Anatomy and Embryology Goettingen - 2013 Seminar: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
|||
| (46 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
=Online Embryology for Medicine and Science= | =Online Embryology for Medicine and Science= | ||
[[Image:Mark Hill.jpg|thumb|Dr Mark Hill]] | [[Image:Mark Hill.jpg|thumb|Dr Mark Hill<br>School of Medical Sciences, [http://goo.gl/maps/ZiCNF The University of NSW], [http://goo.gl/maps/Pzl8U Australia].]] | ||
''6 December 2013'' [http://www.embryologie.uni-goettingen.de Dept. of Anatomy and Embryology, University of Goettingen] [http://translate.google.com/translate?sl=auto&tl=de&js=n&prev=_t&hl=en&ie=UTF-8&u=http%3A%2F%2Fembryology.med.unsw.edu.au%2Fembryology%2Findex.php%3Ftitle%3DAnatomy_and_Embryology_Goettingen_-_2013_Seminar&act=url Translate page - German] | ''6 December 2013'' [http://www.embryologie.uni-goettingen.de Dept. of Anatomy and Embryology, University of Goettingen] [http://translate.google.com/translate?sl=auto&tl=de&js=n&prev=_t&hl=en&ie=UTF-8&u=http%3A%2F%2Fembryology.med.unsw.edu.au%2Fembryology%2Findex.php%3Ftitle%3DAnatomy_and_Embryology_Goettingen_-_2013_Seminar&act=url Translate page - German] | ||
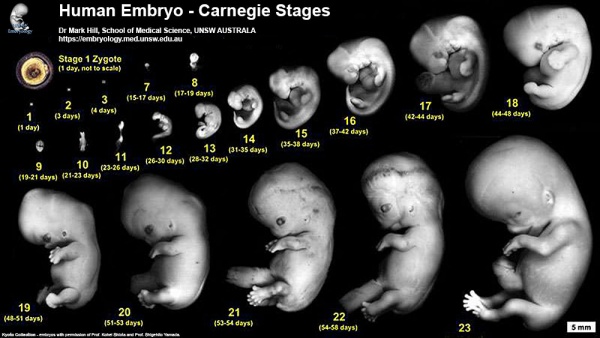
[[File:Human_Carnegie_stage_1-23.jpg|600px]] | |||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
This presentation will describe my experiences in developing online embryology teaching for medical (large group) and science (small group) student groups. | |||
{| | {| | ||
| [[File:Medicine large computer lab.jpg|400px]] | | [[File:Medicine large computer lab.jpg|400px]] | ||
| Line 12: | Line 14: | ||
| Science (small computer lab) | | Science (small computer lab) | ||
|} | |} | ||
{| border='0px' | |||
|- | |||
| width=520px| | |||
<html5media height="450" width="500">File:Human_blastocyst_day_3-6.mp4</html5media> | |||
{| class="wikitable mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" | |||
! About this Movie | |||
|- | |||
| [[Blastocyst Day 3-6 Movie]] shows ''in vitro'' development of a human morula to blastocyst stage occurring between day 3 and day 6 post-fertilisation.<ref><pubmed>20890283</pubmed></ref> (More? [[Movies]]) | |||
<references/> | |||
|} | |||
|} | |||
==Embryology Online== | |||
[[File:Embryology_DVD_2007.jpg|thumb|'''Embryology Offline''' - web material released also as CD (1997) and then DVD (2007) format.]] | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Microfiche_reader.jpg|pre-1997 | |||
File:Embryology website 1997.jpg|1997 | |||
File:Embryology website 2001.jpg|2001 | |||
File:Embryology website 2004.jpg|2004 | |||
File:Embryology website 2007.jpg|2007 | |||
Front-page-image.jpg|[[Main_Page|2009 - Wiki Format]] | |||
</gallery> | |||
{| class="wikitable mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" | |||
! Technology Timeline | |||
|- | |||
| colspan="2"|[[File:Mark_Hill.jpg|50px]] | |||
The changing technology environment we have experienced in the last 50 years, and more recently in the last 20 "internet years". | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
* '''1961''' - Microfiche - miniaturise data, images and text. | |||
* '''1962''' - Slide carousel projector - transport and display content easily. | |||
* '''1960s''' - Overhead projectors - prepared and flexible in-class. | |||
* '''1977''' - Apple computers. | |||
* '''1981''' - IBM computers. | |||
* '''1982''' - Microsoft MS-DOS. | |||
* '''1990''' - Powerpoint - electronic slides. | |||
* '''1991''' - Quicktime - multimedia platform for images and animations. | |||
* '''1993''' - [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mosaic_(web_browser) Mosaic] first web browser. | |||
* '''1994''' - Netscape Navigator web browser. | |||
* '''1995''' - Internet Explorer web browser. | |||
* '''1996''' - Flash - multimedia platform for images and animations. | |||
| | |||
* '''1997''' - Embryology site first online. | |||
* '''1998''' - Google internet search. | |||
* '''1998''' - [http://www.blackboard.com/About-Bb/Our-Story.aspx Blackboard] course management system. | |||
* '''2001''' - [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia Wikipedia] online encyclopaedia running on [http://www.mediawiki.org/wiki/MediaWiki Mediawiki]. | |||
* '''2002''' - [http://moodle.org/ Moodle] course management system. | |||
* '''2004''' - [https://www.facebook.com/ Facebook] social networking service. | |||
