Book - Normal plates of the development of the human embryo (1908)
| Embryology - 28 Apr 2024 |
|---|
| Google Translate - select your language from the list shown below (this will open a new external page) |
|
العربية | català | 中文 | 中國傳統的 | français | Deutsche | עִברִית | हिंदी | bahasa Indonesia | italiano | 日本語 | 한국어 | မြန်မာ | Pilipino | Polskie | português | ਪੰਜਾਬੀ ਦੇ | Română | русский | Español | Swahili | Svensk | ไทย | Türkçe | اردو | ייִדיש | Tiếng Việt These external translations are automated and may not be accurate. (More? About Translations) |
Keibel F. and Elze C. Normal Plates of the Development of the Human Embryo (Homo sapiens). (1908) Vol. 8 in series by Keibel F. Normal plates of the development of vertebrates (Normentafeln zur Entwicklungsgeschichte der Wirbelthiere) Fisher, Jena., Germany.
| Historic Disclaimer - information about historic embryology pages |
|---|
| Pages where the terms "Historic" (textbooks, papers, people, recommendations) appear on this site, and sections within pages where this disclaimer appears, indicate that the content and scientific understanding are specific to the time of publication. This means that while some scientific descriptions are still accurate, the terminology and interpretation of the developmental mechanisms reflect the understanding at the time of original publication and those of the preceding periods, these terms, interpretations and recommendations may not reflect our current scientific understanding. (More? Embryology History | Historic Embryology Papers) |
Normal Plates of the Development of the Human Embryo
- Nomentafel Zur Entwicklungsgeschichte Des Menschen
by Franz Keibel and Curt Elze (1908)
This historic 1908 Volume 8 of the series describes human embryonic development based upon tabled descriptions and plate illustrations. These plates form the early basis of the later staging of human embryos.
| Normal Plates Series: 1897 Pig | 1900 Chicken | 1901 Lungfish | 1904 Sand Lizard | 1905 Rabbit | 1906 Deer | 1907 Tarsiers | 1908 Human | 1909 Northern Lapwing | 1909 South American and African Lungfish | 1910 Salamander | Franz Keibel | Embryology History |
Franz Keibel (1861 - 1929)
Tables
| Human Embryo Pfannenstiel “Klb” | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kroemer-Pfannenstiel. Collection of Prof. Pfannenstiel, Giessen. Carnegie stage 10 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Desig. | Size | Age | Body form | Primitive streak | Primitive segments | Chorda | Nervous system | Eye | Ear | Nose | Hypophysis | Mouth | Digestive trac, liver and pancreas | Branchial pouches, threoid thymus, trachea and lungs | Urogenital system | Heart and vessels | Integument | Skeleton | Extremities | Amnion | Allantois | Remarks |
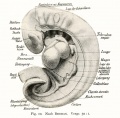
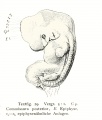
