ANAT2341 Lab 5 - Trilaminar Embryo
| Lab 5: Introduction | Trilaminar Embryo | Early Embryo | Late Embryo | Fetal | Postnatal | Abnormalities | Online Assessment |
Introduction
Begin by very briefly covering the first 3 weeks of development. Our story of GIT development begins in the third week with the formation of the 3 germ cell layers, one layer the endoderm will form the lining of the entire gastrointestinal tract and also contibute the respiratory tract and other organs.
Note that the description below, and throughout the practical, has been substantially simplified.
Week 3
Gastrulation/Neuralation: The inner cell mass forms a flat sheet of cells and cells migrate through a specific region of the sheet (primitive streak) turning the single layer into first 2 then 3 layers (trilaminar embryo).
Folding
The next process to follow is the folding of the embryonic disc which will form the "tube" of the GIT. Forming the ends of this tube are the 2 membranes which form the upper and lower limits of the GIT.
Note that in addition to gastrulation, neuralation (forming the early neural tube that makes the nervous system) and somitogenesis (segmentation of the mesoderm forming the axial skeleton) are the other major processes occuring in week 3 to 4.
Folding of the embryonic disc occurs ventrally around the notochord, which forms a rod-like region running rostro-caudally in the midline.
In relation to the notochord:
- Laterally (either side of the notochord) lies mesoderm.
- Rostrally (above the notochord end) lies the buccopharyngeal membrane, above this again is the mesoderm region forming the heart.
- Caudally (below the notochord end) lies the primitive streak (where gastrulation occurred), below this again is the cloacal membrane.
- Dorsally (above the notochord) lies the neural tube then ectoderm.
- Ventrally (beneath the notochord) lies the mesoderm then endoderm.
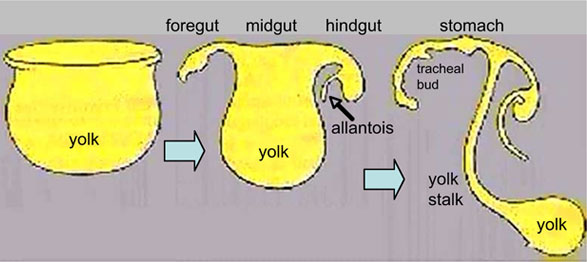
The ventral endoderm (shown yellow) has grown to line a space called the yolk sac. Folding of the embryonic disc "pinches off" part of this yolk sac forming the first primative GIT.
| <html5media height="540" width="390">File:Week3_folding.mp4</html5media> | This animation shows folding of the embryonic disc beginning week 3 of development.
Embryonic disc (midline section) shown to the left and early placenta to the right. The embryonic disc dorsal (ectoderm) top and ventral (endoderm) bottom. Cranial end of disc to the left and caudal end of disc to the right. Note also the early cardiac region shown at the cranial end of disc and the allantois at the caudal end of disc extending into the connecting stalk. Folding of the embryonic disc
|
| <html5media height="340" width="300">File:Endoderm 003.mp4</html5media> | This animation shows the early development of endoderm forming the gastrointestinal tract, yolk sac and allantois. The movie starts approximately week 3 and continues through week 4.
Yellow shows the general lining of the yolk sac (bottom), continuous with the endoderm of the trilaminar embryonic disc (top) during week 3. As the trilaminar disc folds in this week, the foregut and hindgut regions become separated from the external yolk sac. The midgut region remains open to the yolk sac and will separate later. Foregut - Begins at the buccopharyngeal membrane, the foregut region in the head is now called the pharynx. At the lower end of the pharynx a ventral bud forms, that will later form the respiratory tract. Beneath this region the tube grows rapidly forming a dilation of the tube, that will later form the stomach. Beneath this region is the boundary of the foregut and ventrally lies the transverse septum. Midgut - Broadly open to the external yolk sac then with continued folding narrows to a "tube-like" connection the yolk stalk. This stalk will later degenerate and all connection will normally be lost. The yolk sac is pushed to the periphery by the growing amniotic sac, with its connecting yolk stalk in the umbilicus region. The midgut region also grows in length forming a loop lying outside the ventral body wall. Hindgut - The loop of midgut renters the body and the ventral portion of the hindgut extends as a blind-ended tube, or diverticulum, into the connecting stalk. This endoderm extension can be seen in histological sections of the initial placental cord and is called the allantois. The hindgut extends caudal (tailward) ending at the cloacal membrane. |
Week 4
Carnegie stage 10, 23 day, 5-11 somite pairs
Membranes
During the process of gastrulation the embryonic disc formed 3 layers, except in 2 specific membrane regions where ectoderm and endoderm have no mesoderm between them: buccopharyngeal membrane and cloacal membrane. These will form the upper and lower extend of the GIT.
