Fetal Growth
| <html5media height="480" width="400">File:fetal growth.mp4</html5media>
Click Here to play on mobile device
- Links: Fetal Development Movie | MP4 movie | Fetal Development
|
In this cartoon movie of fetal growth, observe the changing relative sizes of the head, body and limbs.
Then consider fetal skeletal changes occurring within the head associated with ossification processes and palate development.
Finally consider fetal changes that are occurring in auditory pathway.
|
Fetal Head Growth
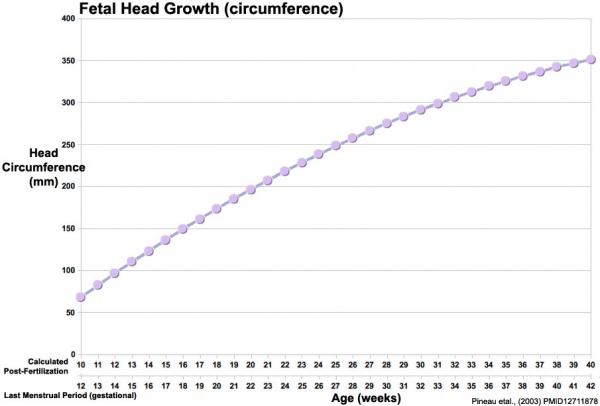
Head Circumference Growth (both gestational and post-fertilisation ages are shown)
Skull Ossification
|
Mesial view of fetal head (CRL 54 mm)
The centers of the occipital bone surround the foramen magnum.
- foramen magnum - large oval opening (foramen) in the occipital bone of the skull.
Behind the maxilla may be seen the palate, the pterygoid, and the alisphenoid in order.
- pterygoid - a paired bone forming part of the palate lies behind the palatine bones.
- alisphenoid - a wing-like cartilaginous bone within the skull forms part of the eye socket.
|
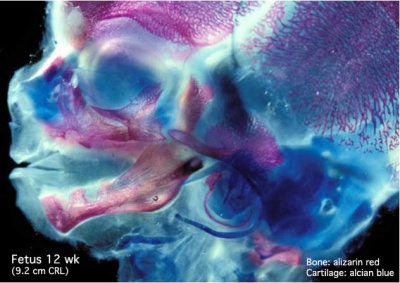
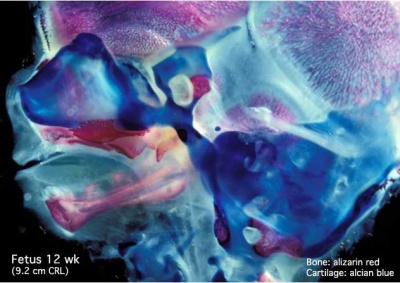
These are 2 views of the same 12 week 92 mm CRL human fetus head, double stained to show both cartilage (blue) and newly-formed bone (red). The head undergoes two different forms of ossification (endochondral and intramembranous) in separate regions of the skull.
| Lateral view (external)
|
Medial view (internal)
|
|
|
| Note the distribution of new bone formation by intramembranous ossification in the plates of the cranial vault, temporal bone, orbit, upper jaw (maxilla) and lower jaw (mandible) regions. Bony regions in the lower jaw (mandible) region also show spaces where tooth formation is occurring.
|
Note the distribution of cartilage from the nasal region through the base of the skull showing endochondral ossification, also occuring in the atlas/axis (with new bone forming). See also the original Meckel's cartilage within the newly forming bony mandible.
|

Late Fetal Skull
Mandible Ossification
Face
The cartilage template of the mandible and the base of the skull are replaced by early bone development.
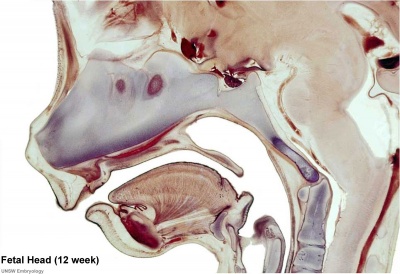
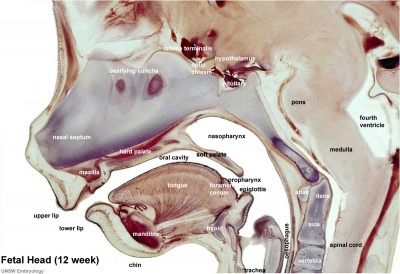
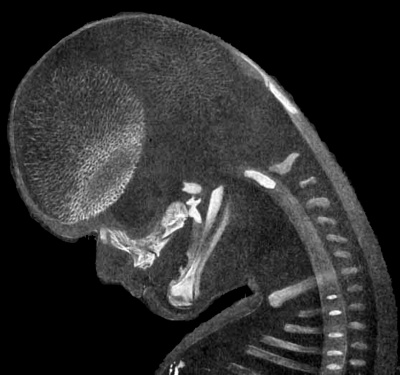
Selected midline medial head view showing key features of head musculoskeletal and neurological development.
