|
|
| (108 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| | {{Header}} |
| | {{Educational Warning}} |
| ==Introduction== | | ==Introduction== |
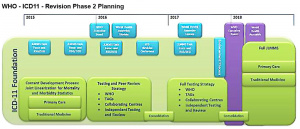
| | [[File:ICD11 planning overview.jpg|thumb|ICD-11 planning overview]] |
| | The International Classification of Diseases (ICD) World Health Organization's classification used worldwide as the standard diagnostic tool for epidemiology, health management and clinical purposes. This includes the analysis of the general health situation of population groups. It is used to monitor the incidence and prevalence of diseases and other health problems. The release date for next version update ({{ICD-11}}) is 2018. Abnormality pages begin with the ICD coding, and {{Embryology}} site content is currently being updated from ICD-10 to ICD-11 coding. The 10th revision, [[#International Classification of Diseases - 10 - Australian Modification (ICD-10-AM)|Australian Modification (ICD-10-AM)]] is currently in use in Australian hospitals for admitted patients. |
|
| |
|
| The International Classification of Diseases (ICD) World Health Organization's classification used worldwide as the standard diagnostic tool for epidemiology, health management and clinical purposes. This includes the analysis of the general health situation of population groups. It is used to monitor the incidence and prevalence of diseases and other health problems. Within this classification "congenital malformations, deformations and chromosomal abnormalities" are (Q00-Q99) but excludes "inborn errors of metabolism" (E70-E90).
| |
|
| |
|
| (ICD) ICD-10 was endorsed by the Forty-third World Health Assembly in May 1990 and came into use in WHO Member States as from 1994. The classification is the latest in a series which has its origins in the 1850s. The first edition, known as the International List of Causes of Death, was adopted by the International Statistical Institute in 1893. WHO took over the responsibility for the ICD at its creation in 1948 when the Sixth Revision, which included causes of morbidity for the first time, was published. The World Health Assembly adopted in 1967 the WHO Nomenclature Regulations that stipulate use of ICD in its most current revision for mortality and morbidity statistics by all Member States.
| | <center>''The ICD is the international standard diagnostic classification for all general epidemiological, many health management purposes and clinical use.''</center> |
|
| |
|
| :''The ICD is the international standard diagnostic classification for all general epidemiological, many health management purposes and clinical use.''
| |
|
| |
|
| | Note - this is not a the full listing of the classifications, only the major sub-headings that relate to development (use the "tables" links to see additional sub-sub-headings). Please refer to the original official [https://icd.who.int/browse11/l-m/en# WHO ICD-11 Database] for detailed information and any personal encoding uses. |
|
| |
|
| :'''Links:''' [[International Classification of Diseases]] | [[Human_Abnormal_Development|Abnormal Development]] | [[Reports]]
| | {{ICD-11 links}} |
|
| |
|
| | ==ICD-11 Chapter 20 Developmental anomalies== |
| | [http://id.who.int/icd/entity/223744320 20 Developmental anomalies] This chapter includes conditions caused by failure of a particular body site or body system to develop correctly during the antenatal period. Exclusions Inborn errors of metabolism (5C50-5C5Z) |
|
| |
|
| International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems 10th Revision (ICD-10) Version for 2010
| | {{ICD-11-20 Developmental anomalies table}} |
|
| |
|
| Note - this is not a full listing of the classifications, only the major sub-headings that relate to development (there are additional sub-sub-headings not yet listed here).
| | {{ICD-11-Structural developmental anomalies one body system table}} |
|
| |
|
| ==Chapter XVII Congenital malformations, deformations and chromosomal abnormalities (Q00-Q99)==
| | {{ICD-11-Multiple developmental anomalies or syndromes table}} |
|
| |
|
| :'''Links:''' [http://apps.who.int/classifications/icd10/browse/2010/en#/XVII Chapter XVII]
| | {{ICD-11-Chromosomal anomalies excluding gene mutations table}} |
| | |
| | {{ICD-11-Disorders of intellectual development table}} |
|
| |
|
| Excludes inborn errors of metabolism ([http://apps.who.int/classifications/icd10/browse/2010/en#/E70 E70-E90])
| | * LD9Y Other specified developmental anomalies |
| | * LD9Z Developmental anomalies, unspecified |
|
| |
|
| ===Congenital malformations of the nervous system (Q00-Q07)=== | | ==Neural== |
| Congenital malformations of the nervous system (Q00-Q07)
| | {{ICD-11 Neural anomalies table}} |
| * Q00 Anencephaly and similar malformations
| |
| ** Q00.0 Anencephaly, Acephaly, Acrania, Amyelencephaly, Hemianencephaly, Hemicephaly
| |
| ** Q00.1 Craniorachischisis
| |
| ** Q00.2 Iniencephaly
| |
| * Q01 Encephalocele Incl.: encephalomyelocele, hydroencephalocele, hydromeningocele, cranial meningocele, cerebral meningoencephalocele Excl.: Meckel-Gruber syndrome (Q61.9)
| |
| ** Q01.0 Frontal encephalocele
| |
| ** Q01.1 Nasofrontal encephalocele
| |
| ** Q01.2 Occipital encephalocele
| |
| ** Q01.8 Encephalocele of other sites
| |
| ** Q01.9 Encephalocele, unspecified
| |
| * Q02 Microcephaly Incl.: Hydromicrocephaly Micrencephalon Excl.: Meckel-Gruber syndrome (Q61.9)
| |
| * Q03 Congenital hydrocephalus Incl.: hydrocephalus in newborn Excl.: Arnold-Chiari syndrome (Q07.0) hydrocephalus: acquired (G91.-) due to congenital toxoplasmosis (P37.1) with spina bifida (Q05.0-Q05.4)
| |
| ** Q03.0 Malformations of aqueduct of Sylvius Aqueduct of Sylvius: anomaly obstruction, congenital stenosis
| |
| ** Q03.1 Atresia of foramina of Magendie and Luschka Dandy-Walker syndrome
| |
| ** Q03.8 Other congenital hydrocephalus
| |
| ** Q03.9 Congenital hydrocephalus, unspecified
| |
| * Q04 Other congenital malformations of brain Excl.: cyclopia (Q87.0) macrocephaly (Q75.3)
| |
| ** Q04.0 Congenital malformations of corpus callosum, Agenesis of corpus callosum
| |
| ** Q04.1 Arhinencephaly
| |
| ** Q04.2 Holoprosencephaly
| |
| ** Q04.3 Other reduction deformities of brain, Absence, Agenesis, Aplasia, Hypoplasia of part of brain, Agyria, Hydranencephaly, Lissencephaly, Microgyria, Pachygyria Excl.: congenital malformations of corpus callosum (Q04.0)
| |
| ** Q04.4 Septo-optic dysplasia
| |
| ** Q04.5 Megalencephaly
| |
| ** Q04.6 Congenital cerebral cysts, Porencephaly, Schizencephaly, Excl.: acquired porencephalic cyst (G93.0)
| |
| ** Q04.8 Other specified congenital malformations of brain, Macrogyria
| |
| ** Q04.9 Congenital malformation of brain, unspecified Congenital: anomaly, deformity, disease or lesion, multiple anomalies NOS of brain
| |
| * Q05 Spina bifida Incl.: hydromeningocele (spinal), meningocele (spinal), meningomyelocele, myelocele, myelomeningocele, rachischisis, spina bifida (aperta)(cystica), syringomyelocele Excl.: Arnold-Chiari syndrome (Q07.0), spina bifida occulta (Q76.0)
| |
| ** Q05.0 Cervical spina bifida with hydrocephalus
| |
| ** Q05.1 Thoracic spina bifida with hydrocephalus Spina bifida: dorsal thoracolumbar with hydrocephalus
| |
| ** Q05.2 Lumbar spina bifida with hydrocephalus, Lumbosacral spina bifida with hydrocephalus
| |
| ** Q05.3 Sacral spina bifida with hydrocephalus
| |
| ** Q05.4 Unspecified spina bifida with hydrocephalus
| |
| ** Q05.5 Cervical spina bifida without hydrocephalus
| |
| ** Q05.6 Thoracic spina bifida without hydrocephalus Spina bifida: dorsal NOS, thoracolumbar NOS
| |
| ** Q05.7 Lumbar spina bifida without hydrocephalus, Lumbosacral spina bifida NOS
| |
| ** Q05.8 Sacral spina bifida without hydrocephalus
| |
| ** Q05.9 Spina bifida, unspecified
| |
| * Q06 Other congenital malformations of spinal cord
| |
| ** Q06.0 Amyelia
| |
| ** Q06.1 Hypoplasia and dysplasia of spinal cord, Atelomyelia, Myelatelia, Myelodysplasia of spinal cord
| |
| ** Q06.2 Diastematomyelia
| |
| ** Q06.3 Other congenital cauda equina malformations
| |
| ** Q06.4 Hydromyelia Hydrorachis
| |
| ** Q06.8 Other specified congenital malformations of spinal cord
| |
| ** Q06.9 Congenital malformation of spinal cord, unspecified Congenital: anomaly, deformity, disease or lesion, NOS of spinal cord or meninges
| |
| * Q07 Other congenital malformations of nervous system Excl.: familial dysautonomia [Riley-Day] (G90.1), neurofibromatosis (nonmalignant) (Q85.0)
| |
