Lecture - Mesoderm Development: Difference between revisions
From Embryology
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 236: | Line 236: | ||
| colspan="5" width="376" height="18" |<center> [[Carnegie_stage_13_-_serial_sections|Stage 13/14 shown in serial embryo sections]] series of Embryology Program</center> | | colspan="5" width="376" height="18" |<center> [[Carnegie_stage_13_-_serial_sections|Stage 13/14 shown in serial embryo sections]] series of Embryology Program</center> | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 16:35, 8 August 2011
Objectives
- Understanding of events during the third week of development
- Understanding the process of early somite development
- Understanding the process of body cavity formation
- Brief understanding of the future fate of mesoderm components
- Brief understanding of early heart formation
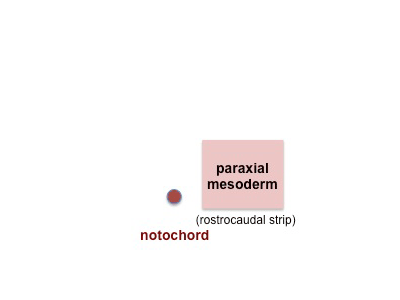
Notochord (Axial mesoderm)
Mesoderm
- generated from epiblast cells migrating through the primitive streak
- epiblast cells expressing fibroblast growth factor (FGF2)
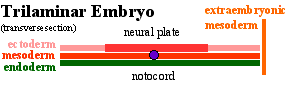
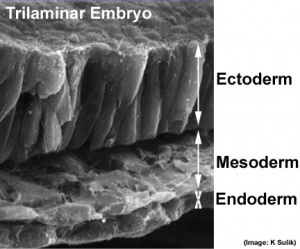
- forms a layer between ectoderm and endoderm with notochord down midline
- present before neural tube formation
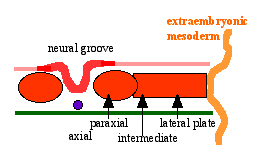
- divides initially into 3 components
- Paraxial mesoderm - somites - musculoskeletal structures
- Intermediate mesoderm - kidney
- Lateral plate mesoderm - body wall structures
Mesoderm Development
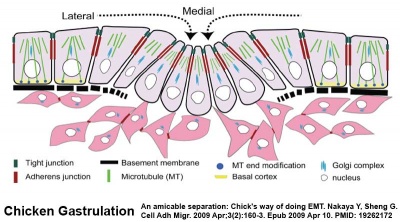
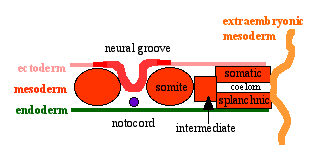
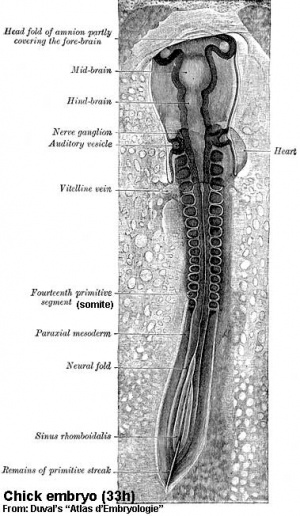
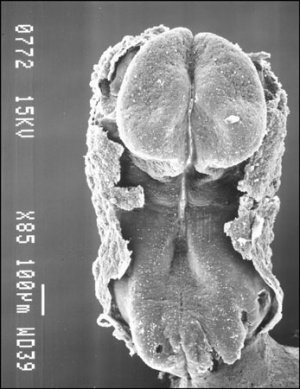
The four images below beginning at week 3 show cross-sections of the trilaminar embryo and the sequence of mesoderm development.
Mesenchyme
- Embryonic connective tissue, describes the cell morphology (Histology is not epithelial organization)
- epithelial to mesenchymal transitions
- mesenchymal to epithelial transitions
Paraxial Mesoderm
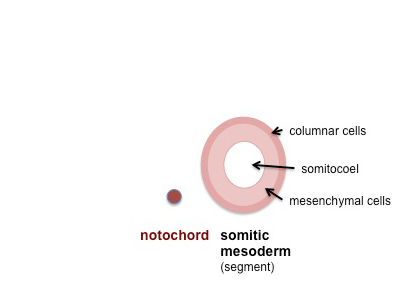
Somite Formation
| Early somite induction signals in the mouse |
- ball forms through epithelialization and interactions (cell-cell, cell-extracellular matrix, ECM) fibronectin, laminin
- has 2 populations of cells - peripheral columnar and central mesenchymal
- early somite has cavity- somitocoel, cavity is lost during growth
- somite enclosed by ECM connected to nearby tissues
Somite Specification
- Different segmental level somites have to generate different segmental body structures?
- somite has to form different tissues?