Note extensive nasal cartilage, nasal conchae, pituitary, secondary palate, oral cavity, tongue, mandible, hyoid, choana, oropharynx.
Also note the developing tongue musculature and its mandibular attachment site.
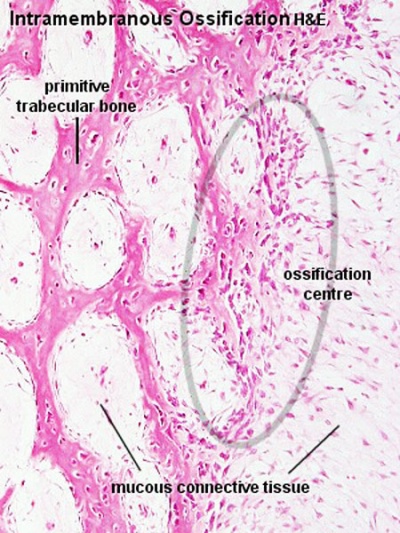
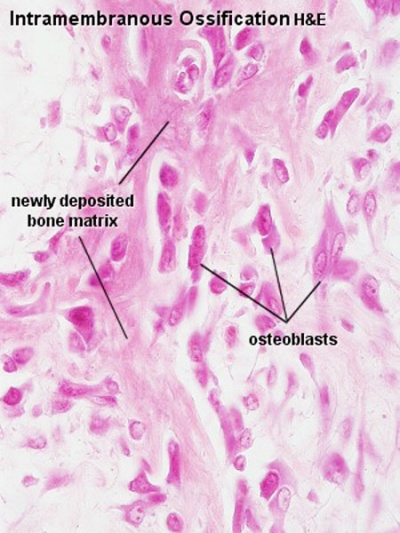
Note that the cranial vault, the portion of the skull enclosing the brain, ossifies by a unique bone formation process, intramembranous ossification.
Because the head contains many different structures also review notes on Special Senses (eye, ear, nose), Respiration (pharynx), Integumentary (Teeth), Endocrine (thyroid, parathyroid, pituitary) and Musculoskeletal (tongue, skull).
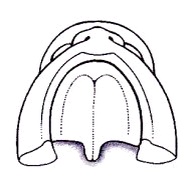
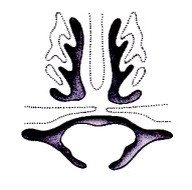
Palate Development
Secondary palate formation is the growth of the palatal shelves towards the midline.
| Inferior view
|
Anterior view
|
| <html5media height="400" width="400">File:Palate_001.mp4</html5media>
|
<html5media height="400" width="400">File:Palate_002.mp4</html5media>
|
|
|
|
|
|
Palate Overview
Embryonic
- week 4 - pharyngeal arch formation, first pharngeal arch contributes mandible and maxilla.
- week 6 - 7 - primary palate formation maxillary processes and frontonasal prominence.
Fetal
- week 9 - secondary palate shelves fuse, separating oral and nasal cavities.
