Developmental Signals - Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor
| Embryology - 28 Apr 2024 |
|---|
| Google Translate - select your language from the list shown below (this will open a new external page) |
|
العربية | català | 中文 | 中國傳統的 | français | Deutsche | עִברִית | हिंदी | bahasa Indonesia | italiano | 日本語 | 한국어 | မြန်မာ | Pilipino | Polskie | português | ਪੰਜਾਬੀ ਦੇ | Română | русский | Español | Swahili | Svensk | ไทย | Türkçe | اردو | ייִדיש | Tiếng Việt These external translations are automated and may not be accurate. (More? About Translations) |
Introduction
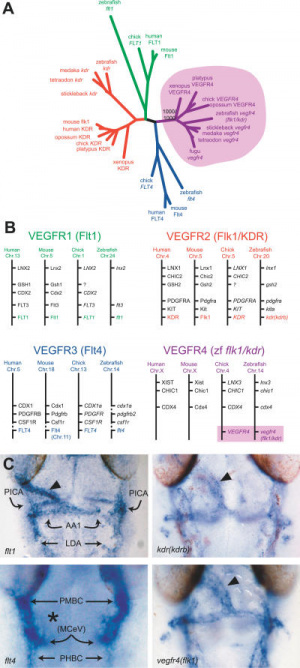
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) secreted protein growth factor family which stimulates the proliferation of vasular endotheial cells and therefore blood vessel growth.
VEGF is secreted but remains associated with cells or extracellular matrix. It is released by heparin. VEGF belongs to the platelet derive growth factor (PDGF) family, has four isoforms are formed by alternative splicing of the same gene.
Note that in addition to the developmental role this factor has been studied in relation to vascular development in tumours.
| Factor Links: AMH | hCG | BMP | sonic hedgehog | bHLH | HOX | FGF | FOX | Hippo | LIM | Nanog | NGF | Nodal | Notch | PAX | retinoic acid | SIX | Slit2/Robo1 | SOX | TBX | TGF-beta | VEGF | WNT | Category:Molecular |
| Blood Vessel Development | Category:VEGF
Some Recent Findings
|
| More recent papers |
|---|
|
This table allows an automated computer search of the external PubMed database using the listed "Search term" text link.
More? References | Discussion Page | Journal Searches | 2019 References | 2020 References Search term: Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor <pubmed limit=5>Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor</pubmed> |
Human VEGF Family
| Table - Human Vegf Family | ||||
| Approved Symbol |
Approved Name | Previous Symbols |
Synonyms | Chromosome |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PGF | placental growth factor | PGFL | "PLGF, PlGF-2, PlGF, SHGC-10760, D12S1900, PIGF" | 14q24.3 |
| VEGFA | vascular endothelial growth factor A | VEGF | "VEGF-A, VPF" | 6p21.1 |
| VEGFB | vascular endothelial growth factor B | VRF | VEGFL | 11q13.1 |
| VEGFC | vascular endothelial growth factor C | VRP | 4q34.3 | |
| VEGFD | vascular endothelial growth factor D | FIGF | VEGF-D | Xp22.2 |
| Links: Developmental Signals - Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor | OMIM Vegf | HGNC | Bmp Family | Fgf Family | Pax Family | Sox Family | Tbx Family | Vegf Family | Wnt Family | ||||
| Human VEGF Family | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Structure
Gene
Protein
Vascular endothelial growth factor A
- Growth factor active in angiogenesis, vasculogenesis and endothelial cell growth.
- Induces endothelial cell proliferation, promotes cell migration, inhibits apoptosis and induces permeabilization of blood vessels.
- Binds to the FLT1/VEGFR1 and KDR/VEGFR2 receptors, heparan sulfate and heparin.
Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2
- Tyrosine-protein kinase that acts as a cell-surface receptor for VEGFA, VEGFC and VEGFD.
- Plays an essential role in the regulation of angiogenesis, vascular development, vascular permeability, and embryonic hematopoiesis.
Platelet-Derived Growth Factor
Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) is a cationic glycoprotein consisting of homo- or heterodimers of polypeptide chains A and/or B (PDGFB). Functions as a potent mitogen for connective tissue cells through two related receptor tyrosine kinases (PDGFRA and PDGFRB).
Function
Respiration
Lung alveolar type 1 cells express VEGFa required for alveolar angiogenesis.[6]
Signaling Pathway
Arterial Differentiation "Two 2002 papers in Cell and Developmental Cell provide evidence that VEGF directs arterial differentiation. Evidence that sensory nerves direct arteriogenesis (Mukouyama et al., 2002) and that the membrane spanning Notch signaling system is downstream of VEGF (Lawson et al., 2002) emphasize the paracrine regulation of vessel formation."
