Gastrointestinal Tract - Pancreas Development: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
{{Template:Glossary}} | {{Template:Glossary}} | ||
{{Template:Footer}} | {{Template:Footer}} | ||
[[Category:Pancreas]] | |||
Revision as of 14:47, 25 August 2010
Introduction
This section of notes gives an overview of how the pancreas develops. At the foregut/midgut junction the septum transversum generates 2 pancreatic buds (dorsal and ventral endoderm) which will fuse to form the pancreas. The dorsal bud arises first and generates most of the pancreas. The ventral bud arises beside the bile duct and forms only part of the head and uncinate process of the pancreas.
See also Endocrine - Pancreas Development
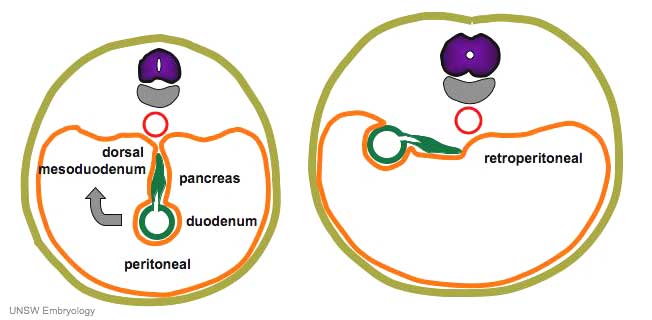
Duodenum/Pancreas Rotation
|
After the stomach the initial portion of the gastrointestinal tract tube is the duodenum which initially lies in the midline within the peritoneal cavity.
This region, along with the attached pancreas, undergoes rotation to become a retroperitoneal structure. This diagram shows the rotation with spinal cord at the top, vertebral body then dorsal aorta then pertioneal wall and cavity. |
References
Search Bookshelf Pancreas Development
Search Pubmed
July 2010
Search Pubmed Now: Pancreas Development
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, May 4) Embryology Gastrointestinal Tract - Pancreas Development. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Gastrointestinal_Tract_-_Pancreas_Development
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G