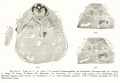
| 3 Human embryo Klb. N.T. Fig. 3a and 3d; Text-fig 5a to 5n. | 138 sections of 10 μ = 1.38 mm. | The age is estimated by Born at from 10 to 14 days. | No dorsal bend. Head end bent down at right angles and cut by 24 sections of 10 μ. | Still indications of a neurenteric canal. Short primitive streak. CIoacal membrane. | 5-6 pairs of primitive segments. | The chorda throughout is contained in the entoderm. | The medullary canal is everywhere wide open, but the brain portion is aire ady marked off from the cord and shows beginning segmentation. | Optic anlage not yet evident. | Primary pharyngeal membrane No oral sinus. | The 1st branchial pouch is formed but does not reach the ectoderm. | Heart ventral, but still paired. Paired aortse. 1st branchial arch artery. Aa. umbilicales. Yv. omphalo-mesentericae. Vessels on the yolk sack full of blood corpuscles. | No amniotic duct evident. | Allantoic duct | Obtained by laparotomy. | ||||||||
| Size
Kroemer gives the following data: "The greatest length of the embryonic anlage from the anterior edge of the amnion of the head cap to the chorion end of the belly-stalk 1.95 mm, the length of the embryo without the belly-stalk from the head to the tail 1.8 mm., the greatest width of the yolk sack barely 1.2 mm, the width of the embryonic disk at the boundary between the amnion and yolk sack (measured in the head view) 0.9 mm. The measurements of the yolk sack were 1.1 mm, (height), 1.4 mm (width), 1.5 mm. (length)." | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Remarks
Fixation: Mailer's fluid. Stain: alum carmine; paraffin. Sections: 10 micron Transverse Literature: Pfannenstiel in Handbuch der Geburtshilfe, published by Winckel, Wiesbaden 1903. — Kroemer, Wachsmodell eines jungen menschl. Embryo. Verhandl. d. Ges. f. Gynakologie, 1903. The wide pericardial cavity is not connected with the peripheral ccelom. The embryonic ccelom is being formed caudally. On the chorion the layer of Langhans cells and syncytium. | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reference: Keibel F. and Elze C. Normal Plates of the Development of the Human Embryo (Homo sapiens). (1908) Vol. 8 in series by Keibel F. Normal plates of the development of vertebrates (Normentafeln zur Entwicklungsgeschichte der Wirbelthiere) Fisher, Jena., Germany. Cited in: 1912 Human Embryology | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1908 Embryo Tables: Klb (stage 10) | Pfannenstiel III (stage 11) | Meyer 300 (stage 12) | Strahl 4mm (stage 13) | Hertwig G31 (stage 14) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Human Embryo Pfannenstiel III | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Collection of Prof. Pfannenstiel, Giessen. Carnegie stage 11 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Desig. | Size | Age | Body form | Primitive streak | Primitive segments | Chorda | Nervous system | Eye | Ear | Nose | Hypophysis | Mouth | Digestive trac, liver and pancreas | Branchial pouches, threoid thymus, trachea and lungs | Urogenital system | Heart and vessels | Integument | Skeleton | Extremities | Amnion | Allantois | Remarks |