Buccopharyngeal membrane
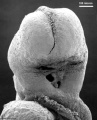
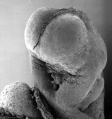
also called mouth or oral membrane
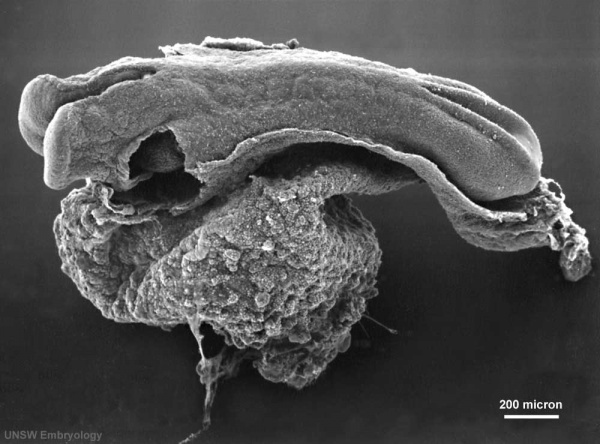
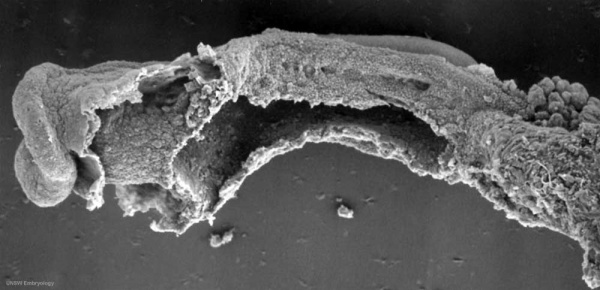
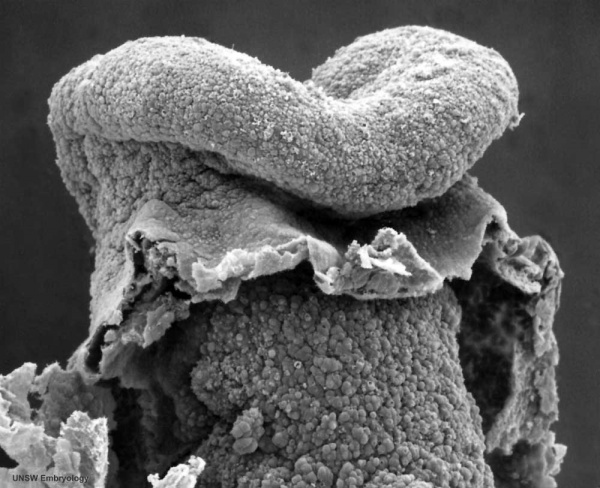
Carnegie stage 10 (21 days, 4-5 somite pairs, ventral sem)
Carnegie stage 11 (25 days, 20 somite pairs)
Cloacal membrane - not clearly visible in the above section
Splanchnic Mesoderm
The cartoon above is a section through the trunk of the trilaminar embryo showing the further development of the 3 layers and the space (coelom) that forms in the mesoderm (only the righthand side is shown, lefthand side would be identical).
Within the embryonic disc lateral plate mesoderm a space (coelom) forms, it lies within the embryo and so is called the intraembryonic coelom. This single "horseshoe-shaped" space will form the 3 major body cavities: pericardial (around the heart), pleural (around the lungs) and peritoneal (around the GIT and visceral organs).
The mesoderm adjacent to the endoderm is now called the splanchnic mesoderm which forms the connective tissue and muscular wall of the GIT.
Note intraembryonic coelomic cavity communicates with extraembryonic coelom (space outside the embryo) through portals (holes) initially on lateral margin of embryonic disc.
| Lab 5: Introduction | Trilaminar Embryo | Early Embryo | Late Embryo | Fetal | Postnatal | Abnormalities | Online Assessment |
Terms
- allantois - An extraembryonic membrane, endoderm in origin extension from the early hindgut, then cloaca into the connecting stalk of placental animals, connected to the superior end of developing bladder. In reptiles and birds, acts as a reservoir for wastes and mediates gas exchange. In mammals is associated/incorporated with connecting stalk/placental cord fetal-maternal interface.
- amnion - An extraembryonic membrane]ectoderm and extraembryonic mesoderm in origin and forms the innermost fetal membrane, produces amniotic fluid. This fluid-filled sac initially lies above the trilaminar embryonic disc and with embryoic disc folding this sac is drawn ventrally to enclose (cover) the entire embryo, then fetus. The presence of this membane led to the description of reptiles, bird, and mammals as amniotes.
- amniotic fluid - The fluid that fills amniotic cavity totally encloses and cushions the embryo. Amniotic fluid enters both the gastrointestinal and respiratory tract following rupture of the buccopharyngeal membrane. The late fetus swallows amniotic fluid.
- buccal - (Latin, bucca = cheek) A term used to relate to the mouth (oral cavity).