* '''2004''' - Embryology website reformatted as 3 column webpages. | |||
* '''2006''' - [https://twitter.com Twitter] microblogging service. | |||
* '''2009''' - Embryology site transferred to new wiki format. | |||
* '''2010''' - [http://itunes.apple.com/au/app/ibooks/id364709193?mt=8 iBooks] e-book application for iPads. | |||
* '''2012''' - ?? | |||
|} | |||
===New Wiki Format 2009=== | |||
* '''familiar''' structure and layout. (the Wiki format) | |||
* '''easy''' to print and search. ([http://php.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php?title=UNSW_Learning_and_Teaching_Seminar_2012&printable=yes print this current page]) | |||
* '''resolved''' student navigation issues. (every page has the same navigation and access to student pages) | |||
* '''contributions''' by researchers staff and students. ([[Contributors|Researcher Contributions]]) | |||
* '''current research''' easily added and used by students. ([[Blastocyst Day 3-6 Movie]]) | |||
{| class="wikitable collapsible collapsed" | |||
! Why Wikis? | |||
|- | |||
| [[File:Mark_Hill.jpg|50px]] | |||
The Software - Wikipedia had been around for a few years and many students were commonly using it initially as a dictionary rather than encyclopaedia. [http://www.mediawiki.org/ MediaWiki] is the database software which runs this application on the web and is separate from the content hosted in Wikipedia. | |||
The Support - [http://www.mediawiki.org/ MediaWiki] is freely available, stable, regularly updated, and has a large group of developers maintaining and making many useful applications ([http://www.mediawiki.org/wiki/Category:Extensions_by_category extensions]) within this software framework. | |||
The Interaction - The format can be used interactively by teacher and student, both can construct, distribute and share knowledge. This can be done easily anytime and anywhere with an internet connection and editing can be restricted to only those designated users and hierarchically within those users. Importantly, an extension allows users access through the familiar UNSW Zpass system. | |||
Visibility - You need to see what is being done! The embryology educational material has since its early development been on the internet and available to all. Learning management systems (LMS) are excellent for what they do, manage courses and students. My experience is that students don't generally like LMS and use it only because they have to. Most are LMS are commercial packages ($$) and their content is generally hidden (which can be important for security/copyright etc) and not easily shared. | |||
|} | |||
{| | |||
| [[File:Php-most used browsers May-Oct 2013.jpg|400px]] | |||
| [[File:Php-most used operating systems May-Oct 2013.jpg|400px]] | |||
|- | |||
| Browser used | |||
| Browser operating systems | |||
|} | |||
==Teaching Contact Hours== | |||
{| | |||
| [[File:Anatomy teaching USA graph.jpg|600px]] | |||
Trends in anatomy disciplines contact teaching hours based on data from USA survey.<ref><pubmed>19890982</pubmed></ref> | |||
| {{Human development movie 1}} | |||
|} | |||
{| class="wikitable collapsible collapsed" | |||
! About this graph | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
* Online survey were constructed to gather basic information about gross anatomy, microscopic anatomy, neuroscience/neuroanatomy, and embryology courses. | |||
* 2009 total of 130 allopathic and 25 osteopathic medical schools in USA. | |||
* Number of responses (Gross anatomy 65, Microscopic anatomy 45, Neuroscience/Neuroanatomy 31, Embryology 43) | |||
'''Reference''' | |||
<references /> | |||
'''University of New South Embryology Contact hours''' | |||
* Medicine - (lecture and practicals, including foundations and phase 2) is '''24 hours'''. | |||
* Science - Lectures 20, Practicals 48. | |||
|} | |||
{| class="wikitable collapsible collapsed" | |||
! New Embryology Topics | |||
|- | |||
| Less contact time, but a growing list of new clinically relevant topics. | |||
* [[Assisted Reproductive Technology]] (In vitro fertilization) | |||
* [[Stem Cells]] | |||
* [[Molecular Development]] (genetics, epigenetics, inheritance) | |||
* [[Prenatal Diagnosis]] (genetic, ultrasound, MRI, fetal cells in maternal) | |||
* [[Fetal Surgery]] (prenatal medicine) | |||
|} | |||
==Medicine Large Class== | |||
{| | |||
| [[File:Medicine large computer lab.jpg|400px|]] | |||
| [[File:BGDsmall.jpg]] | |||