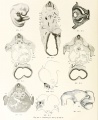
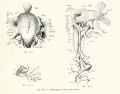
| 6 Pfannenstiel III Fig. Vr and Vv. Textfig. 6a to 6w. | Gr. L. about 2.6 mm. | Embryo bent over the ventral surface and slightly bent spirally. | Tail bud, on its ventral side doubtful remains of primitive streak. | 13-14 pairs of primitive segments. | Chorda emerging from entoderm, Cranially is still entoderm, caudally it is probably primarily independent of the entoderm and in this region it is no longer included in the entoderm. | In brain region medullary canal is open to caudal to the region of the optic vesicle, similarly the caudal end. Anlagen of neuromeres already present. | Primary optic vesicles. They are close to the ectoderm; in their region the medullary canal is wide open. | Anlage of auditory vesicle recognizable as a thickened and at first but little depressed plate of ectoderm. | Hypophysis just indicated. | Primary pharyngeal membrane still closed. Oral sinus. | Wide hepatic bay just cranial to the intestinal umbilicus. No trace yet of hepatic trabeculae. | The two first branchial pouches reach the ectoderm, the 3rd is formed. | Quite rudimentary "pronephric anlage" in 8th, 9th and 10 pairs of primitive segments. No trace yet of a Wolffian duct. Segmental vesicles in the 11th, 12th and 13th pairs of primitive segments. | Heart S-shaped. Posterior mesocardium through a few sections. Aorta paired throughout. | Allantoic duct | Extirpation of uterus on account of carcinoma. | ||||||
| Remarks - Fixation formalin Muller's fluid. Stain Paracarmine. Sections 10 μ. Recent mitoses. Septum transverse. No ventral connection between pericardial and peritoneal cavities. | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reference: Keibel F. and Elze C. Normal Plates of the Development of the Human Embryo (Homo sapiens). (1908) Vol. 8 in series by Keibel F. Normal plates of the development of vertebrates (Normentafeln zur Entwicklungsgeschichte der Wirbelthiere) Fisher, Jena., Germany. Cited in: 1912 Human Embryology and Low A. Description of a human embryo of 13-14 mesodermic somites. (1908) J Anat Physiol. 42(3): 237-51. PMID 17232769 | PMC1289161 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1908 Embryo Tables: Klb (stage 10) | Pfannenstiel III (stage 11) | Meyer 300 (stage 12) | Strahl 4mm (stage 13) | Hertwig G31 (stage 14) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Figures
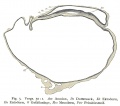
