell Links: Introduction | placode | Rhinencephalon | head | respiratory | Student project | taste | sensory | Category:Smell | ||
|
| Taste Links: Introduction | Student project | Tongue Development | Category:Taste | ||
|
Textbooks
- Human Embryology (2nd ed.) Larson Chapter 12: p375-409
- The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology (6th ed.) Moore and Persaud Chapter 19: p491-511
- Essentials of Human Embryology Larson Chapter12: p252-272
- Before We Are Born (5th ed.) Moore and Persaud Chapter 20: p460-479
- Journal of Cell Biology Collection - The Cell Biology of the Senses
Some Recent Findings
|
References
Search PubMed
Search Pubmed: Sensory System Development
| System Links: Introduction | Cardiovascular | Coelomic Cavity | Endocrine | Gastrointestinal Tract | Genital | Head | Immune | Integumentary | Musculoskeletal | Neural | Neural Crest | Placenta | Renal | Respiratory | Sensory | Birth |
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2026, March 9) Embryology Sensory System Development. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Sensory_System_Development
- © Dr Mark Hill 2026, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G