Lecture - Neural Development: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
(→Movies) |
||
| Line 116: | Line 116: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
==Historic Images== | |||
Bailey, F.R. and Miller, A.M. (1921). Text-Book of Embryology. New York: William Wood and Co. | |||
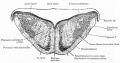
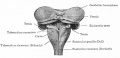
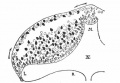
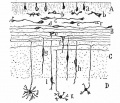
[[Book_-_Text-Book_of_Embryology_17|The nervous system]] | |||
<gallery> | |||
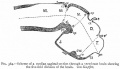
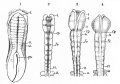
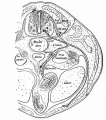
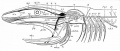
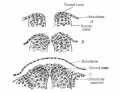
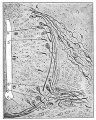
File:Bailey358.jpg|Fig. 358 | |||
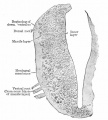
File:Bailey359.jpg|Fig. 359 | |||
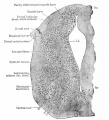
File:Bailey360.jpg|Fig. 360 | |||
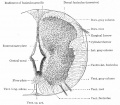
File:Bailey361.jpg|Fig. 361 | |||
File:Bailey362.jpg|Fig. 362 | |||
File:Bailey363.jpg|Fig. 363 | |||
File:Bailey364.jpg|Fig. 364 | |||
File:Bailey365.jpg|Fig. 365 | |||
File:Bailey366.jpg|Fig. 366 | |||
File:Bailey367.jpg|Fig. 367 | |||
File:Bailey368.jpg|Fig. 368 | |||
File:Bailey369.jpg|Fig. 369 | |||
File:Bailey370.jpg|Fig. 370 | |||
File:Bailey371.jpg|Fig. 371 | |||
File:Bailey372.jpg|Fig. 372 | |||
File:Bailey373.jpg|Fig. 373 | |||
File:Bailey374.jpg|Fig. 374 | |||
File:Bailey375.jpg|Fig. 375 | |||
File:Bailey376.jpg|Fig. 376 | |||
File:Bailey377.jpg|Fig. 377 | |||
File:Bailey378.jpg|Fig. 378 | |||
File:Bailey379-382.jpg|Fig. 379-382 | |||
File:Bailey383.jpg|Fig. 383 | |||
File:Bailey384.jpg|Fig. 384 | |||
File:Bailey385.jpg|Fig. 385 | |||
File:Bailey386.jpg|Fig. 386 | |||
File:Bailey387.jpg|Fig. 387 | |||
File:Bailey388.jpg|Fig. 388 | |||
File:Bailey389.jpg|Fig. 389 | |||