- Somite Differentiation
- Compartmentalization accompanied by altered patterns of expression of Pax genes within the somite
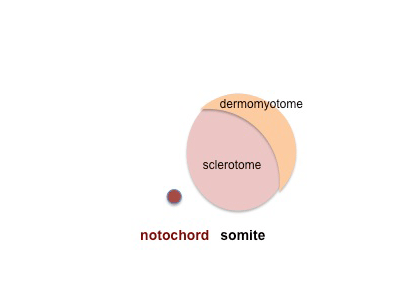
Somite initially forms 2 main components
- ventromedial- sclerotome forms vertebral body and intervertebral disc
- dorsolateral - dermomyotome forms dermis and skeletal muscle
Somite Axial Specification
- rostro-caudal axis appears regulated by Pax/Hox expression, family of DNA binding transcription factors
- Movie: Somite Development
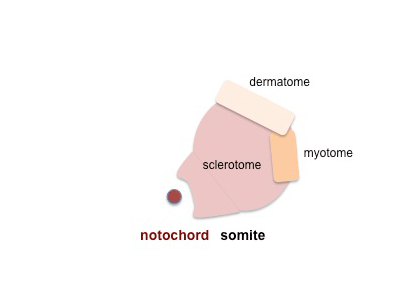
Sclerotome
- sclerotome later becomes subdivided
- rostral and caudal halves separated laterally by von Ebner's fissure
- half somites contribute to a single vertebral level body
- other half intervertebral disc
- therefore final vertebral segmentation ‚"shifts"
Dermomyotome
- later divides into dorsal dermatome and ventral myotome
- (MH - This topic of muscle and skeleton development will be covered in 2 later lectures Musculoskeletal Development and Limb Development)
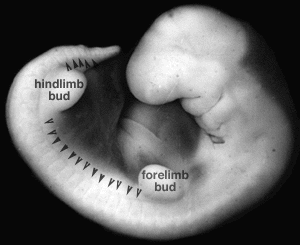
- lateral myotome edge migrates at level of limbs
- upper limb first then lower
- mixes with somatic mesoderm
- dermotome continues to contribute cells to myotome
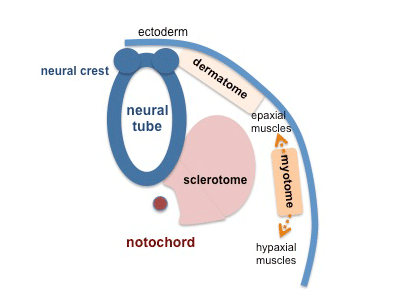
Myotome
- Myotome component of Somite
- epaxial myotome (dorsomedial quarter) forms the dorsal epimere (erector spinae)
- hypaxial myotome (dorsolateral quarter) forms the ventral hypomere, 3 primary muscle layers which are different at neck, thorax and abdomen
Muscle
- Myoblast determining transcription factor MyoD is first expressed in the dorsomedial quadrant of the still epithelial somite whose cells are not yet definitely committed
- basic Helix Loop Helix
- from myotome
Muscle Development Abnormalities
- Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
- Embryonic muscle development normal and changes occur postnatally
- X-linked dystrophy, large gene encoding cytoskeletal protein - Dystrophin
- progressive wasting of muscle, die late teens
- Becker Muscular Dystrophy, milder form, adult onset
Axial Segmentation - Somite Specification Signals
Intermediate Mesoderm
|
|
Lateral Plate Development
- lying at the surrounding edge of he embryonic disc
- a cavity begins in this week to form within the mesoderm itself
Intraembryonic Coelom
- small spaces (vacuoles) begin appearing within the lateral plate mesoderm
- small spaces enlarge forming a single cavity within the lateral plate mesoderm
- divides lateral plate mesoderm into 2 parts at about day 18-19
- this cavity is called the Intraembryonic Coelom
- coelom is a general term for a "cavity" and can lie within the embryo (intraembryonic) and outside the embryo (extraembryonic)
- later anatomical spaces within the embryo and fetus can also be described as coeloms
- when the embryonic disc folds the intraembryonic coelom will form all 3 major body cavities:
- Pericardial
- Pleural
- Peritoneal
Somatic Mesoderm
The intraembryonic coelom divides the lateral plate into 2 portions
- closest to ectoderm
- body wall osteogenic, chrondrogenic and fibrogenic
- except ribs and scapula
Splanchnic Mesoderm
- closest to endoderm
- heart, smooth muscle of gastrointestinal tract (GIT) and blood vessels
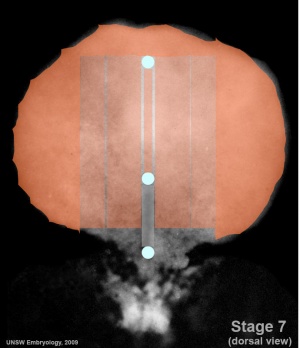
- Carnegie Stages: 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | About Stages | Timeline
Somitogenesis
(not to scale) |
||||
| gastrulation, notochordal process | ||||
| primitive pit, notochordal canal | ||||
 |
Somite Number 1 - 3 neural folds, cardiac primordium, head fold | |||
| Somite Number 4 - 12 neural fold fuses | ||||
| Somite Number 13 - 20 rostral neuropore closes | ||||
| Somite Number 21 - 29 caudal neuropore closes | ||||
| Somite Number 30 leg buds, lens placode, pharyngeal arches | ||||