| ** Q07.0 Arnold-Chiari syndrome
| |
| ** Q07.8 Other specified congenital malformations of nervous system Agenesis of nerve, Displacement of brachial plexus, Jaw-winking syndrome, Marcus Gunn's syndrome
| |
| ** Q07.9 Congenital malformation of nervous system, unspecified Congenital: anomaly, deformity, disease or lesion, NOS of nervous system
| |
|
| |
|
| | {{ICD-11 Neural anomalies collapse table}} |
|
| |
|
| :'''Links:''' [[Neural System - Abnormalities]] | [http://apps.who.int/classifications/icd10/browse/2010/en#/Q00-Q07 Q00-Q07]
| | {{ICD-11 Spina bifida table}} |
|
| |
|
| ===Congenital malformations of eye, ear, face and neck (Q10-Q18)===
| | {{ICD-11 Spina bifida collapse table}} |
|
| |
|
| Excl.: cleft lip and cleft palate (Q35-Q37) congenital malformation of: cervical spine (Q05.0, Q05.5, Q67.5, Q76.0-Q76.4) larynx (Q31.-) lip NEC (Q38.0) nose (Q30.-) parathyroid gland (Q89.2) thyroid gland (Q89.2)
| | {{ICD-11 Cerebral anomalies table}} |
| * Q10 Congenital malformations of eyelid, lacrimal apparatus and orbit Excl.: cryptophthalmos: NOS (Q11.2) syndrome (Q87.0)
| |
| ** Q10.0 Congenital ptosis
| |
| ** Q10.1 Congenital ectropion
| |
| ** Q10.2 Congenital entropion
| |
| ** Q10.3 Other congenital malformations of eyelid Ablepharon Absence or agenesis of: cilia eyelid Accessory: eye muscle Blepharophimosis, congenital Coloboma of eyelid Congenital malformation of eyelid NOS
| |
| ** Q10.4 Absence and agenesis of lacrimal apparatus Absence of punctum lacrimale
| |
| ** Q10.5 Congenital stenosis and stricture of lacrimal duct
| |
| ** Q10.6 Other congenital malformations of lacrimal apparatus Congenital malformation of lacrimal apparatus NOS
| |
| ** Q10.7 Congenital malformation of orbit
| |
| * Q11 Anophthalmos, microphthalmos and macrophthalmos
| |
| ** Q11.0 Cystic eyeball
| |
| ** Q11.1 Other anophthalmos Agenesis Aplasia of eye
| |
| ** Q11.2 Microphthalmos Cryptophthalmos NOS Dysplasia of eye Hypoplasia of eye Rudimentary eye Excl.: cryptophthalmos syndrome (Q87.0)
| |
| ** Q11.3 Macrophthalmos Excl.: macrophthalmos in congenital glaucoma (Q15.0)
| |
| * Q12 Congenital lens malformations
| |
| ** Q12.0 Congenital cataract
| |
| ** Q12.1 Congenital displaced lens
| |
| ** Q12.2 Coloboma of lens
| |
| ** Q12.3 Congenital aphakia
| |
| ** Q12.4 Spherophakia
| |
| ** Q12.8 Other congenital lens malformations
| |
| ** Q12.9 Congenital lens malformation, unspecified
| |
| * Q13 Congenital malformations of anterior segment of eye
| |
| ** Q13.0 Coloboma of iris Coloboma NOS
| |
| ** Q13.1 Absence of iris Aniridia
| |
| ** Q13.2 Other congenital malformations of iris Anisocoria, congenital Atresia of pupil Congenital malformation of iris NOS Corectopia
| |
| ** Q13.3 Congenital corneal opacity
| |
| ** Q13.4 Other congenital corneal malformations Congenital malformation of cornea NOS Microcornea Peter's anomaly
| |
| ** Q13.5 Blue sclera
| |
| ** Q13.8 Other congenital malformations of anterior segment of eye Rieger's anomaly
| |
| ** Q13.9 Congenital malformation of anterior segment of eye, unspecified
| |
| * Q14 Congenital malformations of posterior segment of eye
| |
| ** Q14.0 Congenital malformation of vitreous humour Congenital vitreous opacity
| |
| ** Q14.1 Congenital malformation of retina Congenital retinal aneurysm
| |
| ** Q14.2 Congenital malformation of optic disc Coloboma of optic disc
| |
| ** Q14.3 Congenital malformation of choroid
| |
| ** Q14.8 Other congenital malformations of posterior segment of eye Coloboma of the fundus
| |
| ** Q14.9 Congenital malformation of posterior segment of eye, unspecified
| |
| * Q15 Other congenital malformations of eye Excl.: congenital nystagmus (H55) ocular albinism (E70.3) retinitis pigmentosa (H35.5)
| |
| ** Q15.0 Congenital glaucoma Buphthalmos Glaucoma of newborn Hydrophthalmos Keratoglobus, congenital, with glaucoma Macrocornea with glaucoma Macrophthalmos in congenital glaucoma Megalocornea with glaucoma
| |
| ** Q15.8 Other specified congenital malformations of eye
| |
| ** Q15.9 Congenital malformation of eye, unspecified Congenital: anomaly deformity NOS of eye
| |
| * Q16 Congenital malformations of ear causing impairment of hearing Excl.: congenital deafness (H90.-)
| |
| ** Q16.0 Congenital absence of (ear) auricle
| |
| ** Q16.1 Congenital absence, atresia and stricture of auditory canal (external) Atresia or stricture of osseous meatus
| |
| ** Q16.2 Absence of eustachian tube
| |
| ** Q16.3 Congenital malformation of ear ossicles Fusion of ear ossicles
| |
| ** Q16.4 Other congenital malformations of middle ear Congenital malformation of middle ear NOS
| |
| ** Q16.5 Congenital malformation of inner ear Anomaly: membranous labyrinth organ of Corti
| |
| ** Q16.9 Congenital malformation of ear causing impairment of hearing, unspecified Congenital absence of ear NOS
| |
| * Q17 Other congenital malformations of ear Excl.: preauricular sinus (Q18.1)
| |
| ** Q17.0 Accessory auricle Accessory tragus Polyotia Preauricular appendage or tag Supernumerary: ear lobule
| |
| ** Q17.1 Macrotia
| |
| ** Q17.2 Microtia
| |
| ** Q17.3 Other misshapen ear Pointed ear
| |
| ** Q17.4 Misplaced ear Low-set ears Excl.: cervical auricle (Q18.2)
| |
| ** Q17.5 Prominent ear Bat ear
| |
| ** Q17.8 Other specified congenital malformations of ear Congenital absence of lobe of ear
| |
| ** Q17.9 Congenital malformation of ear, unspecified Congenital anomaly of ear NOS
| |
| * Q18 Other congenital malformations of face and neck Excl.: cleft lip and cleft palate (Q35-Q37) conditions classified to
| |
| ** Q67.0-Q67.4 congenital malformations of skull and face bones (Q75.-) cyclopia (Q87.0) dentofacial anomalies [including malocclusion] (K07.-) malformation syndromes affecting facial appearance (Q87.0) persistent thyroglossal duct (Q89.2)
| |
| ** Q18.0 Sinus, fistula and cyst of branchial cleft Branchial vestige
| |
| ** Q18.1 Preauricular sinus and cyst Fistula (of): auricle, congenital cervicoaural Pretragal sinus and cyst
| |
| ** Q18.2 Other branchial cleft malformations Branchial cleft malformation NOS Cervical auricle Otocephaly
| |
| ** Q18.3 Webbing of neck Pterygium colli
| |
| ** Q18.4 Macrostomia
| |
| ** Q18.5 Microstomia
| |
| ** Q18.6 Macrocheilia Hypertrophy of lip, congenital
| |
| ** Q18.7 Microcheilia
| |
| ** Q18.8 Other specified congenital malformations of face and neck Medial: cyst fistula sinus of face and neck
| |
| ** Q18.9 Congenital malformation of face and neck, unspecified Congenital anomaly NOS of face and neck
| |
|
| |
|
| | {{ICD-11 Cerebral anomalies collapse table}} |
|
| |
|
| | {{ICD-11 Anencephaly table}} |
|
| |
|
| :'''Links:''' [http://apps.who.int/classifications/icd10/browse/2010/en#/Q10-Q18 Q10-Q18] - Congenital malformations of eye, ear, face and neck.
| | {{ICD-11 Anencephaly collapse table}} |
|
| |
|
| ===Congenital malformations of the circulatory system (Q20-Q28)===
| | {{ICD-11 Cerebral palsy table}} |
| * Q20 Congenital malformations of cardiac chambers and connections Excl.: dextrocardia with situs inversus (Q89.3) mirror-image atrial arrangement with situs inversus (Q89.3)
| |
| ** Q20.0 Common arterial trunk Persistent truncus arteriosus
| |
| ** Q20.1 Double outlet right ventricle Taussig-Bing syndrome
| |
| ** Q20.2 Double outlet left ventricle
| |
| ** Q20.3 Discordant ventriculoarterial connection Dextrotransposition of aorta Transposition of great vessels (complete)
| |
| ** Q20.4 Double inlet ventricle Common ventricle Cor triloculare biatriatum Single ventricle
| |
| ** Q20.5 Discordant atrioventricular connection Corrected transposition Laevotransposition Ventricular inversion
| |
| ** Q20.6 Isomerism of atrial appendages Isomerism of atrial appendages with asplenia or polysplenia
| |
| ** Q20.8 Other congenital malformations of cardiac chambers and connections
| |
| ** Q20.9 Congenital malformation of cardiac chambers and connections, unspecified
| |
| * Q21 Congenital malformations of cardiac septa Excl.: acquired cardiac septal defect (I51.0)
| |
| ** Q21.0 Ventricular septal defect
| |
| ** Q21.1 Atrial septal defect Coronary sinus defect Patent or persistent: foramen ovale ostium secundum defect (type II) Sinus venosus defect
| |
| ** Q21.2 Atrioventricular septal defect Common atrioventricular canal Endocardial cushion defect Ostium primum atrial septal defect (type I)
| |
| ** Q21.3 Tetralogy of Fallot Ventricular septal defect with pulmonary stenosis or atresia, dextroposition of aorta and hypertrophy of right ventricle.