File:Bailey390.jpg|Fig. 390 | |||
File:Bailey391.jpg|Fig. 391 | |||
File:Bailey392.jpg|Fig. 392 | |||
File:Bailey393.jpg|Fig. 393 | |||
File:Bailey394.jpg|Fig. 394 | |||
File:Bailey395.jpg|Fig. 395 | |||
File:Bailey396.jpg|Fig. 396 | |||
File:Bailey397.jpg|Fig. 397 | |||
File:Bailey398.jpg|Fig. 398 | |||
File:Bailey399.jpg|Fig. 399 | |||
File:Bailey400.jpg|Fig. 400 | |||
File:Bailey401.jpg|Fig. 401 | |||
File:Bailey402.jpg|Fig. 402 | |||
File:Bailey403.jpg|Fig. 403 | |||
File:Bailey404.jpg|Fig. 404 | |||
File:Bailey405.jpg|Fig. 405 | |||
File:Bailey406.jpg|Fig. 406 | |||
File:Bailey407.jpg|Fig. 407 | |||
File:Bailey408.jpg|Fig. 408 | |||
File:Bailey409.jpg|Fig. 409 | |||
File:Bailey410.jpg|Fig. 410 | |||
File:Bailey411.jpg|Fig. 411 | |||
File:Bailey412.jpg|Fig. 412 | |||
File:Bailey413.jpg|Fig. 413 | |||
File:Bailey414.jpg|Fig. 414 | |||
File:Bailey415.jpg|Fig. 415 | |||
File:Bailey416.jpg|Fig. 416 | |||
File:Bailey417.jpg|Fig. 417 | |||
File:Bailey418.jpg|Fig. 418 | |||
File:Bailey419.jpg|Fig. 419 | |||
File:Bailey420.jpg|Fig. 420 | |||
File:Bailey421.jpg|Fig. 421 | |||
File:Bailey422.jpg|Fig. 422 | |||
File:Bailey423.jpg|Fig. 423 | |||
File:Bailey424.jpg|Fig. 424 | |||
File:Bailey425.jpg|Fig. 425 | |||
File:Bailey426.jpg|Fig. 426 | |||
File:Bailey427.jpg|Fig. 427 | |||
File:Bailey428.jpg|Fig. 428 | |||
File:Bailey429.jpg|Fig. 429 | |||
File:Bailey430.jpg|Fig. 430 | |||
File:Bailey431.jpg|Fig. 431 | |||
File:Bailey432.jpg|Fig. 432 | |||
File:Bailey433.jpg|Fig. 433 | |||
File:Bailey434.jpg|Fig. 434 | |||
File:Bailey435.jpg|Fig. 435 | |||
File:Bailey436.jpg|Fig. 436 | |||
File:Bailey437.jpg|Fig. 437 | |||
File:Bailey438.jpg|Fig. 438 | |||
File:Bailey439.jpg|Fig. 439 | |||
File:Bailey440.jpg|Fig. 440 | |||
File:Bailey441.jpg|Fig. 441 | |||
File:Bailey442.jpg|Fig. 442 | |||
File:Bailey443.jpg|Fig. 443 | |||
File:Bailey444.jpg|Fig. 444 | |||