* Both '''lectures''' and '''laboratories''' in Medicine and Science can be prepared and presented online. ([[BGDA_Lecture_-_Development_of_the_Embryo/Fetus_1|Lecture]], [[BGDA_Practical_-_Fertilization_to_Implantation|Practical]]) | |||
* '''Online textbooks''' are directly linked within the classes. ([[Embryology_Textbooks_-_UNSW|UNSW links]]) | |||
* Additional '''general notes''' are available for students to use as topic background. ([[Human_System_Development|2012]]) | |||
* An extensive '''glossary of terms''' is provided to aid understanding of terminology. ([[Glossary]], [[M#mesoderm|mesoderm]]) | |||
** ''In development everything changes, even the names of structures!'' | |||
* Current related '''clinical and research data''', movies and findings can be provided to show relevance of topics. ([[Movies#Animal_Embryo|Research movies]]) | |||
* '''Quizzes''' available to test student knowledge. ([[Foundations Quiz]]) | |||
* Content can also be modified and used for external education purposes. (Postgraduate Medicine - [[Maternal-Fetal Medicine Trainees - Renal]], K12 - [[Brain Awareness Week 2012]]) | |||
|- | |||
| [[File:Med_computer_audit_June_2012.jpg|400px]] | |||
| [[File:Online_textbook_access_2011.jpg|400px]] | |||
|- | |||
| Medicine practicals computer use (2012) | |||
| Online textbook access (2011) | |||
|} | |||
==Medicine - Independent Learning Projects== | |||
[[File:Cardiac_Embryology_ILP_Watermark.jpg|thumb|link=Cardiac_Embryology|[[Cardiac Embryology]]]] | |||
The Independent Learning Project (ILP) is intended to provide UNSW medical students with a period of in-depth study that engenders an approach to medicine that is constantly questioning and self-critical. ([http://www.med.unsw.edu.au/medweb.nsf/page/Independent+Learning+Project About ILP]) | |||
* '''2006''' - [[ILP2006_-_Carnegie_stage_Animations|Carnegie Stage Embryo Animations]] educational project. | |||
{| class="wikitable mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" | |||
! 2006 ILP Movies | |||
|- | |||
| [[File:Mark_Hill.jpg|50px]] | |||
Shown below are the animations generated from the serial sections of a Human embryo ([[week 8]], [[Carnegie stage 22]]). Click the quicktime or Flash lingo to see the rotating animations. Note Flash animations do not play on iPads. | |||
|- | |||
| {{Movie header}} | |||
{{Stage22movie3D}} | |||
|} | |||
* '''2009''' - [[Cardiac_Embryology|Cardiac Embryology]] educational project. ([http://php.med.unsw.edu.au/cellbiology/index.php?title=ILP_z3212774 Project Background], [http://php.med.unsw.edu.au/cellbiology/index.php?title=Talk:ILP_z3212774 Project Discussion]) | |||
{| class="wikitable mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" | |||
! 2009 ILP Tutorial | |||
|- | |||
| |[[File:Mark_Hill.jpg|50px]] Self-directed Learning. | |||
This project was designed to allow students to work through heart development online using modules designed to teach at 3 levels of understanding, using the "traffic light" approach, (green is easiest, red is hardest). Each module through the same timeline and firstly identifies the learning objectives, then how long it will take to complete the module. | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
{{Cardiac_modules}} | |||
This website is an educational resource designed to teach human cardiac embryology and is a Medicine ILP project carried out by Phoebe Norville. Heart development represents an important area of both embryological and clinical studies, predominantly due to the high incidence of congenital heart disease in the community. Therefore this website aims to teach cardiac embryology to students of all ages with varying degrees of knowledge in the area. The module contains three different levels: | |||
*[[Basic_Cardiac_Embryology|Basic]] - begin here if you are new to heart embryology (high school level) | |||
*[[Intermediate_Cardiac_Embryology|Intermediate]] - begin here if you have some background in heart embryology (university level) | |||
*[[Advanced_Cardiac_Embryology|Advanced]] - begin here after you have completed the earlier levels and have a good background in heart embryology (university level) | |||
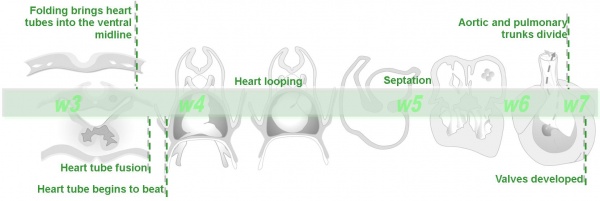
'''Basic Heart Development Timeline''' (weeks of development are shown ''w3'' to ''w7'') | |||
[[File:Basic_Heart_Development_Timeline.jpg|600px]] | |||
|} | |||
==Science Small Class== | |||
{| | |||
| [[File:Medicine_computer_lab.jpg|400px]] | |||
| | |||