| |
| ** Q21.4 Aortopulmonary septal defect Aortic septal defect Aortopulmonary window
| |
| ** Q21.8 Other congenital malformations of cardiac septa Eisenmenger's defect Pentalogy of Fallot Excl.: Eisenmenger's complex (I27.8) syndrome (I27.8)
| |
| ** Q21.9 Congenital malformation of cardiac septum, unspecified Septal (heart) defect NOS
| |
| * Q22 Congenital malformations of pulmonary and tricuspid valves
| |
| ** Q22.0 Pulmonary valve atresia
| |
| ** Q22.1 Congenital pulmonary valve stenosis
| |
| ** Q22.2 Congenital pulmonary valve insufficiency Congenital pulmonary valve regurgitation
| |
| ** Q22.3 Other congenital malformations of pulmonary valve Congenital malformation of pulmonary valve NOS
| |
| ** Q22.4 Congenital tricuspid stenosis Tricuspid atresia
| |
| ** Q22.5 Ebstein's anomaly
| |
| ** Q22.6 Hypoplastic right heart syndrome
| |
| ** Q22.8 Other congenital malformations of tricuspid valve
| |
| ** Q22.9 Congenital malformation of tricuspid valve, unspecified
| |
| * Q23 Congenital malformations of aortic and mitral valves
| |
| ** Q23.0 Congenital stenosis of aortic valve Congenital aortic: atresia stenosis Excl.: congenital subaortic stenosis (Q24.4) that in hypoplastic left heart syndrome (Q23.4)
| |
| ** Q23.1 Congenital insufficiency of aortic valve Bicuspid aortic valve Congenital aortic insufficiency
| |
| ** Q23.2 Congenital mitral stenosis Congenital mitral atresia
| |
| ** Q23.3 Congenital mitral insufficiency
| |
| ** Q23.4 Hypoplastic left heart syndrome Atresia, or marked hypoplasia of aortic orifice or valve, with hypoplasia of ascending aorta and defective develop-ment of left ventricle (with mitral valve stenosis or atresia).
| |
| ** Q23.8 Other congenital malformations of aortic and mitral valves
| |
| ** Q23.9 Congenital malformation of aortic and mitral valves, unspecified
| |
| * Q24 Other congenital malformations of heart Excl.: endocardial fibroelastosis (I42.4)
| |
| ** Q24.0 Dextrocardia Excl.: dextrocardia with situs inversus (Q89.3) isomerism of atrial appendages (with asplenia or polysplenia) (Q20.6) mirror-image atrial arrangement with situs inversus (Q89.3)
| |
| ** Q24.1 Laevocardia Location of heart in left hemithorax with apex pointing to the left, but with situs inversus of other viscera and defects of the heart, or corrected transposition of great vessels.
| |
| ** Q24.2 Cor triatriatum
| |
| ** Q24.3 Pulmonary infundibular stenosis
| |
| ** Q24.4 Congenital subaortic stenosis
| |
| ** Q24.5 Malformation of coronary vessels Congenital coronary (artery) aneurysm
| |
| ** Q24.6 Congenital heart block
| |
| ** Q24.8 Other specified congenital malformations of heart Congenital: diverticulum of left ventricle malformation of: myocardium pericardium Malposition of heart Uhl's disease
| |
| ** Q24.9 Congenital malformation of heart, unspecified Congenital: anomaly disease NOS of heart
| |
| * Q25 Congenital malformations of great arteries
| |
| ** Q25.0 Patent ductus arteriosus Patent ductus Botallo Persistent ductus arteriosus
| |
| ** Q25.1 Coarctation of aorta Coarctation of aorta (preductal)(postductal)
| |
| ** Q25.2 Atresia of aorta
| |
| ** Q25.3 Stenosis of aorta Supravalvular aortic stenosis Excl.: congenital aortic stenosis (Q23.0)
| |
| ** Q25.4 Other congenital malformations of aorta Absence Aplasia Congenital: aneurysm dilatation of aorta Aneurysm of sinus of Valsalva (ruptured) Double aortic arch [vascular ring of aorta] Hypoplasia of aorta Persistent: convolutions of aortic arch right aortic arch Excl.: hypoplasia of aorta in hypoplastic left heart syndrome (Q23.4)
| |
| ** Q25.5 Atresia of pulmonary artery
| |
| ** Q25.6 Stenosis of pulmonary artery Supravalvular pulmonary stenosis
| |
| ** Q25.7 Other congenital malformations of pulmonary artery Aberrant pulmonary artery Agenesis Aneurysm, congenital Anomaly Hypoplasia of pulmonary artery Pulmonary arteriovenous aneurysm
| |
| ** Q25.8 Other congenital malformations of great arteries
| |
| ** Q25.9 Congenital malformation of great arteries, unspecified
| |
| * Q26 Congenital malformations of great veins
| |
| ** Q26.0 Congenital stenosis of vena cava Congenital stenosis of vena cava (inferior)(superior)
| |
| ** Q26.1 Persistent left superior vena cava
| |
| ** Q26.2 Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection
| |
| ** Q26.3 Partial anomalous pulmonary venous connection
| |
| ** Q26.4 Anomalous pulmonary venous connection, unspecified
| |
| ** Q26.5 Anomalous portal venous connection
| |
| ** Q26.6 Portal vein-hepatic artery fistula
| |
| ** Q26.8 Other congenital malformations of great veins Absence of vena cava (inferior)(superior) Azygos continuation of inferior vena cava Persistent left posterior cardinal vein Scimitar syndrome
| |
| ** Q26.9 Congenital malformation of great vein, unspecified Anomaly of vena cava (inferior)(superior) NOS
| |
| * Q27 Other congenital malformations of peripheral vascular system Excl.: anomalies of: cerebral and precerebral vessels (Q28.0-Q28.3) coronary vessels (Q24.5) pulmonary artery (Q25.5-Q25.7) congenital retinal aneurysm (Q14.1) haemangioma and lymphangioma (D18.-)
| |
| ** Q27.0 Congenital absence and hypoplasia of umbilical artery Single umbilical artery
| |
| ** Q27.1 Congenital renal artery stenosis
| |
| ** Q27.2 Other congenital malformations of renal artery Congenital malformation of renal artery NOS Multiple renal arteries
| |
| ** Q27.3 Peripheral arteriovenous malformation Arteriovenous aneurysm Excl.: ac
| |
| ** Quired arteriovenous aneurysm (I77.0)
| |
| ** Q27.4 Congenital phlebectasia
| |
| ** Q27.8 Other specified congenital malformations of peripheral vascular system Aberrant subclavian artery Absence Atresia of artery or vein NEC Congenital: aneurysm (peripheral) stricture, artery varix
| |
| ** Q27.9 Congenital malformation of peripheral vascular system, unspecified Anomaly of artery or vein NOS
| |
| * Q28 Other congenital malformations of circulatory system Excl.: congenital aneurysm: NOS (Q27.8) coronary (Q24.5) peripheral (Q27.8) pulmonary (Q25.7) retinal (Q14.1) ruptured: cerebral arteriovenous malformation (I60.8) malformation of precerebral vessels (I72.-)
| |
| ** Q28.0 Arteriovenous malformation of precerebral vessels Congenital arteriovenous precerebral aneurysm (nonruptured)
| |
| ** Q28.1 Other malformations of precerebral vessels Congenital: malformation of precerebral vessels NOS precerebral aneurysm (nonruptured)
| |
| ** Q28.2 Arteriovenous malformation of cerebral vessels Arteriovenous malformation of brain NOS Congenital arteriovenous cerebral aneurysm (nonruptured)
| |
| ** Q28.3 Other malformations of cerebral vessels Congenital: cerebral aneurysm (nonruptured) malformation of cerebral vessels NOS
| |
| ** Q28.8 Other specified congenital malformations of circulatory system Congenital aneurysm, specified site NEC
| |
| ** Q28.9 Congenital malformation of circulatory system, unspecified
| |
|
| |
|
| | {{ICD-11 Cerebral palsy collapse table}} |
|
| |
|
| | ==Gastrointestinal== |
|
| |
|
| :'''Links:''' [[Cardiovascular System - Abnormalities]] | [http://apps.who.int/classifications/icd10/browse/2010/en#/Q20-Q28 Q20-Q28] - Congenital malformations of the circulatory system.
