Bat Development: Difference between revisions
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
'''Search Pubmed:''' [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?db=pubmed&cmd=search&term= | '''Search Pubmed:''' [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?db=pubmed&cmd=search&term=bat%20development bat development] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?db=pubmed&cmd=search&term=chiroptera%20development chiroptera development] | ||
Revision as of 00:15, 29 April 2011
Introduction
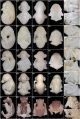
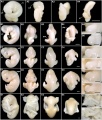
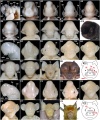
The bat (chiroptera) family consists of about 1,000 species throughout the world today (90 in Australia) and is not a common model of mammalian embryonic development.
The taxon chiroptera can also be further divided into the Megachiroptera (flying foxes) and Microchiroptera suborders. Echolocation sounds have been shown to differ in Microchiroptera (vocal cords) and Megachiroptera (tongue clicks).
Links: original Bat page
Taxon
Chiroptera
Genbank common name: bats
Taxonomy Id: 9397 Rank: order
Genetic code: Translation table 1 (Standard)
Mitochondrial genetic code: Translation table 2 (Vertebrate Mitochondrial)
Lineage( abbreviated ): Eukaryota; Fungi/Metazoa group; Metazoa; Eumetazoa; Bilateria; Coelomata; Deuterostomia; Chordata; Craniata; Vertebrata; Gnathostomata; Teleostomi; Euteleostomi; Sarcopterygii; Tetrapoda; Amniota; Mammalia; Theria; Eutheria; Laurasiatheria
Species Comparison
Carollia perspicillata
- (short-tailed fruit bat) Ovulation has a 24 hour variation with up to 2 days of variation in oviduct transit time, and gestation period is 113 - 120 days.
Myotis thysanodes and M. lucifugus
- Ovulation, fertilization, and implantation occur during the first 2 weeks of May and gestation is 50 - 60 days for both species.
References
- ↑ <pubmed>15861401</pubmed>
Search Pubmed: bat development | chiroptera development
| Animal Development: axolotl | bat | cat | chicken | cow | dog | dolphin | echidna | fly | frog | goat | grasshopper | guinea pig | hamster | horse | kangaroo | koala | lizard | medaka | mouse | opossum | pig | platypus | rabbit | rat | salamander | sea squirt | sea urchin | sheep | worm | zebrafish | life cycles | development timetable | development models | K12 |
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, May 18) Embryology Bat Development. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Bat_Development
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G