ANAT2341 Lab 6: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 49: | Line 49: | ||
{{Neural Crest Links}} | {{Neural Crest Links}} | ||
[[Sensory System Development]] | |||
|- | |- | ||
| {{MPT2011cover_citation}} | | {{MPT2011cover_citation}} | ||
| Line 63: | Line 63: | ||
| Other Online Respiratory Resources | | Other Online Respiratory Resources | ||
| | | | ||
|} | |} | ||
{| class="wikitable mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" | {| class="wikitable mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" | ||
Revision as of 08:07, 10 September 2014
Head Development
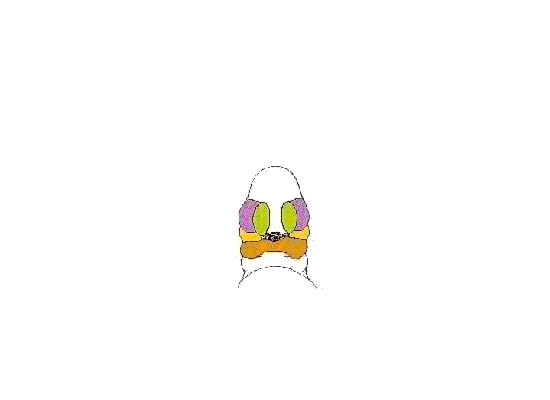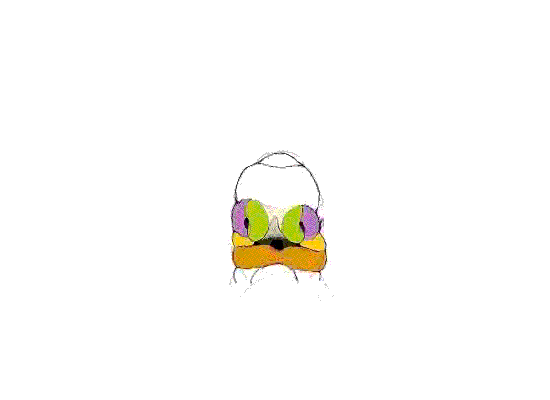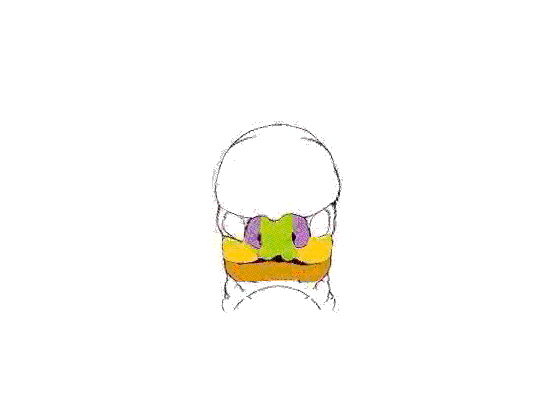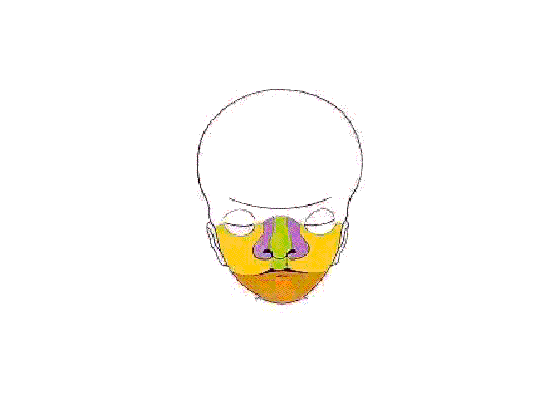
|
Development of the Face
This animation shows a ventral view of development of the human face from approximately week 5 through to neonate. The separate embryonic components that contribute to the face have been colour coded.
The five elements are: 1 Frontonasal Prominence, 2 Maxillary prominences and 2 Mandibular prominences. The stomodeum is the primordial mouth region and a surface central depression lying between the forebrain bulge and the heart bulge. At the floor of the stomodeum indentation is the buccopharyngeal membrane (oral membrane). Note the complex origin of the maxillary region (upper jaw) requiring the fusion of several embryonic elements, abnormalities of this process lead to cleft lip and cleft palate.
|
Aim
To introduce the developmental embryology of the head and face, and their associated abnormalities.
Specific Objectives
- To understand the formation and contribution of the pharyngeal arches to face and neck development.
- To know the main structures derived from components of the pharyngeal arches (groove, pouch and arch connective tissue).
- To briefly understand some abnormalities associated with head development.
Textbooks
| ECHO360 Recording |
|---|
|
Links only work with currently enrolled UNSW students. |
| Lab 6: Introduction | Trilaminar Embryo | Early Embryo | Late Embryo | Fetal | Postnatal | Abnormalities | Online Assessment |
- 2014 Course: Week 2 Lecture 1 Lecture 2 Lab 1 | Week 3 Lecture 3 Lecture 4 Lab 2 | Week 4 Lecture 5 Lecture 6 Lab 3 | Week 5 Lecture 7 Lecture 8 Lab 4 | Week 6 Lecture 9 Lecture 10 Lab 5 | Week 7 Lecture 11 Lecture 12 Lab 6 | Week 8 Lecture 13 Lecture 14 Lab 7 | Week 9 Lecture 15 Lecture 16 Lab 8 | Week 10 Lecture 17 Lecture 18 Lab 9 | Week 11 Lecture 19 Lecture 20 Lab 10 | Week 12 Lecture 21 Lecture 22 Lab 11 | Week 13 Lecture 23 Lecture 24 Lab 12
Student Projects - Group 1 | Group 2 | Group 3 | Group 4 | Group 5 | Group 6 | Group 7 | Group 8 | Moodle