*Science '''lectures''' and '''laboratories''' in Science can be prepared and presented online. ([[BGDA_Lecture_-_Development_of_the_Embryo/Fetus_1|Lecture]], [[BGDA_Practical_-_Fertilization_to_Implantation|Practical]]) | |||
* '''Online textbooks''' are directly linked within the classes. ([[Embryology_Textbooks_-_UNSW|UNSW links]]) | |||
* Additional '''general notes''' are available for students to use as topic background. ([[Human_System_Development|2012]]) | |||
* [[Glossary]] | |||
* Individual Assessments | |||
** Each week online based upon the practical class they have just completed. | |||
* Group Projects | |||
** Earlier group projects in the Science courses had been preparing a poster and a final presentation to the class. | |||
** The online projects also require presentations during their preparation and include a peer assessment process. | |||
|} | |||
{| class="wikitable mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" | |||
! Project Pedagogy | |||
|- | |||
| colspan="2"|[[File:Mark_Hill.jpg|50px]] | |||
These projects extend far beyond the original "research poster concept". It requires ongoing participation from both the teacher and the student, if you are not prepared to have an ongoing contribution, do not even consider setting this type of assessment. | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
'''Students''' | |||
* Groups work independently throughout the semester on a specific topic the group has selected within the general topic set by the teacher. | |||
* Groups are assigned randomly by the teacher, do not want "friends" and "non-friends" groups. | |||
* Online work consists of the "project page" and the "discussion page" where student online interaction occurs. | |||
* Face-to-face time is allowed each week in the last 10 minutes of practical classes. | |||
* Projects are also presented to the class at a "work in progress" phase. | |||
* Each student carries out a "online written assessment" of all other projects late in the semester, when groups are near completion. | |||
* Groups then collate and use these "online written assessments" to edit their own project. | |||
| valign=top| | |||
'''Teacher''' | |||
* Designs specific assessment criteria. | |||
* Designs the general topic and allocates groups. | |||
* Provides handouts and brief tutorials each week in practical class time on: basic editing, copyright/plagiarism , reference sources and referencing and uploading images. | |||
* Provides regular in-class advice, online comments and email support to queries and feedback. | |||
* Analyses project "edit history" and "discussion" comments to identify individual students not contributing to the project. | |||
* Analyses the final submitted project providing specific online feedback. | |||
|} | |||
===Science Group Projects=== | |||
{| class="wikitable mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" | |||
! Project Topics | |||
|- | |||
| colspan="2"|[[File:Mark_Hill.jpg|50px]] How do you select a topic? | |||
These project topics supplement content covered in lectures and practicals. Student can apply their understanding of concepts in development to topics that show relevance of embryology research to both basic sciences and clinical medicine. | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
* Animal Models - Have been use historically to understand human development. More recently they have been used to understand human disease mechanisms and the potential application of stem cells. The students learn to identify the common features of development in different species as well as the differences between species. | |||
* Diagnostic Techniques - Applies an understanding of the tools available to understand abnormal development. Focussing on how the tools work, what they measure and what they show. The students learn to firstly identify features of normal development, before they can understand how (and why) abnormal development can be detected. | |||
* Abnormalities - These are a range of (human) developmental abnormalities with a range of developmental origins and affecting different systems. An understanding of normal development, from the course, is required to interpret specific abnormalities. The students learn to identify the main origins of abnormalities (genetic, environmental and unknown), the history of our understanding and how research has progressed in the topic area. | |||