File:Bailey445.jpg|Fig. 445 | |||
File:Bailey446.jpg|Fig. 446 | |||
File:Bailey447.jpg|Fig. 447 | |||
File:Bailey448.jpg|Fig. 448 | |||
File:Bailey449.jpg|Fig. 449 | |||
File:Bailey450.jpg|Fig. 450 | |||
File:Bailey451-452.jpg|Fig. 451 452 | |||
File:Bailey453.jpg|Fig. 453 | |||
File:Bailey454.jpg|Fig. 454 | |||
File:Bailey455.jpg|Fig. 455 | |||
</gallery> | |||
{{2011ANAT2341}} | {{2011ANAT2341}} | ||
Revision as of 10:50, 19 August 2011
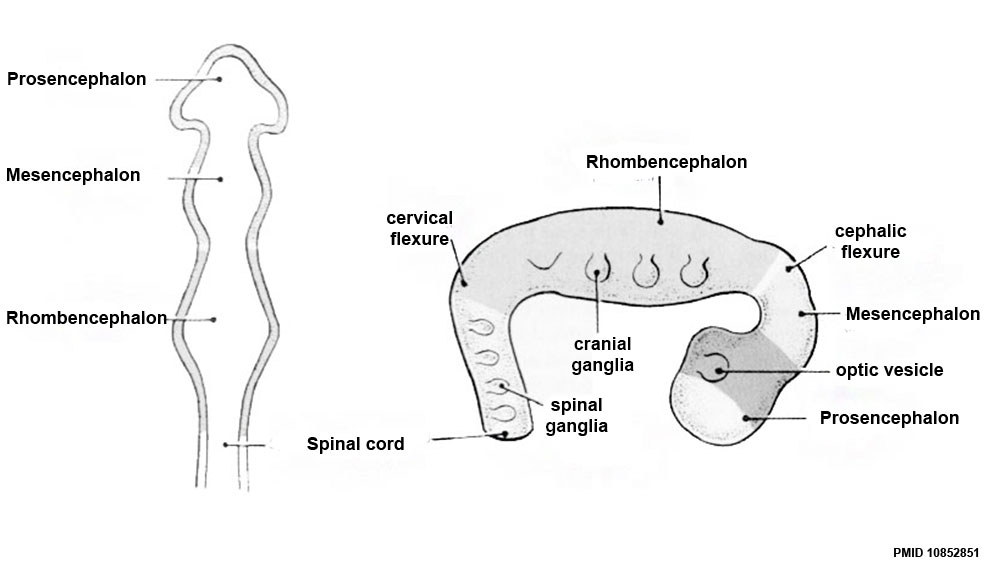
Early Brain Structure
Primary Vesicles
- rostral neural tube forms 3 primary brain vesicles (week 4)
- 3 primary vesicles: prosencephalon (forebrain), mesencephalon (midbrain), rhombencephalon (hindbrain)
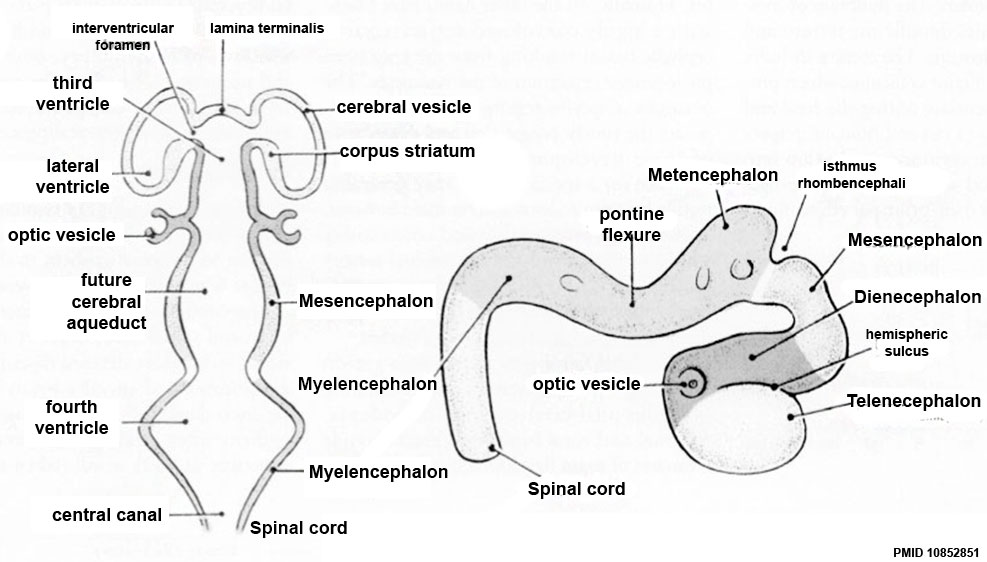
Secondary Vesicles
From the 3 primary vesicles developing to form 5 secondary vesicles
- prosencephalon- telencephalon (endbrain, forms cerebral hemispheres), diencephalon (betweenbrain, forms optic outgrowth)
- mesencephalon
- rhombencephalon- metencephalon (behindbrain), myelencephalon (medullabrain)
Neural Layers
Brain
|
|
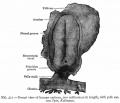
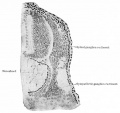
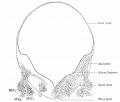
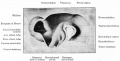
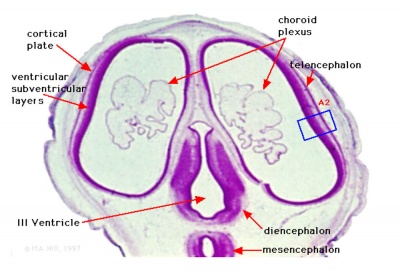
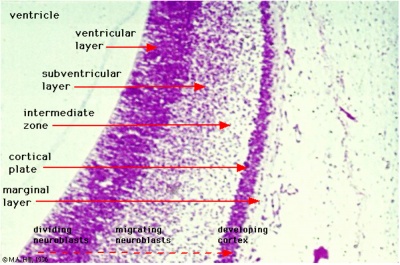
| Human Embryo developing head cross section (Week 8, Stage 22) | Detail of developing cortex (shown in blue box) |
Spinal Cord
|
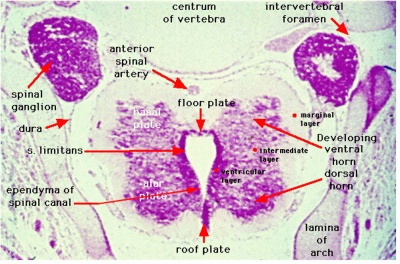
|
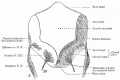
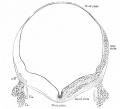
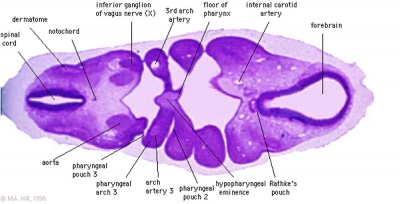
| Stage 13 | Stage 22 |
Fetal Neural
Timeline of events in Human Neural Development
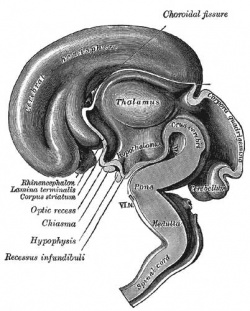
|
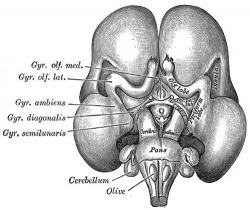
|
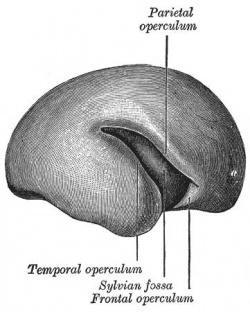
|
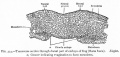
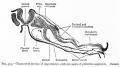
