Computed Tomography
| Embryology - 27 Apr 2024 |
|---|
| Google Translate - select your language from the list shown below (this will open a new external page) |
|
العربية | català | 中文 | 中國傳統的 | français | Deutsche | עִברִית | हिंदी | bahasa Indonesia | italiano | 日本語 | 한국어 | မြန်မာ | Pilipino | Polskie | português | ਪੰਜਾਬੀ ਦੇ | Română | русский | Español | Swahili | Svensk | ไทย | Türkçe | اردو | ייִדיש | Tiếng Việt These external translations are automated and may not be accurate. (More? About Translations) |
Introduction
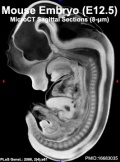
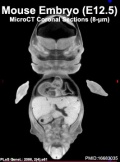
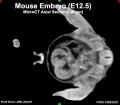
In embryology, the technique of micro-CT (μCT) has recently begun to become relevant in animal models and used for analysis of normal development features and those seen in genetically modified animal models, such as the mouse (More? Mouse Development).
Computed Tomography or computed axial tomography (CAT or CT scan) began in 1970's using x-ray and a computer to produce images either as individual slices or reconstructed to give three dimensional (3D) views of specific anatomical regions or structures.
Other potential developmental research imaging techniques include: positron emission tomography (PET), single photon emission computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, computed tomography, optical bioluminescence, fluorescence and high frequency ultrasound.
- Links: Movies - Computed Tomography | Abnormal Development - Radiation | Category:Computed Tomography
Some Recent Findings
|
| More recent papers |
|---|
|
This table allows an automated computer search of the external PubMed database using the listed "Search term" text link.
More? References | Discussion Page | Journal Searches | 2019 References | 2020 References Search term: Embryo Computed Tomography <pubmed limit=5>Embryo Computed Tomography</pubmed> |
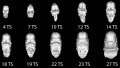
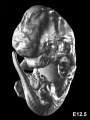
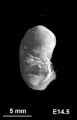
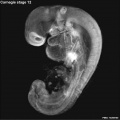
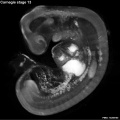
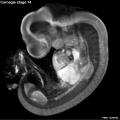
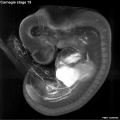
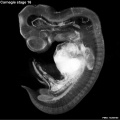
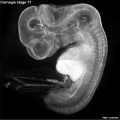
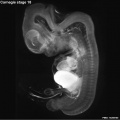
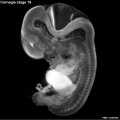
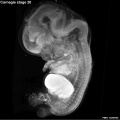
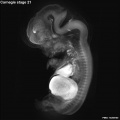
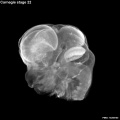
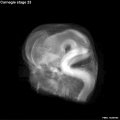
Early Mouse Development MicroCT
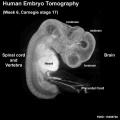
Human Embryo
Week 6
|
| Stage 17 Embryo |
| Page | Play |
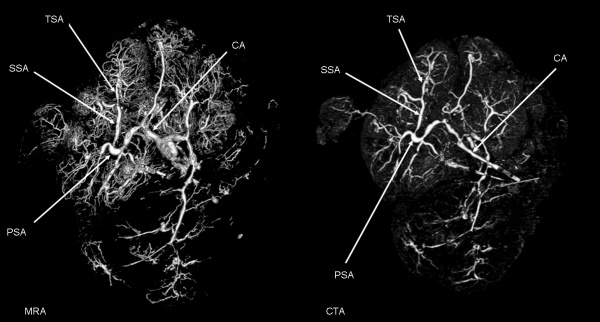
Human Placenta
Right image shows computed tomography angiography (CTA) of the term human placenta viewed from the fetal side.[4]
Legend
- CA - chorionic artery
- PSA - primary stem artery
- SSA - secondary stem artery
- TSA - tertiary stem artery
Newborn
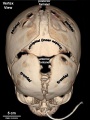
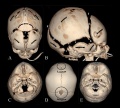
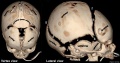
Skull
- Links: Skull Development
Adult
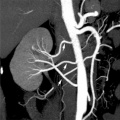
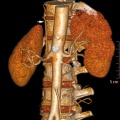
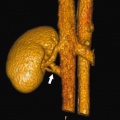
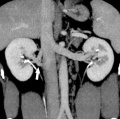
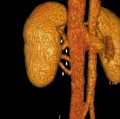
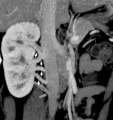
Renal
Vascular Abnormalities[5]
Renal Vascular Anomalies: Multiple renal arteries | Accessory renal artery | Supernumerary right renal vein 1 | Supernumerary right renal vein 1 | Multiple right renal veins 2 | Multiple right renal veins 2 | Cardiovascular System Development