* Sensory Development - Complex developmental systems with different embryonic origins and system interactions. Not enough time in lectures or practicals to cover all systems in detail. | |||
|} | |||
* '''2009''' - Animal Models: [[2009_Group_Project_1|Rabbit]] | [[2009_Group_Project_2|Fly]] | [[2009_Group_Project_3|Zebrafish]] | [[2009_Group_Project_4|Mouse]] | [[2009_Group_Project_5|Project 5 - Frog]] | [[Animal_Development|Related page - Animal Development]] | |||
* '''2010''' - Diagnostic Techniques: [[2010_Group_Project_1|Ultrasound]] | [[2010_Group_Project_2|Chorionic villus sampling]] | [[2010_Group_Project_3|Amniocentesis]] | [[2010_Group_Project_4|Percutaneous Umbilical Cord Blood Sampling]] | [[2010_Group_Project_5|Fetal Fibronectin]] | [[2010_Group_Project_6|Maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein]] | [[Prenatal_Diagnosis|Related page - Prenatal Diagnosis]] | |||
* '''2011''' - Abnormalities: [[2011_Group_Project_1|Turner Syndrome]] | [[2011_Group_Project_2|DiGeorge Syndrome]] | [[2011_Group_Project_3|Klinefelter's Syndrome]] | [[2011_Group_Project_4|Huntington's Disease]] | [[2011_Group_Project_5|Fragile X Syndrome]] | [[2011_Group_Project_6|Tetralogy of Fallot]] | [[2011_Group_Project_7|Angelman Syndrome]] | [[2011_Group_Project_8|Friedreich's Ataxia]] | [[2011_Group_Project_9|Williams-Beuren Syndrome]] | [[2011_Group_Project_10|Duchenne Muscular Dystrolphy]] | [[2011_Group_Project_11|Cleft Palate and Lip]] | [[ANAT2341_2011_Students#Student_Group_Projects|Student Group Projects]] | |||
* '''2012''' - Sensory Development: [[2012_Group_Project_1|Vision]] | [[2012_Group_Project_2|Somatosensory]] | [[2012_Group_Project_3|Taste]] | [[2012_Group_Project_4|Olfaction]] | [[2012_Group_Project_5|Abnormal Vision]] | [[2012_Group_Project_6|Hearing]] | |||
====Online Project support==== | |||
At the beginning of the course students are led through simple tutorial exercises to become familiar with the process. | |||
* establishing the assessment criteria. ([[2011_Lab_2_-_Group_Project|2011]]) | |||
* text editing and formatting. ([[Help:Editing_Basics|Editing Basics]], [[Help:Reference_Tutorial|formatting references]]) | |||
* identifying research sources and their reuse. ([[Help:Image_Tutorial|Images]]| [[Help:Copyright_Tutorial|Copyright]]) | |||
* uploading and images, identifying sources and copyright information. ([[2011_Lab_3_-_Group_Project|Tutorial]] | [[Test_Student_2011|in-class exercise]]) | |||
{| class="wikitable mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" | |||
! Student Contributions | |||
|- | |||
| colspan="2"|[[File:Mark_Hill.jpg|50px]] The assessment criteria requires "an ongoing contribution", how do you identify this? | |||
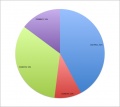
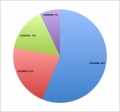
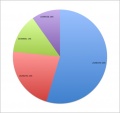
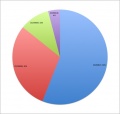
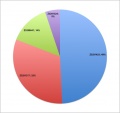
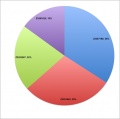
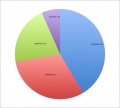
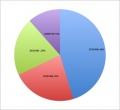
All pages track all edits made. Using this "edit history" log student contributions can be logged and quantified. A quick audit of this log (simply pasted into a spreadsheet to sort, count and graph) does not identify directly what has been edited, though this can also be done both by see and comparison of content added/removed. It does identify the "low contributors" to both the project and discussion pages. An intergroup comparison can also identify whether some groups are having problems with the work. | |||
An edit audit carried out early enough in the project process, allows both teacher and student to identify this issue. | |||
An equal edit contribution would be shown by an even distribution of slices in the pie diagrams. | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
'''2011 Embryology Projects''' Student Edits | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:2011_Project_Group_1_edits.jpg|Group 1 | |||
File:2011_Project_Group_2_edits.jpg|Group 2 | |||
File:2011_Project_Group_3_edits.jpg|Group 3 | |||
File:2011_Project_Group_4_edits.jpg|Group 4 | |||
File:2011_Project_Group_5_edits.jpg|Group 5 | |||
File:2011_Project_Group_6_edits.jpg|Group 6 | |||
File:2011_Project_Group_7_edits.jpg|Group 7 | |||
File:2011_Project_Group_8_edits.jpg|Group 8 | |||
File:2011_Project_Group_9_edits.jpg|Group 9 | |||
File:2011_Project_Group_10_edits.jpg|Group 10 | |||
File:2011_Project_Group_11_edits.jpg|Group 11 | |||