| | {{ICD-11 Gastrointestinal anomalies table}} |
|
| |
|
| ===Congenital malformations of the respiratory system (Q30-Q34)===
| | {{ICD-11 Gastrointestinal anomalies collapse table}} |
|
| |
|
| * Q30 Congenital malformations of nose Excl.: congenital deviation of nasal septum (Q67.4)
| |
| ** Q30.0 Choanal atresia Atresia Congenital stenosis of nares (anterior)(posterior)
| |
| ** Q30.1 Agenesis and underdevelopment of nose Congenital absence of nose
| |
| ** Q30.2 Fissured, notched and cleft nose
| |
| ** Q30.3 Congenital perforated nasal septum
| |
| ** Q30.8 Other congenital malformations of nose Accessory nose Congenital anomaly of nasal sinus wall
| |
| ** Q30.9 Congenital malformation of nose, unspecified
| |
| * Q31 Congenital malformations of larynx Excl.: congenital (laryngeal) stridor NOS (P28.8)
| |
| ** Q31.0 Web of larynx Web of larynx: NOS glottic subglottic
| |
| ** Q31.1 Congenital subglottic stenosis
| |
| ** Q31.2 Laryngeal hypoplasia
| |
| ** Q31.3 Laryngocele
| |
| ** Q31.5 Congenital laryngomalacia
| |
| ** Q31.8 Other congenital malformations of larynx Absence Agenesis Atresia of cricoid cartilage, epiglottis, glottis, larynx or thyroid cartilage Cleft thyroid cartilage Congenital stenosis of larynx NEC Fissure of epiglottis Posterior cleft of cricoid cartilage
| |
| ** Q31.9 Congenital malformation of larynx, unspecified
| |
| * Q32 Congenital malformations of trachea and bronchus Excl.: congenital bronchiectasis (Q33.4)
| |
| ** Q32.0 Congenital tracheomalacia
| |
| ** Q32.1 Other congenital malformations of trachea Anomaly of tracheal cartilage Atresia of trachea Congenital: dilatation malformation stenosis of trachea Congenital tracheocele
| |
| ** Q32.2 Congenital bronchomalacia
| |
| ** Q32.3 Congenital stenosis of bronchus
| |
| ** Q32.4 Other congenital malformations of bronchus Absence Agenesis Atresia Congenital malformation NOS Diverticulum of bronchus
| |
| * Q33 Congenital malformations of lung
| |
| ** Q33.0 Congenital cystic lung Congenital: honeycomb lung lung disease: cystic polycystic Excl.: cystic lung disease, acquired or unspecified (J98.4)
| |
| ** Q33.1 Accessory lobe of lung
| |
| ** Q33.2 Sequestration of lung
| |
| ** Q33.3 Agenesis of lung Absence of lung (lobe)
| |
| ** Q33.4 Congenital bronchiectasis
| |
| ** Q33.5 Ectopic tissue in lung
| |
| ** Q33.6 Hypoplasia and dysplasia of lung Excl.: pulmonary hypoplasia associated with short gestation (P28.0)
| |
| ** Q33.8 Other congenital malformations of lung
| |
| ** Q33.9 Congenital malformation of lung, unspecified
| |
| * Q34 Other congenital malformations of respiratory system
| |
| ** Q34.0 Anomaly of pleura
| |
| ** Q34.1 Congenital cyst of mediastinum
| |
| ** Q34.8 Other specified congenital malformations of respiratory system Atresia of nasopharynx
| |
| ** Q34.9 Congenital malformation of respiratory system, unspecified Congenital: absence anomaly NOS of respiratory organ
| |
|
| |
|
| | ===Circulatory system structural anomalies=== |
| | {{ICD-11-Circulatory system structural anomalies table}} |
|
| |
|
| :'''Links:''' [http://apps.who.int/classifications/icd10/browse/2010/en#/Q30-Q34 Q30-Q34] - Congenital malformations of the respiratory system.
| |
|
| |
|
| ===Cleft lip and cleft palate (Q35-Q37)=== | | ==Viral infection in the foetus or newborn== |
| | {{ICD-11 Viral infection table}} |
|
| |
|
| Use additional code (Q30.2), if desired, to identify associated malformations of the nose. Excl.: Robin's syndrome (Q87.0)
| | {{ICD-11 Viral infection collapse table}} |
| * Q35 Cleft palate Incl.: fissure of palate palatoschisis Excl.: cleft palate with cleft lip (Q37.-)
| |
| ** Q35.1 Cleft hard palate
| |
| ** Q35.3 Cleft soft palate
| |
| ** Q35.5 Cleft hard palate with cleft soft palate
| |
| ** Q35.7 Cleft uvula
| |
| ** Q35.9 Cleft palate, unspecified
| |
| * Q36 Cleft lip Incl.: cheiloschisis congenital fissure of lip harelip labium leporinum Excl.: cleft lip with cleft palate (Q37.-)
| |
| ** Q36.0 Cleft lip, bilateral
| |
| ** Q36.1 Cleft lip, median
| |
| ** Q36.9 Cleft lip, unilateral Cleft lip NOS
| |
| ** Q37 Cleft palate with cleft lip
| |
| * Q37.0 Cleft hard palate with bilateral cleft lip
| |
| ** Q37.1 Cleft hard palate with unilateral cleft lip Cleft hard palate with cleft lip NOS
| |
| ** Q37.2 Cleft soft palate with bilateral cleft lip
| |
| ** Q37.3 Cleft soft palate with unilateral cleft lip Cleft soft palate with cleft lip NOS
| |
| ** Q37.4 Cleft hard and soft palate with bilateral cleft lip
| |
| ** Q37.5 Cleft hard and soft palate with unilateral cleft lip Cleft hard and soft palate with cleft lip NOS
| |
| ** Q37.8 Unspecified cleft palate with bilateral cleft lip
| |
| ** Q37.9 Unspecified cleft palate with unilateral cleft lip Cleft palate with cleft lip NOS
| |
|
| |
|
| :'''Links:''' [http://apps.who.int/classifications/icd10/browse/2010/en#/Q35-Q37 Q35-Q37] - Cleft lip and cleft palate.
| | ==ICD-11 Chapter 19 Certain conditions originating in the perinatal period== |
| | |
| | * Foetus or newborn affected by maternal factors or by complications of pregnancy, labour or delivery |
| | |
| | * Disorders of newborn related to length of gestation or foetal growth |
| | |
| | * Birth injury |
| | |
| | * Infections of the foetus or newborn |
| | |
| | * Haemorrhagic or haematological disorders of foetus or newborn |
| | |
| | * Neurological disorders specific to the perinatal or neonatal period |
| | |
| | * Respiratory disorders specific to the perinatal or neonatal period |
| | |
| | * Cardiovascular disorders present in the perinatal or neonatal period |
| | |
| | * Transitory endocrine or metabolic disorders specific to foetus or newborn |
| | |
| | * Digestive system disorders of foetus or newborn |
| | |
| | * Genitourinary system disorders specific to the perinatal or neonatal period |
| | |
| | * Disorders involving the integument of foetus or newborn |
| | |
| | * Disturbances of temperature regulation of newborn |
| | |
| | * Certain disorders originating in the perinatal period |
| | |
| | * KD5Z Conditions originating in the perinatal or neonatal period, unspecified |
|
| |
|
| ===Other congenital malformations of the digestive system (Q38-Q45)=== | | ==Changes ICD-10 to ICD-11== |
|
| |
|
| * Q38 Other congenital malformations of tongue, mouth and pharynx Excl.: macrostomia (Q18.4) microstomia (Q18.5)
| | Below is a summary of changes from ICD 10 to {{ICD-11}} as listed in the Nov 2015 newsletter.<ref>World Health Organization – Classifications, Terminologies, and Standards [http://www.who.int/classifications/icd/revision/2015_11_ICD11_Newsletter.pdf?ua=1 ICD 11 Update Newsletter (Nov 2015)].</ref> |
| ** Q38.0 Congenital malformations of lips, not elsewhere classified Congenital: fistula of lip malformation of lip NOS Van der Woude's syndrome Excl.: cleft lip (Q36.-) cleft lip with cleft palate (Q37.-) macrocheilia (Q18.6) microcheilia (Q18.7)
| |
| ** Q38.1 Ankyloglossia Tongue tie
| |
| ** Q38.2 Macroglossia
| |
| ** Q38.3 Other congenital malformations of tongue Aglossia Bifid tongue Congenital: adhesion fissure malformation NOS of tongue Hypoglossia Hypoplasia of tongue Microglossia
| |
| ** Q38.4 Congenital malformations of salivary glands and ducts Absence Accessory Atresia (of) salivary gland or duct Congenital fistula of salivary gland
| |
| ** Q38.5 Congenital malformations of palate, not elsewhere classified Absence of uvula Congenital malformation of palate NOS High arched palate Excl.: cleft palate (Q35.-) cleft palate with cleft lip (Q37.-)
| |
| ** Q38.6 Other congenital malformations of mouth Congenital malformation of mouth NOS
| |
| ** Q38.7 Pharyngeal pouch Diverticulum of pharynx Excl.: pharyngeal pouch syndrome (D82.1)
| |
| ** Q38.8 Other congenital malformations of pharynx Congenital malformation of pharynx NOS
| |
| * Q39 Congenital malformations of oesophagus
| |
| ** Q39.0 Atresia of oesophagus without fistula Atresia of oesophagus NOS
| |
| ** Q39.1 Atresia of oesophagus with tracheo-oesophageal fistula Atresia of oesophagus with broncho-oesophageal fistula
| |
| ** Q39.2 Congenital tracheo-oesophageal fistula without atresia Congenital tracheo-oesophageal fistula NOS
| |
| ** Q39.3 Congenital stenosis and stricture of oesophagus
| |
| ** Q39.4 Oesophageal web
| |
| ** Q39.5 Congenital dilatation of oesophagus
| |
| ** Q39.6 Diverticulum of oesophagus Oesophageal pouch
| |
| ** Q39.8 Other congenital malformations of oesophagus Absent Congenital displacement Duplication (of) oesophagus
| |
| ** Q39.9 Congenital malformation of oesophagus, unspecified
| |
| * Q40 Other congenital malformations of upper alimentary tract
| |
| ** Q40.0 Congenital hypertrophic pyloric stenosis Congenital or infantile: constriction hypertrophy spasm stenosis stricture of pylorus
| |
| ** Q40.1 Congenital hiatus hernia Displacement of cardia through oesophageal hiatus Excl.: congenital diaphragmatic hernia (Q79.0)
| |
| ** Q40.2 Other specified congenital malformations of stomach Congenital: displacement of stomach diverticulum of stomach hourglass stomach Duplication of stomach Megalogastria Microgastria
| |
| ** Q40.3 Congenital malformation of stomach, unspecified
| |
| ** Q40.8 Other specified congenital malformations of upper alimentary tract
| |
| ** Q40.9 Congenital malformation of upper alimentary tract, unspecified Congenital: anomaly deformity NOS of upper alimentary tract
| |
| * Q41 Congenital absence, atresia and stenosis of small intestine Incl.: congenital obstruction, occlusion and stricture of small intestine or intestine NOS Excl.: meconium ileus (E84.1)
| |
| ** Q41.0 Congenital absence, atresia and stenosis of duodenum
| |
| ** Q41.1 Congenital absence, atresia and stenosis of jejunum Apple peel syndrome Imperforate jejunum
| |
| ** Q41.2 Congenital absence, atresia and stenosis of ileum
| |
| ** Q41.8 Congenital absence, atresia and stenosis of other specified parts of small intestine
| |
| ** Q41.9 Congenital absence, atresia and stenosis of small intestine, part unspecified Congenital absence, atresia and stenosis of intestine NOS
| |
| * Q42 Congenital absence, atresia and stenosis of large intestine Incl.: congenital obstruction, occlusion and stricture of large intestine
| |
| ** Q42.0 Congenital absence, atresia and stenosis of rectum with fistula
| |
| ** Q42.1 Congenital absence, atresia and stenosis of rectum without fistula Imperforate rectum
| |
| ** Q42.2 Congenital absence, atresia and stenosis of anus with fistula
| |
| ** Q42.3 Congenital absence, atresia and stenosis of anus without fistula Imperforate anus
| |
| ** Q42.8 Congenital absence, atresia and stenosis of other parts of large intestine
| |