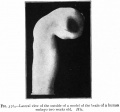
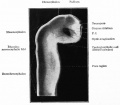
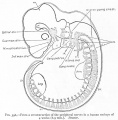
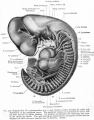
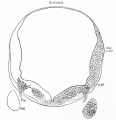
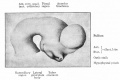
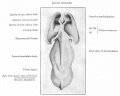
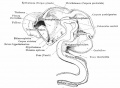
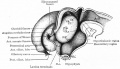
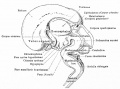
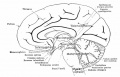
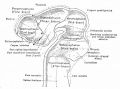
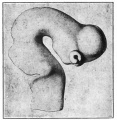
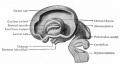
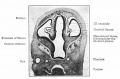
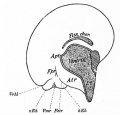
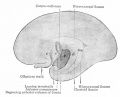
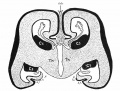
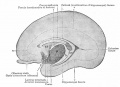
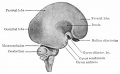
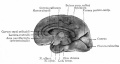
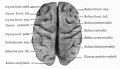
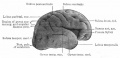
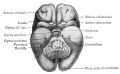
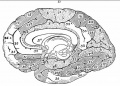
| Human brain at three months (median sagittal section) | Human brain at four months (inferior surface) | Human brain at five months (outer surface) |
During the fetal period there is ongoing growth in size, weight and surface area of the brain and spinal cord. Microscopically there is ongoing: cell migration, extension of processes, cell death and glial cell development.
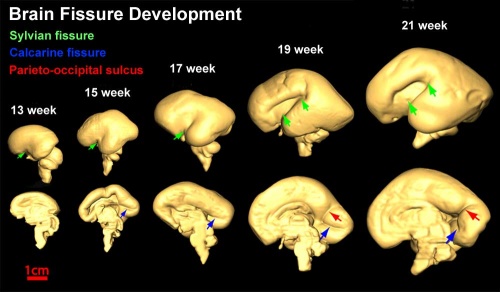
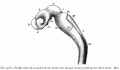
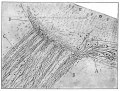
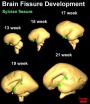
Cortical maturation (sulcation and gyration) and vascularization of the lateral surface of the brain starts with the insular cortex (insula, insulary cortex or insular lobe) region during the fetal period. This cerebral cortex region in the adult brain lies deep within the lateral sulcus between the temporal lobe and the parietal lobe.