|
Week 10 Gestational Age (GA week 12)
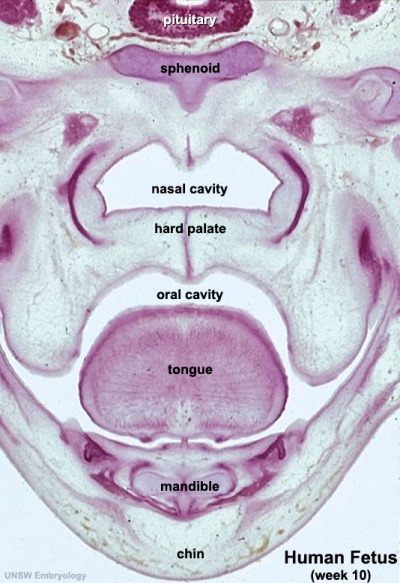
hard palate
|
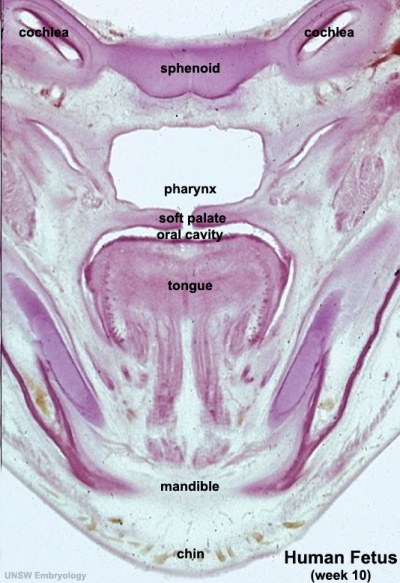
soft palate
|
Hearing
Hearing Timeline
| Developmental Time
|
Event
|
| Week 9
|
Mesenchyme surrounding membranous labryinth (otic capsule) chondrifies.
|
| Week 12-16
|
Capsule adjacent to membranous labryinth undegoes vacuolization to form a cavity (perilymphatic space) around membranous labrynth and fills with perilymph.
|
| Week 18
|
ectodermal plug in external auditory meatus breaks down.
|
| Week 16 - 24
|
Centres of endochondral ossification appear in remaining cartilage of otic capsule form petrous portion of temporal bone. Continues to ossify to form mastoid process of temporal bone.
|
| Week 18 - 22
|
Organ of corti structural elements develop. (GA 20 - 24 weeks)
|
| 26 weeks
|
human brainstem auditory pathway is anatomically formed.
|
| 28 weeks
|
AABR can be recorded.
|
| 3rd Trimester
|
Vibration acoustically of maternal abdominal wall induces startle response in fetus.
|
| Links: hearing | timeline
|
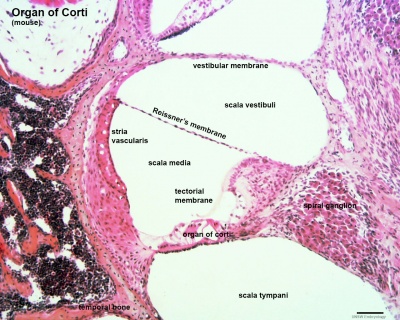
Organ of Corti
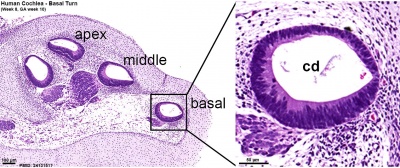
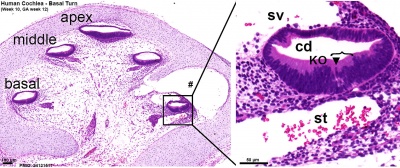
Early fetal cochlea week 8.4 (GA 10.4) and week 10 (GA 12)[1]
Note Kölliker’s organ (KO), a transient epithelial structure that is the source of the future sensory cells.
| Week 8.4
|
Week 10
|
|
|
Adult organ of Corti (mouse) that develops through the fetal period.
- Links: inner ear
Central Pathway
- 26 weeks - human brainstem auditory pathway is anatomically formed.
- 28 weeks - AABR can be recorded.
less than 34 weeks - latencies of AABR components (I, III, and V) decrease as a function of gestation
|
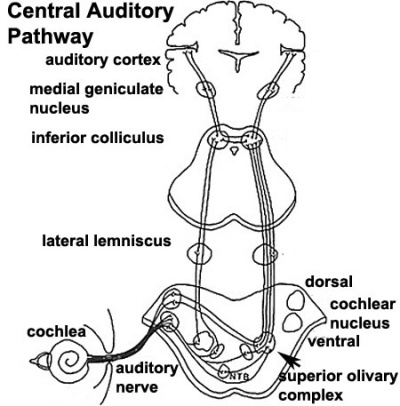
Auditory neural pathway
|
Fetal Interactive Component
| Attempt the Quiz - Fetal
|

Here are a few simple Quiz questions that relate to Fetal development from the lecture and practical.
|
Additional Information
| Additional Information - Content shown under this heading is not part of the material covered in this class. It is provided for those students who would like to know about some concepts or current research in topics related to the current class page.
|
| Palate Development (expand to see terms)
|
- cleft - An anatomical gap or space occuring in abnormal development in or between structures. Most commonly associated with cleft lip and cleft palate. Term is also used to describe the external groove that forms between each pharyngeal arch during their formation.
- cleft lip - An abnormality of face development leading to an opening in the upper lip. Clefting of the lip and or palate occurs with 300+ different abnormalities. Depending on many factors, this cleft may extend further into the oral cavity leading to a cleft palate. In most cases clefting of the lip and palate can be repaired by surgery.
- cleft palate - An abnormality of face development leading to an opening in the palate, the roof of the oral cavity between the mouth and the nose. Clefting of the lip and or palate occurs with 300+ different abnormalities. In most cases clefting of the lip and palate can be repaired by surgery. Palate formation in the embryo occurs at two distinct times and developmental processes called primary and secondary palate formation. This leads to different forms (classifications) and degrees of clefting.
- hard palate - anterior part of the palate that becomes ossified. The posterior palate part is the soft palate.
- epithelial mesenchymal transition - (EMT, epitheliomesenchymal transformation) conversion of an epithelium into a mesenchymal (connective tissue) cellular organization. Process required during lip and palate developmental fusion.
- epitheliomesenchymal transformation - (epithelial mesenchymal transition) conversion of an epithelium into a mesenchymal (connective tissue) cellular organization.
- incisive papilla - anterior midline palate near the incisors lying at the end of the palatine raphe.
- levator veli palatini - Muscle forming part of the soft palate, elevates the soft palate for swallowing.
- mastication - (chewing) Process of crushing and grinding food within the mouth.
- maxilla - (pl. maxillae) upper jaw bone forming from the maxillary process of the first pharyngeal arch.
- medial edge epithelial - (MEE) opposing palatal shelves adhere to each other to form this epithelial seam.
- musculus uvulae Small muscle forming part of the soft palate lying within the uvula, shortens and broadens the uvula.
- palatine raphe (median raphe) palate midline ridge (seam) of the mucosa, from the incisive papilla to the uvula.
- palatal rugae - (palatine rugae, rugae) Transverse series of ridges forming on the secondary hard palate that are sequentially added during development as the palate grows. Involved in the process of mastication.
- palatal vault - (palatine vault) Term describing the curved "arch" shape of the palate that mainly develops postnatally.
- palate - The roof of the mouth (oral cavity) a structure which separates the oral from the nasal cavity. Develops as two lateral palatal shelves which grow and fuse in the midline. Initally a primary palate forms with fusion of the maxillary processes with the nasal processes in early face formation. Later the secondary palate forms the anterior hard palate which will ossify and separate the oral and nasal cavities. The posterior part of the palate is called the soft palate (velum, muscular palate) and contains no bone. Abnormalities of palatal shelf fusion can lead to cleft palate.
- palatine bones - Two bones that with the maxillae form the hard palate.
- palatogenesis - The process of palate formation, divided into primary and secondary palate development.
- palatoglossus - (glossopalatinus, palatoglossal muscle) Small muscle forming part of the soft palate required for swallowing.
- palatopharyngeus - (palatopharyngeal or pharyngopalatinus) Small muscle forming part of the soft palate required for breathing.
- pharyngeal arch - (branchial arch, Greek, branchial = gill) These are a series of externally visible anterior tissue bands lying under the early brain that give rise to the structures of the head and neck. In humans, five arches form (1,2,3,4 and 6) but only four are externally visible on the embryo. Each arch has initially identical structures: an internal endodermal pouch, a mesenchymal (mesoderm and neural crest) core, a membrane (endoderm and ectoderm) and external cleft (ectoderm). Each arch mesenchymal core also contains similar components: blood vessel, nerve, muscular, cartilage. Each arch though initially formed from similar components will differentiate to form different head and neck structures.
- philtrum - (infranasal depression, Greek, philtron = "to love" or "to kiss") Anatomically the surface midline vertical groove in the upper lip. Embryonically formed by the fusion of the frontonasal prominence (FNP) with the two maxillary processes of the first pharyngeal arch. Cleft palate (primary palate) occurs if these three regions fail to fuse during development. Fetal alcohol syndrome is also indicated by flatness and extension of this upper lip region.
- soft palate - (velum, muscular palate) posterior part of the palate that becomes muscular. Forms 5 muscles: tensor veli palatini, palatoglossus, palatopharyngeus, levator veli palatini, musculus uvulae. The anterior palate part is the hard palate.
- T-box 22 - (TBX22) a transcription factor that cause X-linked cleft palate and ankyloglossia in humans. Tbx22 is induced by fibroblast growth factor 8 (FGF8) in the early face while bone morphogenic protein 4 (BMP4) represses and therefore restricts its expression. (More? OMIM - TBX22)
- tensor veli palatini - (tensor palati, tensor muscle of the velum palatinum) Small muscle forming part of the soft palate required for swallowing.
- Transforming Growth Factor-beta - (TGFβ) factors induces both epithelial mesenchymal transition and/or apoptosis during palatal medial edge seam disintegration.
- uvula - (Latin = a little grape) a pendulous posterior end of soft palate used to produce guttural consonants. First named in 1695.
- Van der Woude syndrome - common syndromic cause of clefting (2% of cleft lip and palates). Van der Woude syndrome 1 1q32.2 Van der Woude syndrome 2 1p36.11
- velopharyngeal insufficiency - (VPI) associated with cleft palate repair, describes the velum and lateral and posterior pharyngeal walls failing to separate the oral cavity from the nasal cavity during speech.
|
Secondary Palate - Retinoic acid signalling
Mammadova A, Zhou H, Carels CE & Von den Hoff JW. (2016). Retinoic acid signalling in the development of the epidermis, the limbs and the secondary palate. Differentiation , 92, 326-335. PMID: 27238416 DOI.
Fetal Organ of Corti Development
| Week 18
|
Week 20
|
Week 22
|
- stria vascularis - 18-20 weeks (GA 20 week 3 days - 22 week)
- tectorial membrane - 18 weeks (GA 20 week 3 days)
- Afferent nerve ending - 18 weeks (GA 20 week 3 days)
|
- Nuel space - 20 weeks (GA 22 week 0 days - 24 week)
- Efferent nerve ending - 20 weeks (GA 22 week 0 days)
- Maturation of stereocilia - 20 weeks (GA 22 week 0 days - 24 week 0 days)
|
- tunnel of corti - GA 24 week
- Space between hair and supporting cell - 24 week
- Presence of kinocilium - GA 24 week 0 days
|
<pubmed>7188054</pubmed>
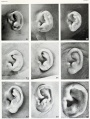
Fetal Auricle Development
Embryo ear cartilage 21 - 50 mmm CRL
External Auditory Meatus Timeline
| Time
|
EAM Appearance
|
| Embryonic period
|
Ectodermal cells proliferate and fill the entire lumen forming a meatal plug
|
| 10 weeks
|
Meatal plug extends in a disc-like fashion. In the horizontal plane the meatus is boot-shaped with a narrow neck and the sole of the meatal plug spreading widely to form the future tympanic membrane medially. Proximal portion of the neck starts to be resorbed.
|
| 13 weeks
|
Disc-like plug innermost surface in contact with the primordial malleus, contributes to the formation of the tympanic membrane.
|
| 16.5 week
|
Meatus is fully patent throughout its length, lumen is still narrow and curved.
|
| 18 week
|
Meatus is already fully expanded to its complete form.
|
Based on data from PMID 1441991
Historic
Mall FP. On ossification centers in human embryos less than one hundred days old. (1906) Amer. J Anat. 5:433-458.
Terms
| Head Terms (expand to view)
|
- branchial arch - see pharyngeal arch.
- clefting - the way in which the upper jaw forms from fusion of the smaller upper prominence of the first pharyngeal arch leads to a common congenital defect in this region called "clefting", which may involve either the upper lip, the palate or both structures, see palate and head abnormalities.
- coronal suture - skull term for the fibrous connective tissue joint that connects the frontal bone with the parietal bones.
- cranial fossae - skull term for the base bones of the cranial vault that form a container and support for the brain.
- cranial vault - skull term for the space formed by bones of the skull that enclose the brain.
- cysts - refers to a cervical sinus abnormality, remants of the cervical sinus remains as a fluid-filled cyst lined by an epithelium, see pharyngeal arch and head abnormalities.
- dolichocephaly - see scaphocephaly.
- fistula - refers to a pharyngeal membrane abnormality, a tract extends from pharynx (tonsillar fossa) beween the carotid arteries (internal and external) to open on side of neck, see pharyngeal arch and head abnormalities.
- lambdoid suture (lambdoidal suture) skull term for the fibrous connective tissue joint that connects the parietal bones with the occipital bone, and is continuous with the occipitomastoid suture.
- metopic suture - skull term for the fibrous connective tissue joint that connects the two fontal bones. In the adult skull this suture is not always present.
- oxycephaly - (turricephaly) term meaning premature fusion of coronal suture + others, see skull and head abnormalities.
- pharyngeal arch - (branchial arch) a structure that forms in the cranial region of the embryo having contributions from all germ layers. In humans, the arches appear in week 4 (GA week 6) in a rostra-caudal sequence and are numbered (1, 2, 3, 4, and 6). Each arch contributes a different part of the head and neck and the associated components.
- pharyngeal cleft - (groove) surface ectoderm that externally separates each pharyngeal arch. In humans, only first pair persist as the outer ear external auditory meatus.
- pharyngeal groove - see pharyngeal cleft.
- pharyngeal membrane - surface ectoderm and pharynx endoderm contact region lying between each pharyngeal arch. In humans, only the first membrane pair persist as the tympanic membrane.
- pharyngeal pouch - pharynx endoderm internal out-pocketing that separates each pharyngeal arch.
- plagiocephaly - term meaning premature unilateral fusion of coronal or lambdoid sutures, see skull and head abnormalities.
- Reichardt's cartilage - (pharyngeal arch 2 cartilage) The superior portion of the hyoid forms the ventral portion of this cartilage and the middle ear stapes is thought to form from the ends of this cartilage.
- sagittal suture - skull term for the fibrous connective tissue joint that connects the two parietal bones in the midline.
- scaphocephaly - (dolichocephaly) term meaning premature fusion of sagittal suture, see skull and head abnormalities.
- sinuses - refers to a pharyngeal groove (cleft) abnormality, when a portion of the pharyngeal groove persists and opens to the skin surface, located laterally on the neck, see pharyngeal arch and head abnormalities.
- squamosal suture - skull term for the fibrous connective tissue joint that connects the squamous portion of the temporal bone with the parietal bones.
- suture - skull term for a fibrous connective tissue joint. In humans, the main sutures are coronal, sagittal, lambdoid and squamosal sutures, with the metopic suture (frontal suture) occurring as an anatomical variant in the adult skull.
- turricephaly - see oxycephaly.
|
| Palate Development (expand to see terms)
|
- cleft - An anatomical gap or space occuring in abnormal development in or between structures. Most commonly associated with cleft lip and cleft palate. Term is also used to describe the external groove that forms between each pharyngeal arch during their formation.
- cleft lip - An abnormality of face development leading to an opening in the upper lip. Clefting of the lip and or palate occurs with 300+ different abnormalities. Depending on many factors, this cleft may extend further into the oral cavity leading to a cleft palate. In most cases clefting of the lip and palate can be repaired by surgery.
- cleft palate - An abnormality of face development leading to an opening in the palate, the roof of the oral cavity between the mouth and the nose. Clefting of the lip and or palate occurs with 300+ different abnormalities. In most cases clefting of the lip and palate can be repaired by surgery. Palate formation in the embryo occurs at two distinct times and developmental processes called primary and secondary palate formation. This leads to different forms (classifications) and degrees of clefting.
- hard palate - anterior part of the palate that becomes ossified. The posterior palate part is the soft palate.
- epithelial mesenchymal transition - (EMT, epitheliomesenchymal transformation) conversion of an epithelium into a mesenchymal (connective tissue) cellular organization. Process required during lip and palate developmental fusion.
- epitheliomesenchymal transformation - (epithelial mesenchymal transition) conversion of an epithelium into a mesenchymal (connective tissue) cellular organization.
- incisive papilla - anterior midline palate near the incisors lying at the end of the palatine raphe.
- levator veli palatini - Muscle forming part of the soft palate, elevates the soft palate for swallowing.
- mastication - (chewing) Process of crushing and grinding food within the mouth.
- maxilla - (pl. maxillae) upper jaw bone forming from the maxillary process of the first pharyngeal arch.
- medial edge epithelial - (MEE) opposing palatal shelves adhere to each other to form this epithelial seam.
- musculus uvulae Small muscle forming part of the soft palate lying within the uvula, shortens and broadens the uvula.
- palatine raphe (median raphe) palate midline ridge (seam) of the mucosa, from the incisive papilla to the uvula.
- palatal rugae - (palatine rugae, rugae) Transverse series of ridges forming on the secondary hard palate that are sequentially added during development as the palate grows. Involved in the process of mastication.
- palatal vault - (palatine vault) Term describing the curved "arch" shape of the palate that mainly develops postnatally.
- palate - The roof of the mouth (oral cavity) a structure which separates the oral from the nasal cavity. Develops as two lateral palatal shelves which grow and fuse in the midline. Initally a primary palate forms with fusion of the maxillary processes with the nasal processes in early face formation. Later the secondary palate forms the anterior hard palate which will ossify and separate the oral and nasal cavities. The posterior part of the palate is called the soft palate (velum, muscular palate) and contains no bone. Abnormalities of palatal shelf fusion can lead to cleft palate.
- palatine bones - Two bones that with the maxillae form the hard palate.
- palatogenesis - The process of palate formation, divided into primary and secondary palate development.
- palatoglossus - (glossopalatinus, palatoglossal muscle) Small muscle forming part of the soft palate required for swallowing.
- palatopharyngeus - (palatopharyngeal or pharyngopalatinus) Small muscle forming part of the soft palate required for breathing.
- pharyngeal arch - (branchial arch, Greek, branchial = gill) These are a series of externally visible anterior tissue bands lying under the early brain that give rise to the structures of the head and neck. In humans, five arches form (1,2,3,4 and 6) but only four are externally visible on the embryo. Each arch has initially identical structures: an internal endodermal pouch, a mesenchymal (mesoderm and neural crest) core, a membrane (endoderm and ectoderm) and external cleft (ectoderm). Each arch mesenchymal core also contains similar components: blood vessel, nerve, muscular, cartilage. Each arch though initially formed from similar components will differentiate to form different head and neck structures.
- philtrum - (infranasal depression, Greek, philtron = "to love" or "to kiss") Anatomically the surface midline vertical groove in the upper lip. Embryonically formed by the fusion of the frontonasal prominence (FNP) with the two maxillary processes of the first pharyngeal arch. Cleft palate (primary palate) occurs if these three regions fail to fuse during development. Fetal alcohol syndrome is also indicated by flatness and extension of this upper lip region.
- soft palate - (velum, muscular palate) posterior part of the palate that becomes muscular. Forms 5 muscles: tensor veli palatini, palatoglossus, palatopharyngeus, levator veli palatini, musculus uvulae. The anterior palate part is the hard palate.
- T-box 22 - (TBX22) a transcription factor that cause X-linked cleft palate and ankyloglossia in humans. Tbx22 is induced by fibroblast growth factor 8 (FGF8) in the early face while bone morphogenic protein 4 (BMP4) represses and therefore restricts its expression. (More? OMIM - TBX22)
- tensor veli palatini - (tensor palati, tensor muscle of the velum palatinum) Small muscle forming part of the soft palate required for swallowing.
- Transforming Growth Factor-beta - (TGFβ) factors induces both epithelial mesenchymal transition and/or apoptosis during palatal medial edge seam disintegration.
- uvula - (Latin = a little grape) a pendulous posterior end of soft palate used to produce guttural consonants. First named in 1695.
- Van der Woude syndrome - common syndromic cause of clefting (2% of cleft lip and palates). Van der Woude syndrome 1 1q32.2 Van der Woude syndrome 2 1p36.11
- velopharyngeal insufficiency - (VPI) associated with cleft palate repair, describes the velum and lateral and posterior pharyngeal walls failing to separate the oral cavity from the nasal cavity during speech.
|
BGDB: Lecture - Gastrointestinal System | Practical - Gastrointestinal System | Lecture - Face and Ear | Practical - Face and Ear | Lecture - Endocrine | Lecture - Sexual Differentiation | Practical - Sexual Differentiation | Tutorial
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2026, March 13) Embryology BGDB Face and Ear - Fetal. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/BGDB_Face_and_Ear_-_Fetal
- What Links Here?
- © Dr Mark Hill 2026, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
- ↑ Locher H, Frijns JH, van Iperen L, de Groot JC, Huisman MA & Chuva de Sousa Lopes SM. (2013). Neurosensory development and cell fate determination in the human cochlea. Neural Dev , 8, 20. PMID: 24131517 DOI.