Model shown in Figure 1. Shh/VEGF/Notch in the Arterial Vasculature Sonic hedgehog (Shh) binding to the receptor complex formed by Patched (Ptc) and Smoothened (Smo) can release the inhibition of Smo by Ptc. The derepressed Smo in turn activates the Gli family of transcription factors. Shh can upregulate the expression of VEGF by mesenchymal cells, but whether the Ptc/Smo/Gli pathway is involved in this Shh-mediated VEGF production is still unclear. VEGF acts on its specific receptors, including Flk-1 and neuropilin-1 (NP-1) and induces arterial-specific EphrinB2 expression on endothelial cells (EC). However, VEGF-induced EphrinB2 expression is dependent on the Notch signaling pathway, and it is unclear (?) if VEGF can activate the Notch pathway in arterial ECs directly. Both the Notch receptor family and their ligand (Delta and Jagged) families are expressed by the EC and smooth muscle cell (SMC)/pericyte in vivo.
(from: Won't You Be My Neighbor? Local Induction of Arteriogenesis Cell, Vol. 110, 289-292, August 9, 2002)
Receptor
Intracellular Signaling
Vascular Endothelial Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase
This phosphatase is involved in vascular development through modulation of a receptor tyrosine kinase (Tie2) activity, the receptor of angiopoietin. Phosphatases remove and kinases add a phosphate group to proteins, phosphorylation is a common intracellular signaling pathway.
Placenta Growth Factor (PlGF)
Name comes from the fact that the gene was cloned from a placenta. See review.[7] Knockout mouse experiments suggest that PIGF is not required for normal vascular development.
- four protein isoforms, differ in heparin binding
- PlGF-1 and PlGF-3 - non-heparin binding diffusible isoforms
- PlGF-2 and PlGF-4 - have heparin binding domains (highly basic 21 amino acids).
- Links: OMIM - PGF
OMIM
About OMIM "Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man OMIM is a comprehensive, authoritative, and timely compendium of human genes and genetic phenotypes. The full-text, referenced overviews in OMIM contain information on all known mendelian disorders and over 12,000 genes. OMIM focuses on the relationship between phenotype and genotype. It is updated daily, and the entries contain copious links to other genetics resources." OMIM
References
- ↑ Bussmann J, Bakkers J & Schulte-Merker S. (2007). Early endocardial morphogenesis requires Scl/Tal1. PLoS Genet. , 3, e140. PMID: 17722983 DOI.
- ↑ Mack JJ & Iruela-Arispe ML. (2018). NOTCH regulation of the endothelial cell phenotype. Curr. Opin. Hematol. , , . PMID: 29547401 DOI.
- ↑ Rhee S, Guerrero-Zayas MI, Wallingford MC, Ortiz-Pineda P, Mager J & Tremblay KD. (2013). Visceral endoderm expression of Yin-Yang1 (YY1) is required for VEGFA maintenance and yolk sac development. PLoS ONE , 8, e58828. PMID: 23554936 DOI.
- ↑ Villefranc JA, Nicoli S, Bentley K, Jeltsch M, Zarkada G, Moore JC, Gerhardt H, Alitalo K & Lawson ND. (2013). A truncation allele in vascular endothelial growth factor c reveals distinct modes of signaling during lymphatic and vascular development. Development , 140, 1497-506. PMID: 23462469 DOI.
- ↑ Lobov IB, Renard RA, Papadopoulos N, Gale NW, Thurston G, Yancopoulos GD & Wiegand SJ. (2007). Delta-like ligand 4 (Dll4) is induced by VEGF as a negative regulator of angiogenic sprouting. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. , 104, 3219-24. PMID: 17296940 DOI.
- ↑ Yang J, Hernandez BJ, Martinez Alanis D, Narvaez del Pilar O, Vila-Ellis L, Akiyama H, Evans SE, Ostrin EJ & Chen J. (2016). The development and plasticity of alveolar type 1 cells. Development , 143, 54-65. PMID: 26586225 DOI.
- ↑ De Falco S. (2012). The discovery of placenta growth factor and its biological activity. Exp. Mol. Med. , 44, 1-9. PMID: 22228176 DOI.
Reviews
Articles
Kuypers E, Collins JJ, Jellema RK, Wolfs TG, Kemp MW, Nitsos I, Pillow JJ, Polglase GR, Newnham JP, Germeraad WT, Kallapur SG, Jobe AH & Kramer BW. (2012). Ovine fetal thymus response to lipopolysaccharide-induced chorioamnionitis and antenatal corticosteroids. PLoS ONE , 7, e38257. PMID: 22693607 DOI.
Online Textbooks
- Molecular Biology of the Cell. 4th edition. Alberts B, Johnson A, Lewis J, et al.New York: Garland Science; 2002.
- Molecular Cell Biology. 4th edition. Lodish H, Berk A, Zipursky SL, et al.New York: W. H. Freeman; 2000.
- Madame Curie Bioscience Database [Internet]. Austin (TX): Landes Bioscience; 2000.
Search PubMed
- Search PubMed: Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor
- All Databases: Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor
External Links
External Links Notice - The dynamic nature of the internet may mean that some of these listed links may no longer function. If the link no longer works search the web with the link text or name. Links to any external commercial sites are provided for information purposes only and should never be considered an endorsement. UNSW Embryology is provided as an educational resource with no clinical information or commercial affiliation.
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 28) Embryology Developmental Signals - Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Developmental_Signals_-_Vascular_Endothelial_Growth_Factor
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
