Neural - Spinal Cord Development
Introduction
Neural development is one of the earliest systems to begin and the last to be completed after birth. This development generates the most complex structure within the embryo and the long time period of development means in utero insult during pregnancy may have consequences to development of the nervous system.
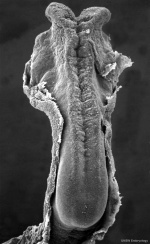
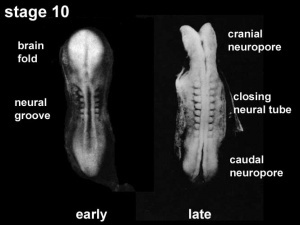
The early central nervous system begins as a simple neural plate that folds to form a groove then tube, open initially at each end. Failure of these opening to close contributes a major class of neural abnormalities (neural tube defects).
Within the neural tube stem cells generate the 2 major classes of cells that make the majority of the nervous system : neurons and glia. Both these classes of cells differentiate into many different types generated with highly specialized functions and shapes. This section covers the establishment of neural populations, the inductive influences of surrounding tissues and the sequential generation of neurons establishing the layered structure seen in the brain and spinal cord.
- Neural development beginnings quite early, therefore also look at notes covering Week 3- neural tube and Week 4-early nervous system.
- Development of the neural crest and sensory systems (hearing/vision/smell) are only introduced in these notes and are covered in other notes sections.
Some Recent Findings
|
Development Overview
Neuralation begins at the trilaminar embryo with formation of the notochord and somites, both of which underly the ectoderm and do not contribute to the nervous system, but are involved with patterning its initial formation. The central portion of the ectoderm then forms the neural plate that folds to form the neural tube, that will eventually form the entire central nervous system.
- Early developmental sequence: Epiblast - Ectoderm - Neural Plate - Neural groove and Neural Crest - Neural Tube and Neural Crest
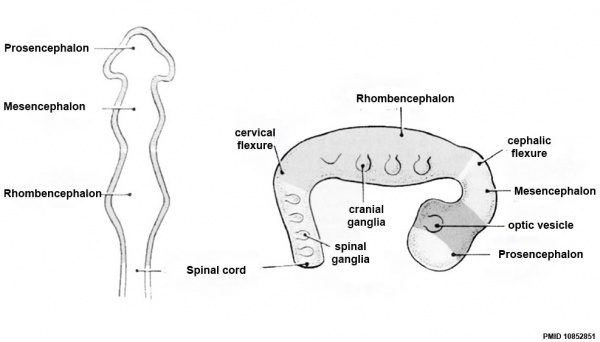
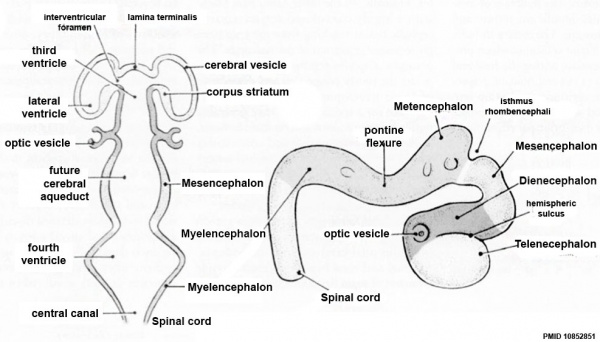
| Neural Tube | Primary Vesicles | Secondary Vesicles | Adult Structures |
|---|---|---|---|
| week 3 | week 4 | week 5 | adult |
| prosencephalon (forebrain) | telencephalon | Rhinencephalon, Amygdala, hippocampus, cerebrum (cortex), hypothalamus, pituitary | Basal Ganglia, lateral ventricles | |
| diencephalon | epithalamus, thalamus, Subthalamus, pineal, posterior commissure, pretectum, third ventricle | ||
| mesencephalon (midbrain) | mesencephalon | tectum, Cerebral peduncle, cerebral aqueduct, pons | |
| rhombencephalon (hindbrain) | metencephalon | cerebellum | |
| myelencephalon | medulla oblongata, isthmus | ||
| spinal cord, pyramidal decussation, central canal | |||
Early Brain Vesicles
Primary Vesicles
Secondary Vesicles
Embryonic Development
Week 8
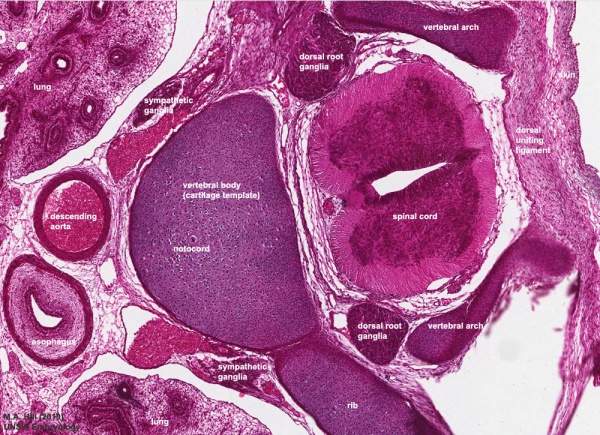
Vertebra and Spinal cord (Carnegie Stage 22)
Plexus Development
The spinal nerves initially leave the spinal cord at each individual segmental levels. At various levels they then form an intersecting network of nerves, a plexus, from which mixed segmental nerves emerge.
Cervical Plexus
Brachial Plexus
- Search PubMed: brachial plexus embryology
Lumbar Plexus
- Search PubMed: lumbar plexus embryology
Sacral Plexus
References
Reviews
<pubmed>19206138</pubmed> <pubmed>19681160</pubmed> <pubmed>19651305</pubmed> <pubmed>18621990</pubmed> <pubmed>18494249</pubmed> <pubmed>16971596</pubmed> <pubmed>17032846</pubmed> <pubmed>15806586</pubmed> <pubmed>15738958</pubmed>
Articles
<pubmed>18230116</pubmed>
Books
- Bayer S.A and Altman J. The Spinal Cord from Gestational Week 4 to the 4th Postnatal Month CRC Press 2002 Print ISBN: 978-0-8493-1420-9 eBook ISBN: 978-1-4200-4018-0 http://www.crcnetbase.com/doi/book/10.1201/9781420040180
Search PubMed
November 2010 search "Spinal Cord Embryology" All (7631) Review (641) Free Full Text (1562)
Search Pubmed: Spinal Cord Embryology | Spinal Cord Development
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, June 2) Embryology Neural - Spinal Cord Development. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Neural_-_Spinal_Cord_Development
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G