Embryology History - John Gurdon
| Embryology - 27 Apr 2024 |
|---|
| Google Translate - select your language from the list shown below (this will open a new external page) |
|
العربية | català | 中文 | 中國傳統的 | français | Deutsche | עִברִית | हिंदी | bahasa Indonesia | italiano | 日本語 | 한국어 | မြန်မာ | Pilipino | Polskie | português | ਪੰਜਾਬੀ ਦੇ | Română | русский | Español | Swahili | Svensk | ไทย | Türkçe | اردو | ייִדיש | Tiếng Việt These external translations are automated and may not be accurate. (More? About Translations) |
Introduction
Sir John Gurdon (born 1933) in 1962 used nuclear transplantation and cloning to show that the nucleus of a differentiated somatic cell retains the totipotency necessary to form a whole organism.
- 2003 Interview - 2003 Current Biology
- 2009 Interview - "The birth of cloning"[1]
- Links: Frog Development | Stem Cells | Shinya Yamanaka
Some Recent Findings
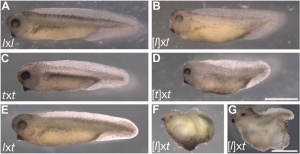
|
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2012 was awarded jointly to Sir John B. Gurdon and Shinya Yamanaka
|
Recent References | References
Research History
- 2012 - The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2012 awarded jointly with Shinya Yamanaka "for the discovery that mature cells can be reprogrammed to become pluripotent".
Key Papers
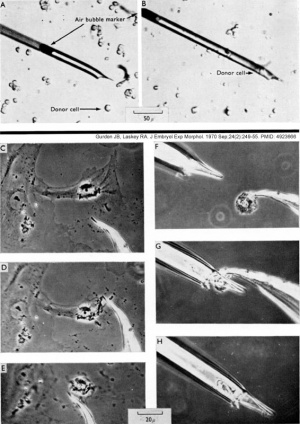
Methods of transplanting nuclei from single cultured cells to unfertilized frogs' eggs[4]
- "Two methods of transplanting single nuclei from monolayers of cultured cells to unfertilized eggs of Xenopus laevis are described, illustrated, and tested.
The detached-cell method is simpler and quicker to operate and is suitable for homogeneous populations of cells which are easily removed from the substrate on which they are growing. The other, attached-cell, method is technically more elaborate, but is applicable to cells whose properties can be individually determined under the phase-contrast microscope and to cells which are not readily dissociated from other cells or from their substrate."
Genetic content of adult somatic cells tested by nuclear transplantation from cultured cells[5]
- "It has yet to be proved that somatic cells of an adult animal possess genes other than those necessary for their own growth and differentiation. A particularly stringent test of the genetic content of the nucleus of a somatic cell is provided by transplanting it to an enucleated egg. The development of the egg tests the capacity of the genes in the transplanted nucleus to elicit normal early development and differentiation. Although this method has been applied to certain cells of embryos, larvae, and newly metamorphosed froglets, it has not been possible, until now, to transfer nuclei successfully from the cells of normal adult animals."
Historic Embryologists
| Embryologists: William Hunter | Wilhelm Roux | Caspar Wolff | Wilhelm His | Oscar Hertwig | Julius Kollmann | Hans Spemann | Francis Balfour | Charles Minot | Ambrosius Hubrecht | Charles Bardeen | Franz Keibel | Franklin Mall | Florence Sabin | George Streeter | George Corner | James Hill | Jan Florian | Thomas Bryce | Thomas Morgan | Ernest Frazer | Francisco Orts-Llorca | José Doménech Mateu | Frederic Lewis | Arthur Meyer | Robert Meyer | Erich Blechschmidt | Klaus Hinrichsen | Hideo Nishimura | Arthur Hertig | John Rock | Viktor Hamburger | Mary Lyon | Nicole Le Douarin | Robert Winston | Fabiola Müller | Ronan O'Rahilly | Robert Edwards | John Gurdon | Shinya Yamanaka | Embryology History | Category:People | ||
|
References
Reviews
<pubmed>16134025</pubmed> <pubmed>15824436</pubmed> <pubmed></pubmed>
Articles
<pubmed></pubmed> <pubmed>10761853</pubmed> <pubmed>3308408</pubmed> <pubmed>5531072</pubmed> <pubmed>5967799</pubmed> <pubmed>13903027</pubmed> <pubmed>13726553</pubmed>
Search PubMed
Search PubMed Now: Gurdon+J
External Links
External Links Notice - The dynamic nature of the internet may mean that some of these listed links may no longer function. If the link no longer works search the web with the link text or name. Links to any external commercial sites are provided for information purposes only and should never be considered an endorsement. UNSW Embryology is provided as an educational resource with no clinical information or commercial affiliation.
- Wellcome Trust/Cancer Research UK Gurdon Institute is part of Cambridge University with funding from the listed two main sponsors, and other sources, supports research into the complementary areas of Cancer and Developmental Biology.
- John Gurdon - Research Lab
- Berkeley interview March 16, 2006 | YouTube
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 27) Embryology Embryology History - John Gurdon. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Embryology_History_-_John_Gurdon
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G