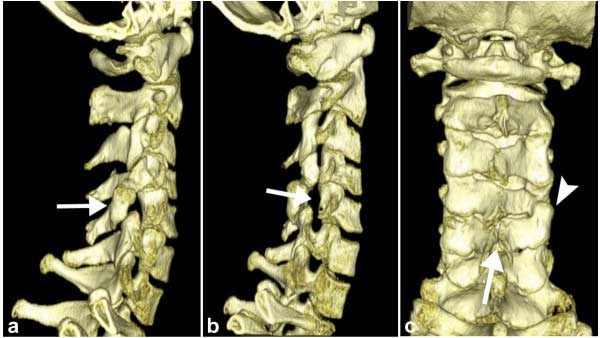
Axial Skeleton
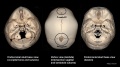
Absent Cervical Spine Pedicle (volume render CT)[6]
| a arrow | b arrow | c arrow |
|---|---|---|
| Lateral view VRTshows the dorsally displaced right articular pillar of C5. | Abnormal enlarged right intervertebral foramen of C4-5. which is a consequence of the absent cervical pedicle is displayed on an oblique view VRT image. | Spina bifida occulta at the same level as well as a reversed facet-joint on the right (arrowhead in c) are well depicted on a dorsal view VRT images (c). |
Movies
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
- Links: Movies - Computed Tomography
Optical Coherence Tomography
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) is a non-invasive imaging technique generating high resolution (axial resolution 5–7 μm) cross-sectional images. The techniques has been used clinically for diagnosis and management in:
- ophthalmology (spectral-domain OCT) for retinal diseases.
- dermatology for evaluation of skin lesions, skin changes, parasitic infestations.
Radiation Exposure
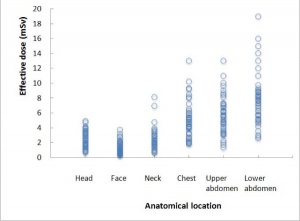
Computed tomography is a source of medical X-ray radiation exposure to the general population. The risk to an individual patient on the basis of dose levels of developing a malignant tumour due to CT is low and acceptable compared to the substantial benefit. There is though a large range/variation in radiation exposure between individual institutions and equipment settings.
Total radiology collective effective dose
- UK (2005-2006) approximately 60% from CT.
- Germany (2000-2005) for cancer patients from all X-ray procedures was approximately 82%.
- USA about 67%
References
- ↑ <pubmed>20163731</pubmed>| BMC Developmental Biology
- ↑ <pubmed>20190279</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>16683035</pubmed>| PLoS Genetics
- ↑ <pubmed>20226038</pubmed>| BMC Physiol.
- ↑ <pubmed>20461189</pubmed>| PMC2864862 | Korean J Radiol
- ↑ <pubmed>21062465</pubmed>| BMC Med Imaging.
- ↑ <pubmed>21044293</pubmed>| BMC Med Imaging.
Books
Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) NBK5330 | PMID:20641179
Search Pubmed
Search Pubmed: Embryo Computed Tomography | Computed Tomography | Micro-computed tomography apparatus
External Links
External Links Notice - The dynamic nature of the internet may mean that some of these listed links may no longer function. If the link no longer works search the web with the link text or name. Links to any external commercial sites are provided for information purposes only and should never be considered an endorsement. UNSW Embryology is provided as an educational resource with no clinical information or commercial affiliation.
- University of Calgary 3D Morphometrics Lab
- Duke Center for In Vivo Microscopy A 4D Atlas and Morphologic Database
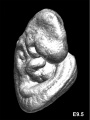
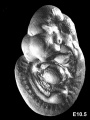
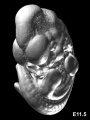
- Normal C57BL/6 mouse embryos from embryonic day E10.5 to E19.5
- Normal C57BL/6 mouse neonates from post-natal day 0 to 32
- Mutant mouse embryos with cardiac septation defects (conditional ablation of the Smoothened receptor gene, Mef2C-AHF-Cre;Smoflox/- mutants)
- Drishti and Drishti-2 stands for vision or insight in Sanskrit, an Indian language. Ajay Limaye
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 27) Embryology Computed Tomography. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Computed_Tomography
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G