File:2011_Project_Group_1-11_edits.jpg|All Groups (1-11) edits | |||
</gallery> | |||
|} | |||
{| class="wikitable mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" | |||
! Peer Assessment | |||
|- | |||
| colspan="2"|[[File:Mark_Hill.jpg|50px]] How do you engage the students in the assessment process? | |||
Students present their project in the class and have a set "soft deadline" for completing the project and at this deadline students stop the work on their own project. An individual assessment item is set where each student looks, using the assessment criteria, at all the other projects. This assessment is pasted on the project discussion page and the students own page. The following week, groups then collate these assessments and have the opportunity to improve their own project based upon these comments. | |||
Note the process also makes the students look at the other projects and see what is "good" and "bad" and use this when they return to work on their own project. | |||
|} | |||
==Histology Practical Class Support== | |||
[[File:unswmedicine.gif|right]] | |||
[[File:ALTC logo.jpg|150px|right]] | |||
* Students in both Science and Medicine classes now learn histology and pathology through the use of "virtual slides". | |||
* Slides are projected onto screens and monitors and students own computers to view the slides. | |||
* In these classes students work through a series of unlabelled slides guided by an academic coordinator and supported by tutors. | |||
* Students can access the slides outside of the class hours and now can also access self-directed learning support from specifically designed online resources. | |||
===Virtual Slides=== | |||
* Developed by colleagues in Medicine supported by ALTC grant. The repository includes virtual slide collections for Anatomy, Pathology, Botany/Ecology and Zoology (total ~600 slides). ([http://vslides.unsw.edu.au Virtual Slides]) | |||
* Requires zpass login. Unlabelled slides the students work through in practical classes. | |||
* Software is similar to that on [http://www.path.uiowa.edu/virtualslidebox/nlm_histology/content_index_db.html UIOWA - Virtual Slidebox] | |||
===Histology Slide Support=== | |||
* Background and self-directed learning for students working with virtual slides. | |||
* [[Histology Glossary}}, additional information, cartoon images, animations, links and labelled histology slides. | |||
* Labelled histology slides used are from a different set of images, so students still need to identify structures themselves in the virtual slide set. | |||
===Science=== | |||
* Introductory course - [[ANAT2511 - Fundamentals of Anatomy]] | |||
* Histology course - [[ANAT2241 Histology - Basic and Systematic]] | |||
===Medicine=== | |||
{| | |||
| [[File:Foundsmall.jpg|left]] | |||
| '''Medicine Foundations:''' [[Foundations - Histology Cells and Tissues|Histology Introduction]] | [[Foundations - Histology Epithelia and Skin|Skin Histology]] | |||
|- | |||
| [[File:HMsmall.jpg|left]] | |||
| '''Medicine Health Maintenance:''' [[Gastrointestinal Tract - Pancreas Histology|Pancreas Histology]] | [[Gastrointestinal_Tract_-_Liver_Histology|Liver Histology]] | [[Gastrointestinal_Tract_-_Gall_Bladder_Histology|Gall Bladder Histology]] | [[Renal System Histology]] | [[HM_Practical_-_Blood_Vessel_Histology|Blood Vessel Histology]] | |||
|- | |||
| [[File:AEsmall.jpg|left]] | |||
| '''Medicine Ageing and Endings:''' [[Bone Histology]] | [[Gastrointestinal_Tract_-_Colon_Histology|Colon Histology]] | |||
|} | |||
==iBooks== | |||
* ePublishing or digital publishing. (pdf, eBook, [[Embryology_iBooks|'''iBooks''']]) | |||
* A potential explosion in this sector, everyone is a publisher. | |||
** how do you assess good (re)sources? | |||
* free software and can be freely published. ([http://www.apple.com/ibooks-author iBook Author], [https://itunesconnect.apple.com/WebObjects/iTunesConnect.woa connect]) | |||
* Downloadable and independent of internet connection, remote locations. | |||
{{Footer}} | |||
[[Category:Education]][[Category:2013]] | [[Category:Education]][[Category:2013]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:43, 15 June 2017
Online Embryology for Medicine and Science
6 December 2013 Dept. of Anatomy and Embryology, University of Goettingen Translate page - German
Introduction
This presentation will describe my experiences in developing online embryology teaching for medical (large group) and science (small group) student groups.