| ** Q42.9 Congenital absence, atresia and stenosis of large intestine, part unspecified
| |
| * Q43 Other congenital malformations of intestine
| |
| ** Q43.0 Meckel's diverticulum Persistent: omphalomesenteric duct vitelline duct
| |
| ** Q43.1 Hirschsprung's disease Aganglionosis Congenital (aganglionic) megacolon
| |
| ** Q43.2 Other congenital functional disorders of colon Congenital dilatation of colon
| |
| ** Q43.3 Congenital malformations of intestinal fixation Congenital adhesions [bands]: omental, anomalous peritoneal Jackson's membrane Malrotation of colon Rotation: failure of incomplete insufficient of caecum and colon Universal mesentery
| |
| ** Q43.4 Duplication of intestine
| |
| ** Q43.5 Ectopic anus
| |
| ** Q43.6 Congenital fistula of rectum and anus Excl.: congenital fistula: rectovaginal (Q52.2) urethrorectal (Q64.7) pilonidal fistula or sinus (L05.-) with absence, atresia and stenosis (Q42.0,Q42.2)
| |
| ** Q43.7 Persistent cloaca Cloaca NOS
| |
| ** Q43.8 Other specified congenital malformations of intestine Congenital: blind loop syndrome diverticulitis, colon diverticulum, intestine Dolichocolon Megaloappendix Megaloduodenum Microcolon Transposition of: appendix colon intestine
| |
| ** Q43.9 Congenital malformation of intestine, unspecified
| |
| * Q44 Congenital malformations of gallbladder, bile ducts and liver
| |
| ** Q44.0 Agenesis, aplasia and hypoplasia of gallbladder Congenital absence of gallbladder
| |
| ** Q44.1 Other congenital malformations of gallbladder Congenital malformation of gallbladder NOS Intrahepatic gallbladder
| |
| ** Q44.2 Atresia of bile ducts
| |
| ** Q44.3 Congenital stenosis and stricture of bile ducts
| |
| ** Q44.4 Choledochal cyst
| |
| ** Q44.5 Other congenital malformations of bile ducts Accessory hepatic duct Congenital malformation of bile duct NOS Duplication: biliary duct cystic duct
| |
| ** Q44.6 Cystic disease of liver Fibrocystic disease of liver
| |
| ** Q44.7 Other congenital malformations of liver Accessory liver Alagille's syndrome Congenital: absence of liver hepatomegaly malformation of liver NOS
| |
| * Q45 Other congenital malformations of digestive system Excl.: congenital: diaphragmatic hernia (Q79.0) hiatus hernia (Q40.1)
| |
| ** Q45.0 Agenesis, aplasia and hypoplasia of pancreas Congenital absence of pancreas
| |
| ** Q45.1 Annular pancreas
| |
| ** Q45.2 Congenital pancreatic cyst
| |
| ** Q45.3 Other congenital malformations of pancreas and pancreatic duct Accessory pancreas Congenital malformation of pancreas or pancreatic duct NOS Excl.: diabetes mellitus: congenital (E10.-) neonatal (P70.2) fibrocystic disease of pancreas (E84.-)
| |
| ** Q45.8 Other specified congenital malformations of digestive system Absence (complete)(partial) of alimentary tract NOS Duplication Malposition, congenital of digestive organs NOS
| |
| ** Q45.9 Congenital malformation of digestive system, unspecified Congenital: anomaly deformity NOS of digestive system
| |
|
| |
|
| | New Chapters |
| | * Chapter 3 Diseases of the Blood and Blood forming Organs |
| | * Chapter 4 Disorders of the Immune System. |
| | * Chapter 5 Conditions related to Sexual Health. |
| | * Chapter 8 Sleep-Wake Disorders |
| | * Chapter 26 Extension codes |
| | * Chapter 27 Traditional Medicine |
| | New Concepts |
| | * Foundation: Everything in ICD |
| | * Entity: Each element in the foundation |
| | * Linearization: also known as a Classification |
| | * Stem code: Category (includes former ‘dagger’ codes) |
| | * Extension code: Additional information |
| | * Linearization parents: Classification hierarchy, Chapter, Block, Category Content Model |
| | * {{ICD-11}} categories have a short and a long definition. |
| | * All {{ICD-11}} categories include separate information on anatomy, aetiology, and other aspects. These can be accessed through searches, or when browsing in the tabular list. |
| | New Coding Scheme |
| | * The chapter numbering: now arabic numbers, not roman numerals |
| | * The coding scheme for categories: now minimum 4 characters, 2 levels of subcategories |
| | * Asterisk codes become Clinical forms or Extension codes. Additional sub-classifications become Extension codes |
| | Terminology |
| | * ICD-10 had a range of expressions to describe a causal relationship between conditions in a code title. In ICD 11, the preferred term is “due to”. |
| | * ICD-10 had a range of expressions indicating the coincidence of two conditions in a code title (e.g. “in” or “with”). In {{ICD-11}}, the preferred term is “associated with”. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
| :'''Links:''' [http://apps.who.int/classifications/icd10/browse/2010/en#/Q38-Q45 Q38-Q45] - Other congenital malformations of the digestive system. | | :'''Links:''' [[Talk:International_Classification_of_Diseases#ICD-10|Original ICD-10 page content]] |
|
| |
|
| ===Congenital malformations of genital organs (50-56)=== | | ==International Classification of Diseases - 10 - Australian Modification (ICD-10-AM)== |
|
| |
|
| Excl.: androgen resistance syndrome (E34.5) syndromes associated with anomalies in the number and form of chromosomes (90-99) testicular feminization syndrome (E34.5)
| | ICD-10-AM is the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, Tenth Revision, Australian Modification. It consists of a tabular list of diseases and accompanying index. |
| * Q50 Congenital malformations of ovaries, fallopian tubes and broad ligaments
| |
| ** Q50.0 Congenital absence of ovary Excl.: Turner's syndrome (96.-)
| |
| ** Q50.1 Developmental ovarian cyst
| |
| ** Q50.2 Congenital torsion of ovary
| |
| ** Q50.3 Other congenital malformations of ovary Accessory ovary Congenital malformation of ovary NOS Ovarian streak
| |
| ** Q50.4 Embryonic cyst of fallopian tube Fimbrial cyst
| |
| ** Q50.5 Embryonic cyst of broad ligament Cyst: epoophoron Gartner's duct parovarian
| |
| ** Q50.6 Other congenital malformations of fallopian tube and broad ligament Absence Accessory Atresia (of) fallopian tube or broad ligament Congenital malformation of fallopian tube or broad ligament NOS
| |
| * Q51 Congenital malformations of uterus and cervix
| |
| ** Q51.0 Agenesis and aplasia of uterus Congenital absence of uterus
| |
| ** Q51.1 Doubling of uterus with doubling of cervix and vagina
| |
| ** Q51.2 Other doubling of uterus Doubling of uterus NOS
| |
| ** Q51.3 Bicornate uterus
| |
| ** Q51.4 Unicornate uterus
| |
| ** Q51.5 Agenesis and aplasia of cervix Congenital absence of cervix
| |
| ** Q51.6 Embryonic cyst of cervix
| |
| ** Q51.7 Congenital fistulae between uterus and digestive and urinary tracts
| |
| ** Q51.8 Other congenital malformations of uterus and cervix Hypoplasia of uterus and cervix
| |
| ** Q51.9 Congenital malformation of uterus and cervix, unspecified
| |
| * Q52 Other congenital malformations of female genitalia
| |
| ** Q52.0 Congenital absence of vagina
| |
| ** Q52.1 Doubling of vagina Septate vagina Excl.: doubling of vagina with doubling of uterus and cervix (51.1)
| |
| ** Q52.2 Congenital rectovaginal fistula Excl.: cloaca (43.7)
| |
| ** Q52.3 Imperforate hymen
| |
| ** Q52.4 Other congenital malformations of vagina Congenital malformation of vagina NOS Cyst: canal of Nuck, congenital embryonic vaginal
| |
| ** Q52.5 Fusion of labia
| |
| ** Q52.6 Congenital malformation of clitoris
| |
| ** Q52.7 Other congenital malformations of vulva Congenital: absence cyst malformation NOS of vulva
| |
| ** Q52.8 Other specified congenital malformations of female genitalia
| |
| ** Q52.9 Congenital malformation of female genitalia, unspecified
| |
| * Q53 Undescended testicle
| |
| ** Q53.0 Ectopic testis Unilateral or bilateral ectopic testes
| |
| ** Q53.1 Undescended testicle, unilateral
| |
| ** Q53.2 Undescended testicle, bilateral
| |
| ** Q53.9 Undescended testicle, unspecified Cryptorchism NOS
| |
| * Q54 Hypospadias Excl.: epispadias (64.0)
| |
| ** Q54.0 Hypospadias, balanic Hypospadias: coronal glandular
| |
| ** Q54.1 Hypospadias, penile
| |
| ** Q54.2 Hypospadias, penoscrotal
| |
| ** Q54.3 Hypospadias, perineal
| |
| ** Q54.4 Congenital chordee
| |
| ** Q54.8 Other hypospadias
| |
| ** Q54.9 Hypospadias, unspecified
| |
| * Q55 Other congenital malformations of male genital organs Excl.: congenital hydrocele (P83.5) hypospadias (54.-)
| |
| ** Q55.0 Absence and aplasia of testis Monorchism
| |
| ** Q55.1 Hypoplasia of testis and scrotum Fusion of testes
| |
| ** Q55.2 Other congenital malformations of testis and scrotum Congenital malformation of testis or scrotum NOS Polyorchism Retractile testis Testis migrans
| |
| ** Q55.3 Atresia of vas deferens
| |
| ** Q55.4 Other congenital malformations of vas deferens, epididymis, seminal vesicles and prostate Absence or aplasia of: prostate spermatic cord Congenital malformation of vas deferens, epididymis, seminal vesicles or prostate NOS
| |
| ** Q55.5 Congenital absence and aplasia of penis
| |
| ** Q55.6 Other congenital malformations of penis Congenital malformation of penis NOS Curvature of penis (lateral) Hypoplasia of penis
| |
| ** Q55.8 Other specified congenital malformations of male genital organs
| |
| ** Q55.9 Congenital malformation of male genital organ, unspecified Congenital: anomaly deformity NOS of male genital organ
| |
| * Q56 Indeterminate sex and pseudohermaphroditism Excl.: pseudohermaphroditism: female, with adrenocortical disorder (E25.-) male, with androgen resistance (E34.5) with specified chromosomal anomaly (96-99)
| |
| ** Q56.0 Hermaphroditism, not elsewhere classified Ovotestis
| |
| ** Q56.1 Male pseudohermaphroditism, not elsewhere classified Male pseudohermaphroditism NOS
| |
| ** Q56.2 Female pseudohermaphroditism, not elsewhere classified Female pseudohermaphroditism NOS
| |
| ** Q56.3 Pseudohermaphroditism, unspecified
| |
| ** Q56.4 Indeterminate sex, unspecified Ambiguous genitalia
| |
|
| |
|
| | ICD-10-AM was developed by the National Centre for Classification in Health and has been in use since 1998. It was developed with assistance from clinicians and clinical coders to ensure that the classification is current and appropriate for Australian clinical practice. ICD-10-AM is a derived version of the World Health Organization (WHO) ICD-10. It uses an alphanumeric coding scheme for diseases and external causes of injury. It is structured by body system and aetiology, and comprises three, four and five character categories. ICD-10-AM is updated on a regular basis, with the regular updates of ICD-10 being included as part of the updating process. |
|
| |
|
| :'''Links:''' [http://apps.who.int/classifications/icd10/browse/2010/en#/Q50-Q56 Q50-Q56] - Congenital malformations of genital organs.
