File:BMP superfamily canonical signalling.jpg
Original file (946 × 752 pixels, file size: 134 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
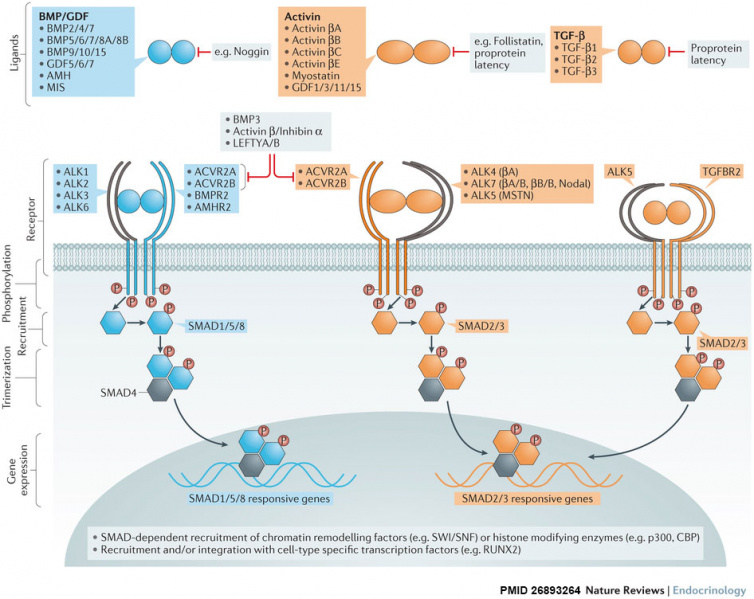
BMP Superfamily Canonical Signalling
| Over 30 bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) superfamily ligands have been discovered in humans. Most are secreted as mature disulfide-linked dimers, with the exception of TGF-β1, TGF-β2 and TGF-β3, which can be secreted in a latent form and require proteolytic activation. BMPs signal through a multimeric cell surface complex consisting of two type I receptors and two type II receptors.
Activated type I receptors recruit and phosphorylate pathway-specific R-SMADs (SMAD1, SMAD5 and SMAD8 (blue pathway), and SMAD2 and SMAD3 (orange pathway)), which can form trimers with SMAD4 and translocate to the nucleus. SMADs have intrinsic DNA-binding activity and are able to regulate gene expression by recruitment of chromatin-remodelling machinery and integration with tissue-specific transcription factors. SMAD8 is also known as SMAD9. The pathway can be antagonized by many mechanisms including neutralization of ligands by secreted traps such as noggin or follistatin, secretion of latent ligands bound to their propeptides, or via titration of receptors by nonsignalling ligands such as BMP3, activin β/inhibin α dimers or LEFTY monomers. |
|
| Factor Links: AMH | hCG | BMP | sonic hedgehog | bHLH | HOX | FGF | FOX | Hippo | LIM | Nanog | NGF | Nodal | Notch | PAX | retinoic acid | SIX | Slit2/Robo1 | SOX | TBX | TGF-beta | VEGF | WNT | Category:Molecular |
Reference
<pubmed>26893264</pubmed>
Copyright
Your order details and publisher terms and conditions are available by clicking the link below: http://s100.copyright.com/CustomerAdmin/PLF.jsp?ref=33184fc8-b8d8-4793-8362-2b8e22fcb6c4
Order Details Licensee: Mark A Hill License Date: Sep 11, 2016 License Number: 3946190772930 Publication: Nature Reviews Endocrinology Title: BMP signalling in skeletal development, disease and repair Type Of Use: post on a website
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 26) Embryology BMP superfamily canonical signalling.jpg. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/File:BMP_superfamily_canonical_signalling.jpg
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 10:21, 12 September 2016 |  | 946 × 752 (134 KB) | Z8600021 (talk | contribs) | ==BMP Superfamily Canonical Signalling== Over 30 bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) superfamily ligands have been discovered in humans. Most are secreted as mature disulfide-linked dimers, with the exception of TGF-β1, TGF-β2 and TGF-β3, which can be... |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following page uses this file: