Renal System Histology
| Embryology - 28 Apr 2024 |
|---|
| Google Translate - select your language from the list shown below (this will open a new external page) |
|
العربية | català | 中文 | 中國傳統的 | français | Deutsche | עִברִית | हिंदी | bahasa Indonesia | italiano | 日本語 | 한국어 | မြန်မာ | Pilipino | Polskie | português | ਪੰਜਾਬੀ ਦੇ | Română | русский | Español | Swahili | Svensk | ไทย | Türkçe | اردو | ייִדיש | Tiếng Việt These external translations are automated and may not be accurate. (More? About Translations) |
Introduction
This section of notes gives an overview mainly of adult renal histology, see also Renal System Development notes. A key structure of the kidney functional unit, the nephron, is the glomerulus (renal corpuscle), which represents the initial vascular/renal interface.
Page also provides further background information for Medicine phase 1 Health Maintenance B Urinary Tract Histology Practical - Moodle - Virtual Slides.
This support page content is not part of the HMB practical class.
Renal Virtual Slides
Moodle - Virtual Slides (requires Moodle log in)
- Kidney LS and TS (rat, stain - PAS, Tartrazine)
- Kidney Pelvis
- Renal vascular structures
- Ureter TS
- Ureter TS
- Urinary bladder
- Renal Histology: Histology | Histology Stains | Renal Development
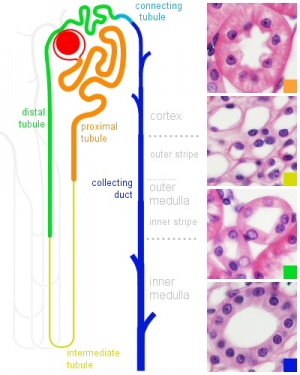
- Kidney - Nephron overview | Glomerulus | Vascular and renal poles | Medullary ray | tubules
- Ureter - Ureter labeled | Ureter epithelium
- Bladder - overview | wall 1 | wall 2 | transitional epithelium | Urinary Bladder Development
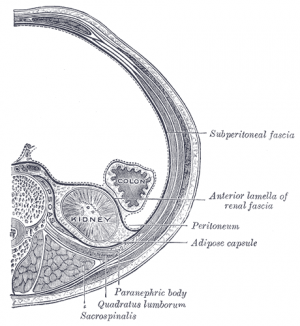
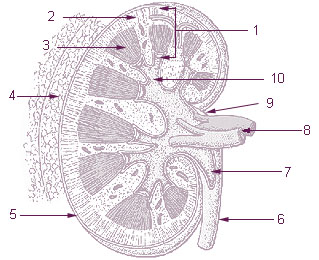
Kidney Anatomy
|
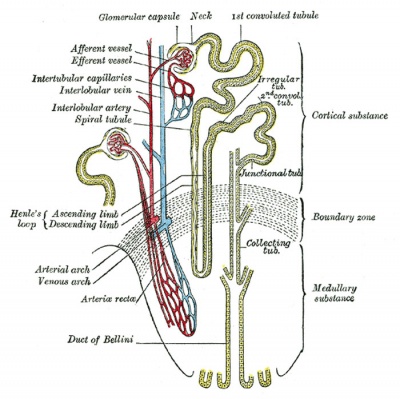
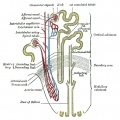
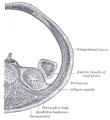
Adult nephron structure |
Nephron
|
Nephron Histology
- Development - mean glomerular number shown to level at 36 weeks, increasing from about 15,000 at 15 weeks to 740,000 at 40 weeks.
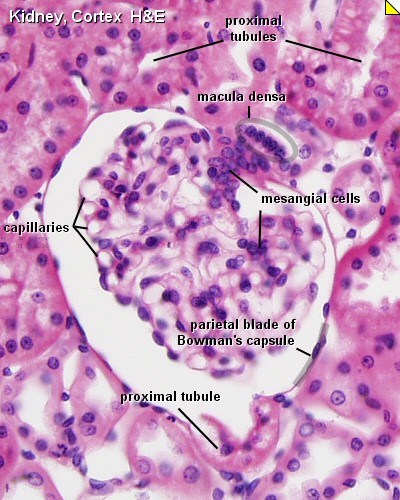
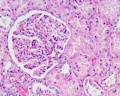
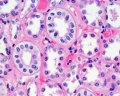
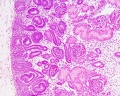
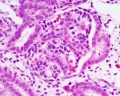
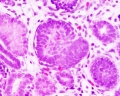
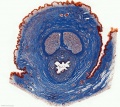
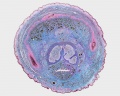
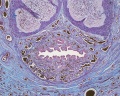
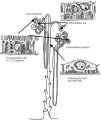
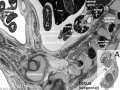
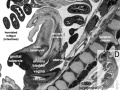
Glomerulus
|
|
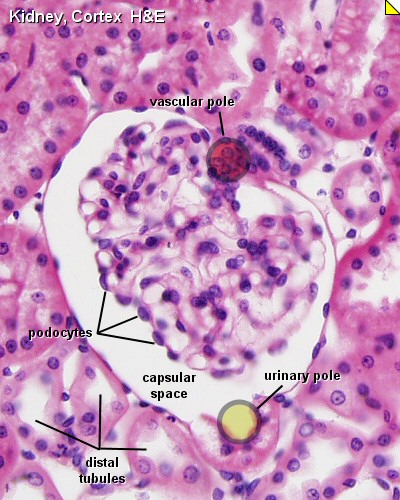
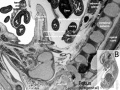
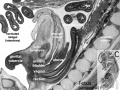
| Glomerulus structure | Vascular and renal poles |
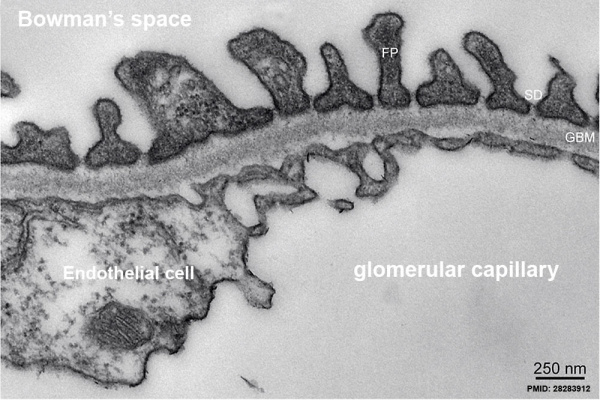
Mouse renal podocyte (EM)[1] |
Transmission electron micrscopy of a mouse glomerular capillary revealing the structural composition of the glomerulus.
|
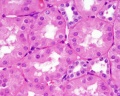
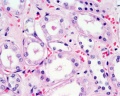
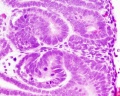
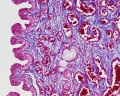
Nephron Tubules
Nephron overview
- Renal System Histology: Nephron tubule overview | glomerulus structure | vascular and renal poles | Medullary rays | Nephron tubules
Large Images
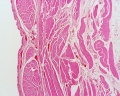
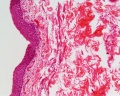
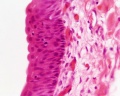
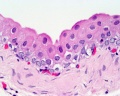
Ureter Histology
|
|
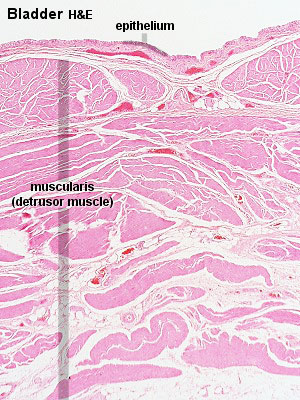
Bladder Histology
Can be described anatomically by its 4 layers from inside outward:
Note that while the smooth muscle fibre layer organisation is described as longitudinal or circular, this is only a general organisation of fibre direction, and is better described as a "spiral" organisation. |
|
Fetal Kidney
- Fetal Renal Links: fetal kidney histology 01 | fetal kidney histology 02 | fetal kidney histology 03 | fetal kidney histology 04
Fetal Urethra Histology
Images
Mouse renal podocyte EM[1]
External Links
External Links Notice - The dynamic nature of the internet may mean that some of these listed links may no longer function. If the link no longer works search the web with the link text or name. Links to any external commercial sites are provided for information purposes only and should never be considered an endorsement. UNSW Embryology is provided as an educational resource with no clinical information or commercial affiliation.
- Blue Histology Urinary System
- UNSW Virtual Slides Urinary Tract Histology
- UIOWA Virtual Slidebox of Histology Urinary tract
Practical Overview
Normal Histology
- kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, urethra
Anatomy
- retroperitoneal
- kidney - bean shaped
- rich blood supply
Kidney Function
- elimination of foreign substances
- regulation of the amount of water in the body
- control of the concentration of most compounds in the extracellular fluid
- filtration - glomeruli of the kidney
- selective resorption and excretion - tubular system of the kidney
Capsule
|
Cortex
|
Medulla
|
Blood Supply
- renal artery
- interlobar arteries (across medulla thru renal columns)
- arcuate arteries (cortico-medullary junction)
- interlobular arteries
- afferent glomerular arterioles
- glomerular capillary network
- efferent glomerular arterioles
Vasa Recta
- descending arterioles (arteriole rectae) + ascending venules (venulae rectae)
Glomerulus
- glomerulus - round (~0.2 mm in diameter) blind beginning of the nephron
- vascular pole - invaginated by a tuft of capillaries
- urinary pole - substances leave the capillaries enter the renal tubule
- Bowman's capsule - anatomical glomerulus is enclosed by two layers of epithelium.
- outer or parietal layer of Bowman's capsule form a simple squamous epithelium.
- inner layer, podocytes in the visceral layer, are extremely complex in shape.
- Mesangial cells in the glomerulus form the connective tissue that gives structural support to podocytes and vessels (Podocytes, mesangial cells, glomerular capillaries)
- Juxtaglomerular cells - smooth muscle cells afferent glomerular arteriole (epithelial-like cells)
- Macular Densa
- distal convoluted tubule near vascular pole (narrower and taller than rest of DCT)
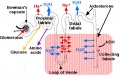
Tubules
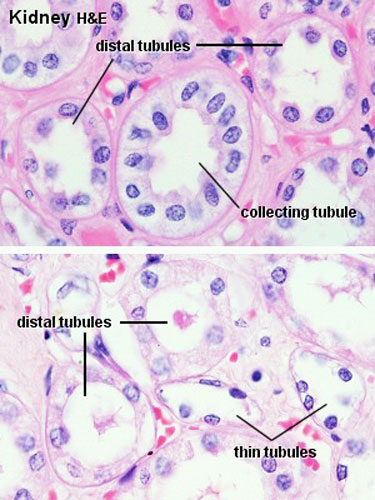
Proximal Convoluted Tubules (PCT)
- brush border
- star-shaped
- larger outside diameter
Distal Convoluted Tubules (DCT)
- clean lumen surface
- apical nuclei
Collecting Tubules (CT)
- larger lumen than DCT (about size of PCT)
- cuboidal cells and smaller than DCT
Renal Pyramids
- medullary straight tubules, ducts and vasa recta
- apical renal papilla - simple cuboidal/columnar epithelia
- calyx - lined by transitional epithelia
Note the urinary system transitional epithelium is also known as urothelium.
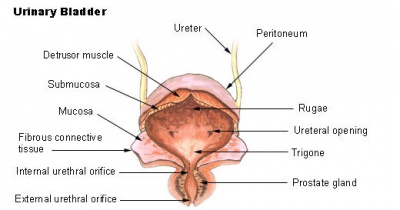
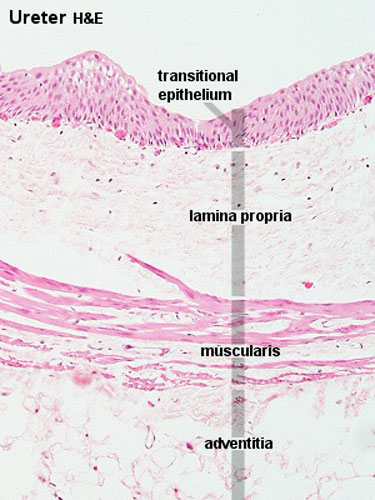
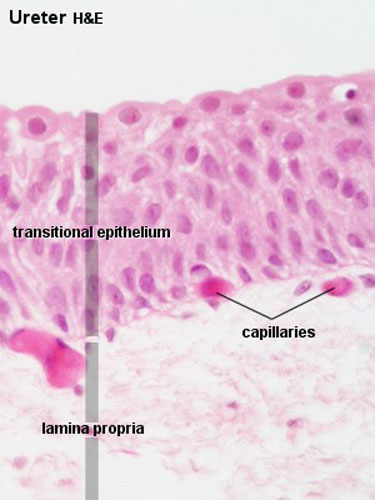
Ureters
- epithelium - transitional epithelia
- lamina propria - mainly of dense connective tissue, with many bundles of coarse collagenous fibres
- muscularis - consists of an inner longitudinal and outer circular layer of smooth muscle cells
- In lower parts of the ureter and the bladder an additional outer longitudinal layer of muscles is added to the first two.
Bladder
- epithelium - transitional epithelia
- apical plaques - thickened domain allows great changes in surface area.
- lamina propria - mainly of dense connective tissue, with many bundles of coarse collagenous fibres
- muscularis - consists of an inner longitudinal and outer circular layer of smooth muscle cells
- In the bladder (and lower parts of the ureter) an additional outer longitudinal layer of muscles is added to the first two.
Urethra
- penile urethra within corpus spongiosum
- pseudostratified columnar epithelia
- distal end - stratified squamous
- continuous with outer skin
References
Terms
| Renal Terms | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
|
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 28) Embryology Renal System Histology. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Renal_System_Histology
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G



![Mouse renal podocyte EM[1]](/embryology/images/thumb/d/d0/Mouse_renal_podocyte_EM01.jpg/90px-Mouse_renal_podocyte_EM01.jpg)