Renal System - Abnormalities: Difference between revisions
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
(Prune Belly Syndrome) | (Prune Belly Syndrome) | ||
[[File:Prune belly.jpg| | [[File:Prune belly.jpg|400px|Prune Belly Syndrome]] | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 10:38, 3 June 2010
Introduction
How and why do things go wrong in development?
| Abnormality Links: abnormal development | abnormal genetic | abnormal environmental | Unknown | teratogens | ectopic pregnancy | cardiovascular abnormalities | coelom abnormalities | endocrine abnormalities | gastrointestinal abnormalities | genital abnormalities | head abnormalities | integumentary abnormalities | musculoskeletal abnormalities | limb abnormalities | neural abnormalities | neural crest abnormalities | placenta abnormalities | renal abnormalities | respiratory abnormalities | hearing abnormalities | vision abnormalities | twinning | Developmental Origins of Health and Disease | ICD-11 | ||
|
Some Recent Findings
Congenital urological anomalies diagnosed in adulthood[1] "Despite worldwide availability of prenatal ultrasound, many patients are diagnosed in adult life with congenital anomalies such as ureteropelvic junction obstruction (UPJO), undescended testicle (UDT), ureterocele, hypospadias, vesicoureteral reflux (VUR) and primary obstructing megaureter (POM)."
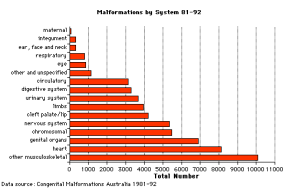
Statistics - Top Ten
The ten most frequently reported birth defects in Victoria between 2003-2004 (More? Australian Statistics - Victoria)
- Hypospadias
- Obstructive Defects of the Renal Pelvis or Obstructive Genitourinary Defects
- Ventricular Septal Defect
- Congenital Dislocated Hip
- Trisomy 21 or Down syndrome
- Hydrocephalus
- Cleft Palate
- Trisomy 18 or Edward Syndrome - multiple abnormalities of the heart, diaphragm, lungs, kidneys, ureters and palate 86% discontinued.
- Renal Agenesis/Dysgenesis - reduction in neonatal death and stillbirth since 1993 may be due to the more severe cases being identified in utero and being represented amongst the increased proportion of terminations (approximately 31%).
- Cleft Lip and Palate - occur with another defect in 33.7% of cases.
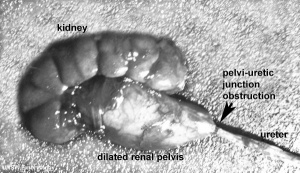
Obstructive Renal Pelvis Defect
Obstructive Renal Pelvis Defect (obstructive defects of the renal pelvis, uteropelvic junction obstruction, pelvo-uterero junction obstruction) is a term describing a developmental renal abnormality due to partial or complete blockage of the drainage of the kidney pelvis requiring surgical correction.
The blockage can also have several causes including:
The blockage leads to an accumulation of urine in the affected region, with several potential effects: nephron damage from compression (hydronephrosis); decreased urine output leading to lack of amniotic fluid (oligohydramnios); respiratory development effects due to the lack of amniotic fluid. The most common type of obstruction is at the uteropelvic junction (UPJ), between the junction of the ureter and the kidney. Blockage lower as the ureter enters the bladder, the ureterovesicular junction (UVJ), usually involves only one kidney and the back flow enlarges the affected ureter (megaureter).
Renal Agenesis/Dysgenesis
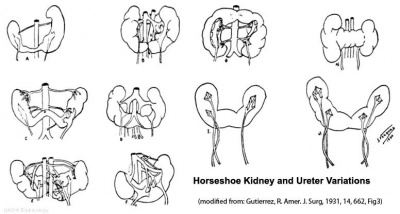
Renal Fusion
Triad Syndrome
(Prune Belly Syndrome)
References
- ↑ <pubmed>18631884</pubmed>
Reviews
Articles
Search Pubmed
Search Pubmed: Obstructive Renal Pelvis Defects | Renal Agenesis | hydronephrosis
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, May 9) Embryology Renal System - Abnormalities. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Renal_System_-_Abnormalities
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G