| | (text from - Australian Consortium for Classification Development) |
|
| |
|
| ===Congenital malformations of the urinary system===
| |
| * Q60 Renal agenesis and other reduction defects of kidney
| |
| * Q61 Cystic kidney disease
| |
| * Q62 Congenital obstructive defects of renal pelvis and congenital malformations of ureter
| |
| * Q63 Other congenital malformations of kidney
| |
| * Q64 Other congenital malformations of urinary system
| |
|
| |
|
| | :'''Links:''' [https://www.accd.net.au/Icd10.aspx ICD-10-AM/ACHI/ACS] |
|
| |
|
| :'''Links:''' [http://apps.who.int/classifications/icd10/browse/2010/en#/Q60-Q64 Q60-Q64] - Congenital malformations of the urinary system.
| |
|
| |
|
| ===Congenital malformations and deformations of the musculoskeletal system=== | | ==References== |
| * Q65 Congenital deformities of hip Excl.: clicking hip (R29.4)
| | {{Ref-WHO-ICD10 1992}} |
| ** Q65.0 Congenital dislocation of hip, unilateral
| |
| ** Q65.1 Congenital dislocation of hip, bilateral
| |
| ** Q65.2 Congenital dislocation of hip, unspecified
| |
| ** Q65.3 Congenital subluxation of hip, unilateral
| |
| ** Q65.4 Congenital subluxation of hip, bilateral
| |
| ** Q65.5 Congenital subluxation of hip, unspecified
| |
| ** Q65.6 Unstable hip Dislocatable hip Subluxatable hip
| |
| ** Q65.8 Other congenital deformities of hip Anteversion of femoral neck Congenital acetabular dysplasia Congenital coxa: valga vara
| |
| ** Q65.9 Congenital deformity of hip, unspecified
| |
| * Q66 Congenital deformities of feet Excl.: reduction defects of feet (Q72.-) valgus deformities (acquired) (M21.0) varus deformities (acquired) (M21.1)
| |
| ** Q66.0 Talipes equinovarus
| |
| ** Q66.1 Talipes calcaneovarus
| |
| ** Q66.2 Metatarsus varus
| |
| ** Q66.3 Other congenital varus deformities of feet Hallux varus, congenital
| |
| ** Q66.4 Talipes calcaneovalgus
| |
| ** Q66.5 Congenital pes planus Flat foot: congenital rigid spastic (everted)
| |
| ** Q66.6 Other congenital valgus deformities of feet Metatarsus valgus
| |
| ** Q66.7 Pes cavus
| |
| ** Q66.8 Other congenital deformities of feet Clubfoot NOS Hammer toe, congenital Talipes: NOS asymmetric Tarsal coalition Vertical talus
| |
| ** Q66.9 Congenital deformity of feet, unspecified
| |
| * Q67 Congenital musculoskeletal deformities of head, face, spine and chest Excl.: congenital malformation syndromes classified to Q87.- Potter's syndrome (Q60.6)
| |
| ** Q67.0 Facial asymmetry
| |
| ** Q67.1 Compression facies
| |
| ** Q67.2 Dolichocephaly
| |
| ** Q67.3 Plagiocephaly
| |
| ** Q67.4 Other congenital deformities of skull, face and jaw Depressions in skull Deviation of nasal septum, congenital Hemifacial atrophy or hypertrophy Squashed or bent nose, congenital Excl.: dentofacial anomalies [including malocclusion] (K07.-) syphilitic saddle nose (A50.5)
| |
| ** Q67.5 Congenital deformity of spine Congenital scoliosis: NOS postural Excl.: infantile idiopathic scoliosis (M41.0) scoliosis due to congenital bony malformation (Q76.3)
| |
| ** Q67.6 Pectus excavatum Congenital funnel chest
| |
| ** Q67.7 Pectus carinatum Congenital pigeon chest
| |
| ** Q67.8 Other congenital deformities of chest Congenital deformity of chest wall NOS
| |
| * Q68 Other congenital musculoskeletal deformities Excl.: reduction defects of limb(s) (Q71-Q73)
| |
| ** Q68.0 Congenital deformity of sternocleidomastoid muscle Congenital (sternomastoid) torticollis Contracture of sternocleidomastoid (muscle) Sternomastoid tumour (congenital)
| |
| ** Q68.1 Congenital deformity of hand Congenital clubfinger Spade-like hand (congenital)
| |
| ** Q68.2 Congenital deformity of knee Congenital: dislocation of knee genu recurvatum
| |
| ** Q68.3 Congenital bowing of femur Excl.: anteversion of femur (neck) (Q65.8)
| |
| ** Q68.4 Congenital bowing of tibia and fibula
| |
| ** Q68.5 Congenital bowing of long bones of leg, unspecified
| |
| ** Q68.8 Other specified congenital musculoskeletal deformities Congenital: deformity of: clavicle elbow forearm scapula dislocation of: elbow shoulder
| |
| * Q69 Polydactyly
| |
| ** Q69.0 Accessory finger(s)
| |
| ** Q69.1 Accessory thumb(s)
| |
| ** Q69.2 Accessory toe(s) Accessory hallux
| |
| ** Q69.9 Polydactyly, unspecified Supernumerary digit(s) NOS
| |
| * Q70 Syndactyly
| |
| ** Q70.0 Fused fingers Complex syndactyly of fingers with synostosis
| |
| ** Q70.1 Webbed fingers Simple syndactyly of fingers without synostosis
| |
| ** Q70.2 Fused toes Complex syndactyly of toes with synostosis
| |
| ** Q70.3 Webbed toes Simple syndactyly of toes without synostosis
| |
| ** Q70.4 Polysyndactyly
| |
| ** Q70.9 Syndactyly, unspecified Symphalangy NOS
| |
| * Q71 Reduction defects of upper limb
| |
| ** Q71.0 Congenital complete absence of upper limb(s)
| |
| ** Q71.1 Congenital absence of upper arm and forearm with hand present
| |
| ** Q71.2 Congenital absence of both forearm and hand
| |
| ** Q71.3 Congenital absence of hand and finger(s)
| |
| ** Q71.4 Longitudinal reduction defect of radius Clubhand (congenital) Radial clubhand
| |
| ** Q71.5 Longitudinal reduction defect of ulna
| |
| ** Q71.6 Lobster-claw hand
| |
| ** Q71.8 Other reduction defects of upper limb(s) Congenital shortening of upper limb(s)
| |
| ** Q71.9 Reduction defect of upper limb, unspecified
| |
| * Q72 Reduction defects of lower limb
| |
| ** Q72.0 Congenital complete absence of lower limb(s)
| |
| ** Q72.1 Congenital absence of thigh and lower leg with foot present
| |
| ** Q72.2 Congenital absence of both lower leg and foot
| |
| ** Q72.3 Congenital absence of foot and toe(s)
| |
| ** Q72.4 Longitudinal reduction defect of femur Proximal femoral focal deficiency
| |
| ** Q72.5 Longitudinal reduction defect of tibia
| |
| ** Q72.6 Longitudinal reduction defect of fibula
| |
| ** Q72.7 Split foot
| |
| ** Q72.8 Other reduction defects of lower limb(s) Congenital shortening of lower limb(s)
| |
| ** Q72.9 Reduction defect of lower limb, unspecified
| |
| * Q73 Reduction defects of unspecified limb
| |
| ** Q73.0 Congenital absence of unspecified limb(s) Amelia NOS
| |
| ** Q73.1 Phocomelia, unspecified limb(s) Phocomelia NOS
| |
| ** Q73.8 Other reduction defects of unspecified limb(s) Longitudinal reduction deformity of unspecified limb(s) Ectromelia NOS Hemimelia NOS Reduction defect of limb(s) NOS
| |
| * Q74 Other congenital malformations of limb(s) Excl.: polydactyly (Q69.-) reduction defect of limb (Q71-Q73) syndactyly (Q70.-)
| |
| ** Q74.0 Other congenital malformations of upper limb(s), including shoulder girdle Accessory carpal bones Cleidocranial dysostosis Congenital pseudarthrosis of clavicle Macrodactylia (fingers) Madelung's deformity Radioulnar synostosis Sprengel's deformity Triphalangeal thumb
| |
| ** Q74.1 Congenital malformation of knee Congenital: absence of patella dislocation of patella genu: valgum varum Rudimentary patella Excl.: congenital: dislocation of knee (Q68.2) genu recurvatum (Q68.2) nail patella syndrome (Q87.2)