- buccopharyngeal membrane - (oral membrane) (Latin, bucca = cheek) A membrane which forms the external upper membrane limit (cranial end) of the early gastrointestinal tract (GIT). This membrane develops during gastrulation by ectoderm and endoderm without a middle (intervening) layer of mesoderm. The membrane lies at the floor of the ventral depression (stomodeum) where the oral cavity will open and will breakdown to form the initial "oral opening" of the gastrointestinal tract. The equivilent membrane at the lower end of the gastrointestinal tract is the cloacal membrane.
- cloacal membrane - Forms the external lower membrane limit (caudal end) of the early gastrointestinal tract (GIT). This membrane is formed during gastrulation by ectoderm and endoderm without a middle (intervening) layer of mesoderm. The membrane breaks down to form the initial "anal opening" of the gastrointestinal tract.
- coelom - Term used to describe a space. There are extraembryonic and intraembryonic coeloms that form during vertebrate development. The single intraembryonic coelom will form the 3 major body cavities: pleural, pericardial and peritoneal.
- foregut - The first of the three part/division (foregut - midgut - hindgut) of the early forming gastrointestinal tract. The foregut runs from the buccopharyngeal membrane to the midgut and forms all the tract (esophagus and stomach) from the oral cavity to beneath the stomach. In addition, a ventral bifurcation of the foregut will also form the respiratory tract epithelium.
- gastrula - (Greek, gastrula = little stomach) A stage of an animal embryo in which the three germ layers ([E#endoderm|endoderm]/mesoderm/ectoderm) have just formed.
- gastrulation - The process of differentiation forming a gastrula. Term means literally means "to form a gut" but is more in development, as this process converts the bilaminar embryo (epiblast/hypoblast) into the trilaminar embryo ([E#endoderm endoderm]/mesoderm/ectoderm) establishing the 3 germ layers that will form all the future tissues of the entire embryo. This process also establishes the the initial body axes.
- hindgut - The last of the three part/division foregut - midgut - hindgut) of the early forming gastrointestinal tract. The hindgut forms all the tract from the distral transverse colon to the cloacal membrane and extends into the connecting stalk (placental cord) as the allantois. In addition, a ventral of the hindgut will also form the urinary tract (bladder, urethra) epithelium.
- intraembryonic coelom - The "horseshoe-shaped" space (cavity) that forms initially in the third week of development in the lateral plate mesoderm that will eventually form the 3 main body cavities: pericardial, pleural, peritoneal. The intraembryonic coelom communicates transiently with the extraembryonic coelom.
- neuralation - The general term used to describe the early formation of the nervous system. It is often used to describe the early events of differentiation of the central ectoderm region to form the neural plate, then neural groove, then neural tube. The nervous system includes the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) from the neural tube and the peripheral nervous system (peripheral sensory and sympathetic ganglia) from neural crest. In humans, early neuralation begins in week 3 and continues through week 4.
- neural crest - region of cells at the edge of the neural plate that migrates throughout the embryo and contributes to many different tissues. In the gastrointestinal tract it contributes mainly the enteric nervous system within the wall of the gut responsible for peristalsis and secretion.
- pharynx - uppermost end of gastrointestinal and respiratory tract, in the embryo beginning at the buccopharyngeal membrane and forms a major arched cavity within the phrayngeal arches.
- somitogenesis The process of segmentation of the paraxial mesoderm within the trilaminar embryo body to form pairs of somites, or balls of mesoderm. A somite is added either side of the notochord (axial mesoderm) to form a somite pair. The segmentation does not occur in the head region, and begins cranially (head end) and extends caudally (tailward) adding a somite pair at regular time intervals. The process is sequential and therefore used to stage the age of many different species embryos based upon the number visible somite pairs. In humans, the first somite pair appears at day 20 and adds caudally at 1 somite pair/4 hours (mouse 1 pair/90 min) until on average 44 pairs eventually form.
- splanchnic mesoderm - Gastrointestinal tract (endoderm) associated mesoderm formed by the separation of the lateral plate mesoderm into two separate components by a cavity, the intraembryonic coelom. Splanchnic mesoderm is the embryonic origin of the gastrointestinal tract connective tissue, smooth muscle, blood vessels and contribute to organ development (pancreas, spleen, liver). The intraembryonic coelom will form the three major body cavities including the space surrounding the gut, the peritoneal cavity. The other half of the lateral plate mesoderm (somatic mesoderm) is associated with the ectoderm of the body wall.
- stomodeum - (stomadeum, stomatodeum) A ventral surface depression on the early embryo head surrounding the buccopharyngeal membrane, which lies at the floor of this depression. This surface depression lies between the maxillary and mandibular components of the first pharyngeal arch.
| Lab 5: Introduction | Trilaminar Embryo | Early Embryo | Late Embryo | Fetal | Postnatal | Abnormalities | Online Assessment |
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2026, February 28) Embryology ANAT2341 Lab 5 - Trilaminar Embryo. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/ANAT2341_Lab_5_-_Trilaminar_Embryo
- © Dr Mark Hill 2026, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G