|

|
| Medicine (large computer lab) | Science (small computer lab) |
|
<html5media height="450" width="500">File:Human_blastocyst_day_3-6.mp4</html5media>
|
Embryology Online
| Technology Timeline | |
|---|---|

The changing technology environment we have experienced in the last 50 years, and more recently in the last 20 "internet years". | |
|
|
New Wiki Format 2009
- familiar structure and layout. (the Wiki format)
- easy to print and search. (print this current page)
- resolved student navigation issues. (every page has the same navigation and access to student pages)
- contributions by researchers staff and students. (Researcher Contributions)
- current research easily added and used by students. (Blastocyst Day 3-6 Movie)
| Why Wikis? |
|---|

The Software - Wikipedia had been around for a few years and many students were commonly using it initially as a dictionary rather than encyclopaedia. MediaWiki is the database software which runs this application on the web and is separate from the content hosted in Wikipedia. The Support - MediaWiki is freely available, stable, regularly updated, and has a large group of developers maintaining and making many useful applications (extensions) within this software framework. The Interaction - The format can be used interactively by teacher and student, both can construct, distribute and share knowledge. This can be done easily anytime and anywhere with an internet connection and editing can be restricted to only those designated users and hierarchically within those users. Importantly, an extension allows users access through the familiar UNSW Zpass system. Visibility - You need to see what is being done! The embryology educational material has since its early development been on the internet and available to all. Learning management systems (LMS) are excellent for what they do, manage courses and students. My experience is that students don't generally like LMS and use it only because they have to. Most are LMS are commercial packages ($$) and their content is generally hidden (which can be important for security/copyright etc) and not easily shared. |
|
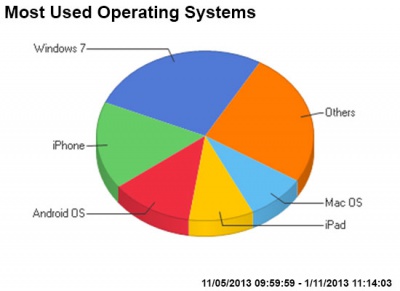
|
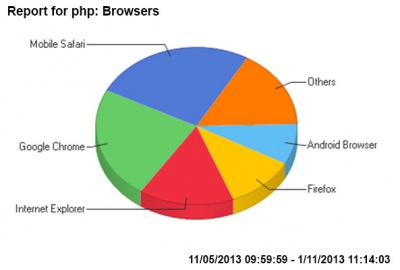
| Browser used | Browser operating systems |
Teaching Contact Hours
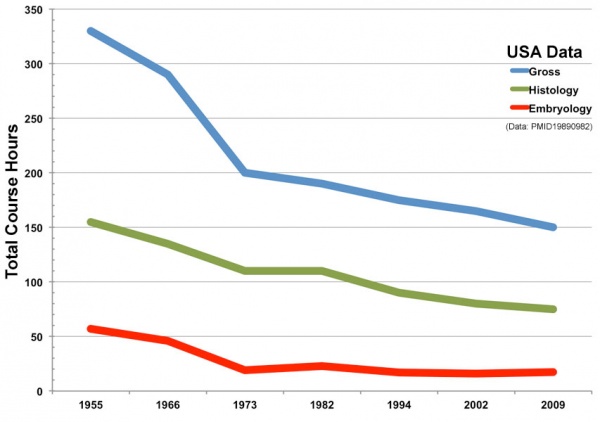
Trends in anatomy disciplines contact teaching hours based on data from USA survey.[1] |
|
| About this graph |
|---|
Reference
University of New South Embryology Contact hours
|
| New Embryology Topics |
|---|
Less contact time, but a growing list of new clinically relevant topics.
|
Medicine Large Class

|

|
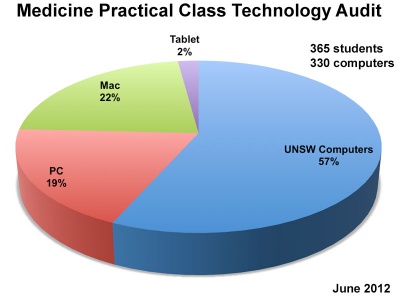
|
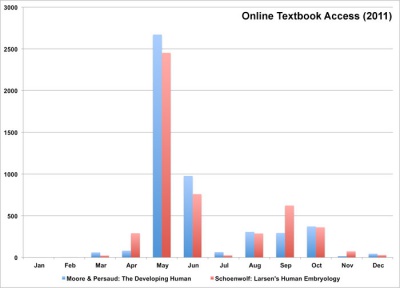
|
| Medicine practicals computer use (2012) | Online textbook access (2011) |
Medicine - Independent Learning Projects
The Independent Learning Project (ILP) is intended to provide UNSW medical students with a period of in-depth study that engenders an approach to medicine that is constantly questioning and self-critical. (About ILP)
- 2006 - Carnegie Stage Embryo Animations educational project.