| |
| ** Q74.2 Other congenital malformations of lower limb(s), including pelvic girdle Congenital: fusion of sacroiliac joint malformation (of): ankle (joint) sacroiliac (joint) Excl.: anteversion of femur (neck) (Q65.8)
| |
| ** Q74.3 Arthrogryposis multiplex congenita
| |
| ** Q74.8 Other specified congenital malformations of limb(s)
| |
| ** Q74.9 Unspecified congenital malformation of limb(s) Congenital anomaly of limb(s) NOS
| |
| * Q75 Other congenital malformations of skull and face bones Excl.: congenital malformation of face NOS (Q18.-) congenital malformation syndromes classified to Q87.- dentofacial anomalies [including malocclusion] (K07.-) musculoskeletal deformities of head and face (Q67.0-Q67.4) skull defects associated with congenital anomalies of brain such as: anencephaly (Q00.0) encephalocele (Q01.-) hydrocephalus (Q03.-) microcephaly (Q02)
| |
| ** Q75.0 Craniosynostosis Acrocephaly Imperfect fusion of skull Oxycephaly Trigonocephaly
| |
| ** Q75.1 Craniofacial dysostosis Crouzon's disease
| |
| ** Q75.2 Hypertelorism
| |
| ** Q75.3 Macrocephaly
| |
| ** Q75.4 Mandibulofacial dysostosis Syndrome: Franceschetti Treacher-Collins
| |
| ** Q75.5 Oculomandibular dysostosis
| |
| ** Q75.8 Other specified congenital malformations of skull and face bones Absence of skull bone, congenital Congenital deformity of forehead Platybasia
| |
| ** Q75.9 Congenital malformation of skull and face bones, unspecified Congenital anomaly of: face bones NOS skull NOS
| |
| * Q76 Congenital malformations of spine and bony thorax Excl.: congenital musculoskeletal deformities of spine and chest (Q67.5-Q67.8)
| |
| ** Q76.0 Spina bifida occulta Excl.: meningocele (spinal) (Q05.-) spina bifida (aperta)(cystica) (Q05.-)
| |
| ** Q76.1 Klippel-Feil syndrome Cervical fusion syndrome
| |
| ** Q76.2 Congenital spondylolisthesis Congenital spondylolysis Excl.: spondylolisthesis (acquired) (M43.1) spondylolysis (acquired) (M43.0)
| |
| ** Q76.3 Congenital scoliosis due to congenital bony malformation Hemivertebra fusion or failure of segmentation with scoliosis
| |
| ** Q76.4 Other congenital malformations of spine, not associated with scoliosis Congenital: absence of vertebra fusion of spine kyphosis lordosis malformation of lumbosacral (joint) (region) Hemivertebra Malformation of spine Platyspondylisis Supernumerary vertebra unspecified or not associated with scoliosis
| |
| ** Q76.5 Cervical rib Supernumerary rib in cervical region
| |
| ** Q76.6 Other congenital malformations of ribs Accessory rib Congenital: absence of rib fusion of ribs malformation of ribs NOS Excl.: short rib syndrome (Q77.2)
| |
| ** Q76.7 Congenital malformation of sternum Congenital absence of sternum Sternum bifidum
| |
| ** Q76.8 Other congenital malformations of bony thorax
| |
| ** Q76.9 Congenital malformation of bony thorax, unspecified
| |
| * Q77 Osteochondrodysplasia with defects of growth of tubular bones and spine Excl.: mucopolysaccharidosis (E76.0-E76.3)
| |
| ** Q77.0 Achondrogenesis Hypochondrogenesis
| |
| ** Q77.1 Thanatophoric short stature
| |
| ** Q77.2 Short rib syndrome Asphyxiating thoracic dysplasia [Jeune]
| |
| ** Q77.3 Chondrodysplasia punctata
| |
| ** Q77.4 Achondroplasia Hypochondroplasia Osteosclerosis congenita
| |
| ** Q77.5 Dystrophic dysplasia
| |
| ** Q77.6 Chondroectodermal dysplasia Ellis-van Creveld syndrome
| |
| ** Q77.7 Spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia
| |
| ** Q77.8 Other osteochondrodysplasia with defects of growth of tubular bones and spine
| |
| ** Q77.9 Osteochondrodysplasia with defects of growth of tubular bones and spine, unspecified
| |
| * Q78 Other osteochondrodysplasias
| |
| ** Q78.0 Osteogenesis imperfecta Fragilitas ossium Osteopsathyrosis
| |
| ** Q78.1 Polyostotic fibrous dysplasia Albright(-McCune)(-Sternberg) syndrome
| |
| ** Q78.2 Osteopetrosis Albers-Schönberg syndrome
| |
| ** Q78.3 Progressive diaphyseal dysplasia Camurati-Engelmann syndrome
| |
| ** Q78.4 Enchondromatosis Maffucci's syndrome Ollier's disease
| |
| ** Q78.5 Metaphyseal dysplasia Pyle's syndrome
| |
| ** Q78.6 Multiple congenital exostoses Diaphyseal aclasis
| |
| ** Q78.8 Other specified osteochondrodysplasias Osteopoikilosis
| |
| ** Q78.9 Osteochondrodysplasia, unspecified Chondrodystrophy NOS Osteodystrophy NOS
| |
| * Q79 Congenital malformations of the musculoskeletal system, not elsewhere classified Excl.: congenital (sternomastoid) torticollis (Q68.0)
| |
| ** Q79.0 Congenital diaphragmatic hernia Excl.: congenital hiatus hernia (Q40.1)
| |
| ** Q79.1 Other congenital malformations of diaphragm Absence of diaphragm Congenital malformation of diaphragm NOS Eventration of diaphragm
| |
| ** Q79.2 Exomphalos Omphalocele Excl.: umbilical hernia (K42.-)
| |
| ** Q79.3 Gastroschisis
| |
| ** Q79.4 Prune belly syndrome
| |
| ** Q79.5 Other congenital malformations of abdominal wall Excl.: umbilical hernia (K42.-)
| |
| ** Q79.6 Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
| |
| ** Q79.8 Other congenital malformations of musculoskeletal system Absence of: muscle tendon Accessory muscle Amyotrophia congenita Congenital: constricting bands shortening of tendon Poland's syndrome
| |
| ** Q79.9 Congenital malformation of musculoskeletal system, unspecified Congenital: anomaly NOS deformity NOS of musculoskeletal system NOS
| |
|
| |
|
| | | <references/> |
| :'''Links:''' [http://apps.who.int/classifications/icd10/browse/2010/en#/Q65-Q79 Q65-Q79] - Congenital malformations and deformations of the musculoskeletal system.
| |
| | |
| ===Other congenital malformations===
| |
| | |
| :'''Links:''' [http://apps.who.int/classifications/icd10/browse/2010/en#/Q80-Q89 Q80-Q89]- Other congenital malformations.
| |
| | |
| ===Chromosomal abnormalities, not elsewhere classified===
| |
| | |
| * Q90 Down's syndrome
| |
| ** Q90.0 Trisomy 21, meiotic nondisjunction
| |
| ** Q90.1 Trisomy 21, mosaicism (mitotic nondisjunction)
| |
| ** Q90.2 Trisomy 21, translocation
| |
| ** Q90.9 Down's syndrome, unspecified Trisomy 21 NOS
| |
| * Q91 Edwards' syndrome and Patau's syndrome
| |
| ** Q91.0 Trisomy 18, meiotic nondisjunction
| |
| ** Q91.1 Trisomy 18, mosaicism (mitotic nondisjunction)
| |
| ** Q91.2 Trisomy 18, translocation ** Q91.3 Edwards' syndrome, unspecified
| |
| ** Q91.4 Trisomy 13, meiotic nondisjunction
| |
| ** Q91.5 Trisomy 13, mosaicism (mitotic nondisjunction)
| |
| ** Q91.6 Trisomy 13, translocation
| |
| ** Q91.7 Patau's syndrome, unspecified
| |
| * Q92 Other trisomies and partial trisomies of the autosomes, not elsewhere classified Incl.: unbalanced translocations and insertions Excl.: trisomies of chromosomes 13, 18, 21 (Q90-Q91)
| |
| ** Q92.0 Whole chromosome trisomy, meiotic nondisjunction
| |
| ** Q92.1 Whole chromosome trisomy, mosaicism (mitotic nondisjunction)
| |
| ** Q92.2 Major partial trisomy Whole arm or more duplicated.