- sulcation - The process of brain growth in the second to third trimester which forms sulci, grooves or folds visible on fetal brain surface as gyri grow (gyration). Abnormalities of these processes can lead to a smooth brain (lissencephaly).
- gyration - The development of surface folds on the brain (singular, gyrus)
Insular Gyral and Sulcal Development
- 13-17 gestational weeks - appearance of the first sulcus
- 18-19 gestational weeks - development of the periinsular sulci
- 20-22 gestational weeks - central sulci and opercularization of the insula
- 24-26 gestational weeks - covering of the posterior insula
- 27-28 gestational weeks - closure of the laeteral sulcus (Sylvian fissure or lateral fissure)
(Data from[1])
- Between 29-41 weeks volumes of: total brain, cerebral gray matter, unmyelinated white matter, myelinated, and cerebrospinal fluid (from MRI)
- grey matter- mainly neuronal cell bodies; white matter- mainly neural processes and glia.
- total brain tissue volume increased linearly over this period at a rate of 22 ml/week.
- Total grey matter also showed a linear increase in relative intracranial volume of approximately 1.4% or 15 ml/week.
- The rapid increase in total grey matter is mainly due to a fourfold increase in cortical grey matter.
- Quantification of extracerebral and intraventricular CSF was found to change only minimally.
(Text - modified from [2])
Neural development will continue after birth with substantial glial development, growth, death and reorganization occuring during the postnatally.
References
Movies
| Mouse E11.5 microCT scan | Human Adult Brain |
|
| Neural Sylvian Fissure |
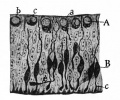
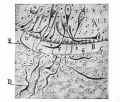
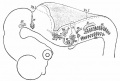
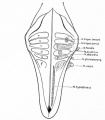
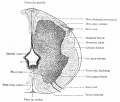
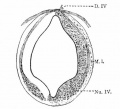
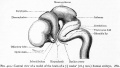
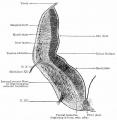
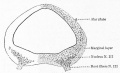
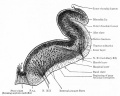
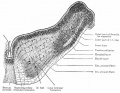
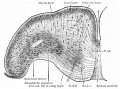
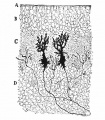
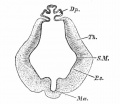
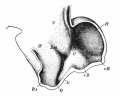
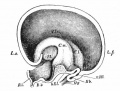
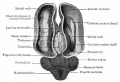
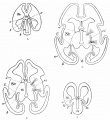
Historic Images
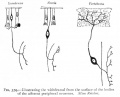
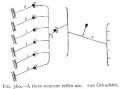
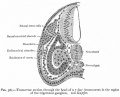
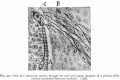
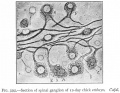
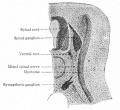
Bailey, F.R. and Miller, A.M. (1921). Text-Book of Embryology. New York: William Wood and Co.
Co-ordinator Note
Dr Mark Hill |
ANAT2341 Embryology S2 2011
|
Course Content 2011
2011 Timetable: | Embryology Introduction | Fertilization | Cell Division/Fertilization | Week 1 and 2 Development | Week 3 Development | Week 1 to 3 | Mesoderm Development | Ectoderm, Early Neural, Neural Crest | Trilaminar Embryo to Early Embryo | Early Vascular Development | Placenta | Vascular and Placenta | Endoderm, Early Gastrointestinal | Respiratory Development | Endoderm and Respiratory | Head Development | Neural Crest Development | Head and Neural Crest | Musculoskeletal Development | Limb Development | Musculoskeletal | Renal Development | Genital | Kidney and Genital | Sensory | Stem Cells | Stem Cells | Endocrine Development | Endocrine | Heart | Integumentary Development | Heart and Integumentary | Fetal | Birth and Revision | Fetal
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, May 17) Embryology Lecture - Neural Development. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Lecture_-_Neural_Development
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G