| 2006 ILP Movies | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Shown below are the animations generated from the serial sections of a Human embryo (week 8, Carnegie stage 22). Click the quicktime or Flash lingo to see the rotating animations. Note Flash animations do not play on iPads. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
These 3d movies were part of the UNSW Medical degree Independent Learning Project (ILP) prepared by Aashish Kumar (2006). |
- 2009 - Cardiac Embryology educational project. (Project Background, Project Discussion)
| 2009 ILP Tutorial | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 Self-directed Learning. Self-directed Learning.
This project was designed to allow students to work through heart development online using modules designed to teach at 3 levels of understanding, using the "traffic light" approach, (green is easiest, red is hardest). Each module through the same timeline and firstly identifies the learning objectives, then how long it will take to complete the module. | ||||
Basic Heart Development Timeline (weeks of development are shown w3 to w7) |
Science Small Class

|
|
Science Group Projects
- 2009 - Animal Models: Rabbit | Fly | Zebrafish | Mouse | Project 5 - Frog | Related page - Animal Development
- 2010 - Diagnostic Techniques: Ultrasound | Chorionic villus sampling | Amniocentesis | Percutaneous Umbilical Cord Blood Sampling | Fetal Fibronectin | Maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein | Related page - Prenatal Diagnosis
- 2011 - Abnormalities: Turner Syndrome | DiGeorge Syndrome | Klinefelter's Syndrome | Huntington's Disease | Fragile X Syndrome | Tetralogy of Fallot | Angelman Syndrome | Friedreich's Ataxia | Williams-Beuren Syndrome | Duchenne Muscular Dystrolphy | Cleft Palate and Lip | Student Group Projects
- 2012 - Sensory Development: Vision | Somatosensory | Taste | Olfaction | Abnormal Vision | Hearing
Online Project support
At the beginning of the course students are led through simple tutorial exercises to become familiar with the process.
- establishing the assessment criteria. (2011)
- text editing and formatting. (Editing Basics, formatting references)
- identifying research sources and their reuse. (Images| Copyright)
- uploading and images, identifying sources and copyright information. (Tutorial | in-class exercise)
Histology Practical Class Support
- Students in both Science and Medicine classes now learn histology and pathology through the use of "virtual slides".
- Slides are projected onto screens and monitors and students own computers to view the slides.
- In these classes students work through a series of unlabelled slides guided by an academic coordinator and supported by tutors.
- Students can access the slides outside of the class hours and now can also access self-directed learning support from specifically designed online resources.
Virtual Slides
- Developed by colleagues in Medicine supported by ALTC grant. The repository includes virtual slide collections for Anatomy, Pathology, Botany/Ecology and Zoology (total ~600 slides). (Virtual Slides)
- Requires zpass login. Unlabelled slides the students work through in practical classes.
- Software is similar to that on UIOWA - Virtual Slidebox
Histology Slide Support
- Background and self-directed learning for students working with virtual slides.
- [[Histology Glossary}}, additional information, cartoon images, animations, links and labelled histology slides.
- Labelled histology slides used are from a different set of images, so students still need to identify structures themselves in the virtual slide set.
Science
- Introductory course - ANAT2511 - Fundamentals of Anatomy
- Histology course - ANAT2241 Histology - Basic and Systematic
Medicine
| Medicine Foundations: Histology Introduction | Skin Histology | |
| Medicine Health Maintenance: Pancreas Histology | Liver Histology | Gall Bladder Histology | Renal System Histology | Blood Vessel Histology | |
| Medicine Ageing and Endings: Bone Histology | Colon Histology |
iBooks
- ePublishing or digital publishing. (pdf, eBook, iBooks)
- A potential explosion in this sector, everyone is a publisher.
- how do you assess good (re)sources?
- free software and can be freely published. (iBook Author, connect)
- Downloadable and independent of internet connection, remote locations.
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, May 25) Embryology Anatomy and Embryology Goettingen - 2013 Seminar. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Anatomy_and_Embryology_Goettingen_-_2013_Seminar
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G