| |
| ** Q92.3 Minor partial trisomy Less than whole arm duplicated.
| |
| ** Q92.4 Duplications seen only at prometaphase
| |
| ** Q92.5 Duplications with other complex rearrangements
| |
| ** Q92.6 Extra marker chromosomes
| |
| ** Q92.7 Triploidy and polyploidy
| |
| ** Q92.8 Other specified trisomies and partial trisomies of autosomes
| |
| ** Q92.9 Trisomy and partial trisomy of autosomes, unspecified
| |
| * Q93 Monosomies and deletions from the autosomes, not elsewhere classified
| |
| ** Q93.0 Whole chromosome monosomy, meiotic nondisjunction
| |
| ** Q93.1 Whole chromosome monosomy, mosaicism (mitotic nondisjunction)
| |
| ** Q93.2 Chromosome replaced with ring or dicentric
| |
| ** Q93.3 Deletion of short arm of chromosome 4 Wolff-Hirschorn syndrome
| |
| ** Q93.4 Deletion of short arm of chromosome 5 Cri-du-chat syndrome
| |
| ** Q93.5 Other deletions of part of a chromosome Angelman syndrome
| |
| ** Q93.6 Deletions seen only at prometaphase
| |
| ** Q93.7 Deletions with other complex rearrangements
| |
| ** Q93.8 Other deletions from the autosomes
| |
| ** Q93.9 Deletion from autosomes, unspecified
| |
| * Q95 Balanced rearrangements and structural markers, not elsewhere classified Incl.: Robertsonian and balanced reciprocal translocations and insertions
| |
| ** Q95.0 Balanced translocation and insertion in normal individual
| |
| ** Q95.1 Chromosome inversion in normal individual
| |
| ** Q95.2 Balanced autosomal rearrangement in abnormal individual
| |
| ** Q95.3 Balanced sex/autosomal rearrangement in abnormal individual
| |
| ** Q95.4 Individuals with marker heterochromatin
| |
| ** Q95.5 Individuals with autosomal fragile site
| |
| ** Q95.8 Other balanced rearrangements and structural markers
| |
| ** Q95.9 Balanced rearrangement and structural marker, unspecified
| |
| * Q96 Turner's syndrome Excl.: Noonan's syndrome (Q87.1)
| |
| ** Q96.0 Karyotype 45,X
| |
| ** Q96.1 Karyotype 46,X iso (XQ)
| |
| ** Q96.2 Karyotype 46,X with abnormal sex chromosome, except iso (XQ)
| |
| ** Q96.3 Mosaicism, 45,X/46,XX or XY
| |
| ** Q96.4 Mosaicism, 45,X/other cell line(s) with abnormal sex chromosome
| |
| ** Q96.8 Other variants of Turner's syndrome
| |
| ** Q96.9 Turner's syndrome, unspecified
| |
| * Q97 Other sex chromosome abnormalities, female phenotype, not elsewhere classified Excl.: Turner's syndrome (Q96.-)
| |
| ** Q97.0 Karyotype 47,XXX
| |
| ** Q97.1 Female with more than three X chromosomes
| |
| ** Q97.2 Mosaicism, lines with various numbers of X chromosomes
| |
| ** Q97.3 Female with 46,XY karyotype
| |
| ** Q97.8 Other specified sex chromosome abnormalities, female phenotype
| |
| ** Q97.9 Sex chromosome abnormality, female phenotype, unspecified
| |
| * Q98 Other sex chromosome abnormalities, male phenotype, not elsewhere classified
| |
| ** Q98.0 Klinefelter's syndrome karyotype 47,XXY
| |
| ** Q98.1 Klinefelter's syndrome, male with more than two X chromosomes
| |
| ** Q98.2 Klinefelter's syndrome, male with 46,XX karyotype
| |
| ** Q98.3 Other male with 46,XX karyotype
| |
| ** Q98.4 Klinefelter's syndrome, unspecified
| |
| ** Q98.5 Karyotype 47,XYY
| |
| ** Q98.6 Male with structurally abnormal sex chromosome
| |
| ** Q98.7 Male with sex chromosome mosaicism
| |
| ** Q98.8 Other specified sex chromosome abnormalities, male phenotype
| |
| ** Q98.9 Sex chromosome abnormality, male phenotype, unspecified
| |
| * Q99 Other chromosome abnormalities, not elsewhere classified
| |
| ** Q99.0 Chimera 46,XX/46,XY Chimera 46,XX/46,XY true hermaphrodite
| |
| ** Q99.1 46,XX true hermaphrodite 46,XX with streak gonads 46,XY with streak gonads Pure gonadal dysgenesis
| |
| ** Q99.2 Fragile X chromosome Fragile X syndrome
| |
| ** Q99.8 Other specified chromosome abnormalities
| |
| ** Q99.9 Chromosomal abnormality, unspecified
| |
| | |
| | |
| :'''Links:''' [http://apps.who.int/classifications/icd10/browse/2010/en#/Q90-Q99 Q90-Q99] - Chromosomal abnormalities, not elsewhere classified.
| |
| | |
| ==Chapter XVI Certain conditions originating in the perinatal period (P00-P96)==
| |
| | |
| Includes conditions that have their origin in the perinatal period even though death or morbidity occurs later.
| |
| | |
| :Excludes congenital malformations, deformations and chromosomal abnormalities (Q00-Q99); endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases (E00-E90); injury, poisoning and certain other consequences of external causes (S00-T98); neoplasms (C00-D48); tetanus neonatorum (A33)
| |
| | |
| | |
| * P00-P04 - Fetus and newborn affected by maternal factors and by complications of pregnancy, labour and delivery.
| |
| * P05-P08 - Disorders related to length of gestation and fatal growth.
| |
| * P10-P15 - Birth trauma.
| |
| * P20-P29 - Respiratory and cardiovascular disorders specific to the perinatal period.
| |
| * P35-P39 - Infections specific to the perinatal period.
| |
| * P50-P61 - Haemorrhagic and haematological disorders of fetus and newborn.
| |
| * P70-P74 - Transitory endocrine and metabolic disorders specific to fetus and newborn.
| |
| * P75-P78 - Digestive system disorders of fetus and newborn.
| |
| * P80-P83 - Conditions involving the integument and temperature regulation of fetus and newborn.
| |
| * P90-P96 - Other disorders originating in the perinatal period.
| |
| | |
| | |
| :'''Links:''' [http://apps.who.int/classifications/icd10/browse/2010/en#/XVI Chapter XVI]
| |
| | |
| ==Chapter XV Pregnancy, childbirth and the puerperium (O00-O99)==
| |
| The codes included in this chapter are to be used for conditions related to or aggravated by the pregnancy, childbirth or by the puerperium (maternal causes or obstetric causes)
| |
| | |
| :Excludes Certain diseases or injuries complicating pregnancy, childbirth and the puerperium classified elsewhere: external causes (for mortality) (V, W, X, Y); injury, poisoning and certain other consequences of external cause (S00-T88.1, , T88.6-T98); mental and behavioural disorders associated with the puerperium (F53.-); obstetrical tetanus (A34); postpartum necrosis of pituitary gland (E23.0); puerperal osteomalacia (M83.0); supervision of high-risk pregnancy (Z35.-); supervision of normal pregnancy (Z34.-).
| |
| | |
| * O00-O08 - Pregnancy with abortive outcome.
| |
| * O10-O16 - Oedema, proteinuria and hypertensive disorders in pregnancy, childbirth and the puerperium.
| |
| * O20-O29 - Other maternal disorders predominantly related to pregnancy.
| |
| * O30-O48 - Maternal care related to the fetus and amniotic cavity and possible delivery problems.
| |
| * O60-O75 - Complications of labour and delivery.
| |
| * O80-O84 - Delivery.
| |
| * O85-O92 - Complications predominantly related to the puerperium.
| |
| * O94-O99 - Other obstetric conditions, not elsewhere classified.
| |
| | |
| | |
| :'''Links:''' [http://apps.who.int/classifications/icd10/browse/2010/en#/XV Chapter XV]
| |
|
| |
|
| ==External Links== | | ==External Links== |
| Line 728: |
Line 150: |
| {{External Links}} | | {{External Links}} |
|
| |
|
| * '''World Health Organization''' [http://www.who.int/classifications/icd/en/index.html International Classification of Diseases-10] | | * '''World Health Organization''' |
| | ** [http://apps.who.int/classifications/icd10/browse/2016/en 2016 English] |
| | ** [http://www.who.int/classifications/icd/en/index.html International Classification of Diseases - 10] |
| | ** [https://icd.who.int/dev11 International Classification of Diseases - 11] |
| | * '''Australian Modification''' International Classification of Diseases - 10th revision [https://www.accd.net.au/Icd10.aspx ICD-10-AM/ACHI/ACS] |
| | * '''USA''' |
| | ** Centers for Disease Control [http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/icd/icd10cm.htm International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-10-CM)] |
| | ** The National Library of Medicine (2014 April 14 ) [https://www.nlm.nih.gov/pubs/techbull/ma14/ma14_mplus_icd10.html MedlinePlus Connect] now supports ICD-10-CM (International Classification of Diseases, 10th edition, Clinical Modification) queries. Upon receiving a problem code request with an ICD-10-CM code, MedlinePlus Connect returns relevant health information from MedlinePlus, Genetics Home Reference, and other reliable health resources. MedlinePlus Connect will continue to deliver targeted responses to ICD-9-CM and SNOMED CT requests as well. |
| | ** US Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services [https://www.cms.gov/Medicare/Coding/ICD10/index.html ICD-10] |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
| {{Template:Glossary}} | | {{Glossary}} |
|
| |
|
| {{Template:Footer}} | | {{Footer}} |
|
| |
|
| [[Category:Abnormal Development]] | | [[Category:Abnormal Development]][[Category:ICD-11]][[Category:ICD-11 Table]] |