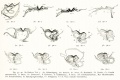
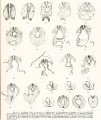
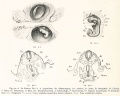
Plates
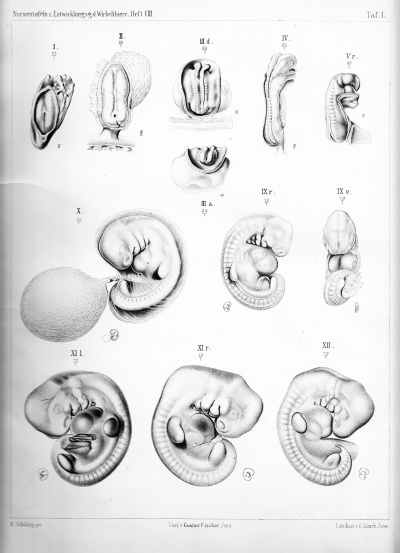
Plate 1 |
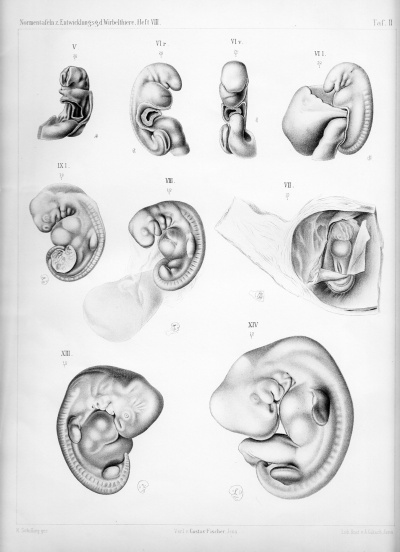
Plate 2 |
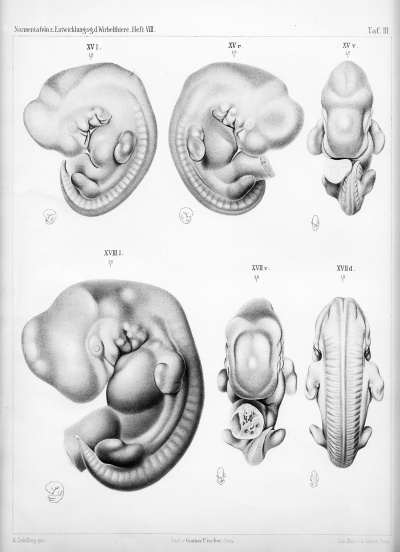
Plate 3 |
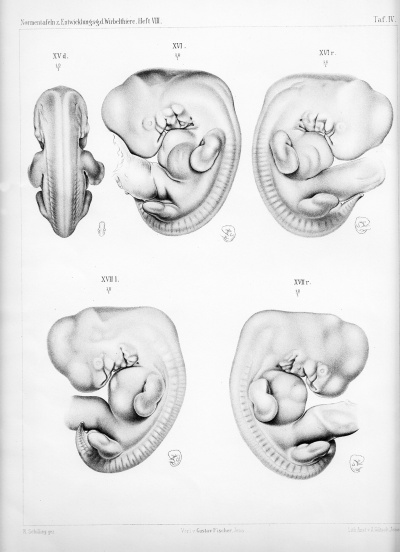
Plate 4 |
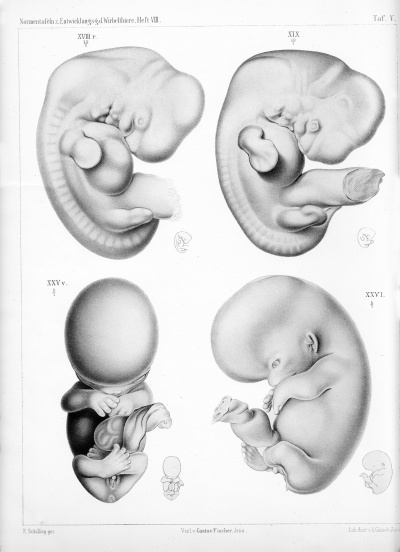
Plate 5 |
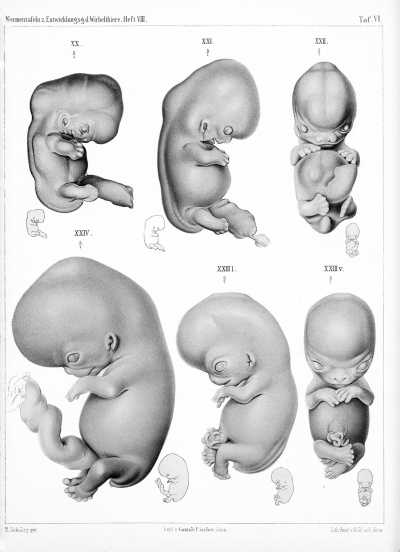
Plate 6 |
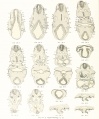
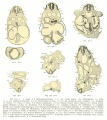
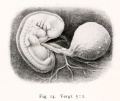
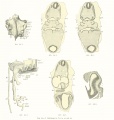
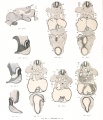
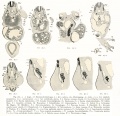
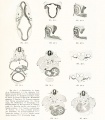
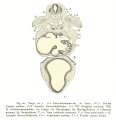
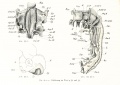
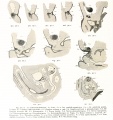
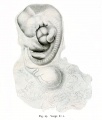
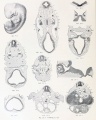
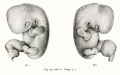
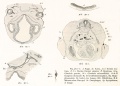
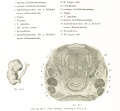
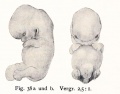
- Human Figures: Fig 1 | Fig 2 | Fig 3 | Fig 4 | Fig 5 | Fig 6 | Fig 7 | Fig 8 | Fig 9 | Fig 10 | Fig 11 | Fig 12 | Fig 13 | Fig 14 | Fig 15 | Fig 16a | Fig 16b | Fig 17 | Fig 18 | Fig 19 | Fig 20 | Fig 21 | Fig 22 | Fig 23 | Fig 24 | Fig 25 | Fig 27 | Fig 27 | Fig 28 | Fig 29 | Fig 30a | Fig 30b | Fig 31 | Fig 32 | Fig 33 | Fig 34a | Fig 34b | Fig 35 | Fig 36 | Fig 37 | Plate 1 | Plate 2 | Plate 3 | Plate 4 | Plate 5 | Plate 6 | Franz Keibel
| Normal Plates Series: 1897 Pig | 1900 Chicken | 1901 Lungfish | 1904 Sand Lizard | 1905 Rabbit | 1906 Deer | 1907 Tarsiers | 1908 Human | 1909 Northern Lapwing | 1909 South American and African Lungfish | 1910 Salamander | Franz Keibel | Embryology History |
| Historic Disclaimer - information about historic embryology pages |
|---|
| Pages where the terms "Historic" (textbooks, papers, people, recommendations) appear on this site, and sections within pages where this disclaimer appears, indicate that the content and scientific understanding are specific to the time of publication. This means that while some scientific descriptions are still accurate, the terminology and interpretation of the developmental mechanisms reflect the understanding at the time of original publication and those of the preceding periods, these terms, interpretations and recommendations may not reflect our current scientific understanding. (More? Embryology History | Historic Embryology Papers) |
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 28) Embryology Book - Normal plates of the development of the human embryo (1908). Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Book_-_Normal_plates_of_the_development_of_the_human_embryo_(1908)
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G