ANAT2241 Muscle Tissue
| ANAT2241 This practical support page content is not part of the virtual science practical class and provides additional information for student self-directed learning purposes. All practical class pages are located on Moodle - ANAT2241 |
General Objective
To know the structure and ultrastructure of the three main types of muscle and how it relates to their varied functions.
Specific Objectives
- To identify striated skeletal (striated), cardiac and smooth muscle on the basis of histological features.
- To distinguish connective tissue in association with muscle cells and fascicles of muscle cells.
- To describe the ultrastructural features of the different types of muscle cells.
Learning Activities
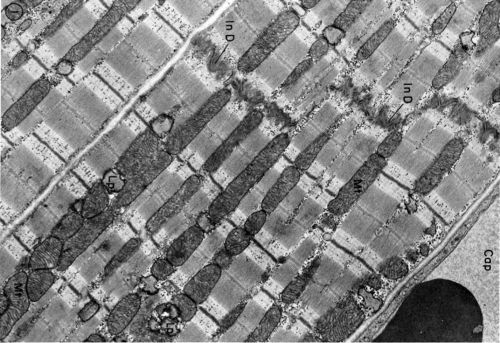
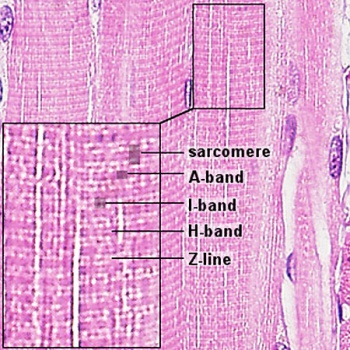
Examine electron micrographs of skeletal muscle in longitudinal section (LS) and identify the following features:
- A band (dark staining; anisotropic)
- I band (light staining; isotropic)
- H band (pale zone in centre of A band)
- M line in centre of H band
- Z discs (in centre of I band) delineating the sarcomere
- Sarcoplasmic reticulum
- T tubules (transverse tubular system) and triads.
Virtual Slides: Muscle Tissue
|
|
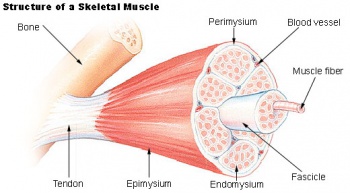
| Skeletal muscle structure cartoon | Skeletal muscle sarcomeres |
Muscle Contraction
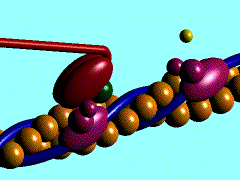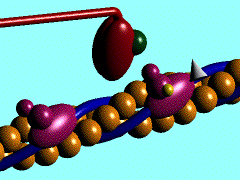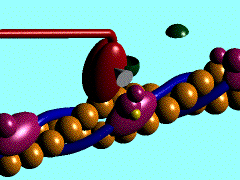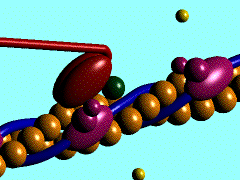
Skeletal, cardiac and smooth muscle all contract using the same mechanism: actin thin filaments being drawn together by myosin thick filaments.
- In skeletal and cardiac muscle these thick and thin filaments are organised in series into sarcomeres along the length of the muscle cell. This regular organization gives the muscle cells a striated appearance.
- In smooth muscle these thick and thin filaments are not organised into sarcomeres but are spread throughout the cell cytoplasm.
This animation shows the molecular interactions that occur within the skeletal muscle sarcomere between actin and myosin during skeletal muscle contraction. This irregular organization gives the muscle a non-striated appearance.
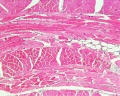
Skeletal Muscle Histology
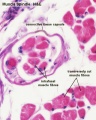
- Muscle Histology: Muscle Development | Human HE x4 longitudinal and transverse | Human HE x40 transverse | Human HE x40 longitudinal | Human HE x40 longitudinal | Human HE x4 longitudinal and transverse | Muscle Spindle HE x40 | Human HE x40 | Human HE x40 | Human HE x40 | Human HE x100 | Human HE x100 | Fetal human muscle | Myotendinous junction label | Myotendinous junction HE x40 | Whipf 1 | Whipf 2 | Whipf 3 | Tongue HE x10 transverse | Tongue x100 | Muscle spindle HE x20 | Muscle spindle HE x40
Electron Microscopy - Virtual Slides
|
|
| |||||||||
|
|
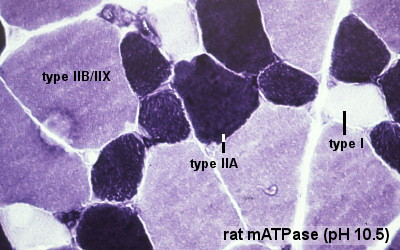
Muscle Fibre Types
Muscle fiber types
- type IIB, IIA, IIX, and I fibres - based only on the myosin ATPase activity.
- Type I fibres appear red, due to the presence of myoglobin.
- Type II fibres appear white, due to the absence of myoglobin and their glycolytic nature.
- A group of individual myofibres within a muscle will be innervated by a single motor neuron (motor unit).
- The electrical properties of the motor neuron will regulate the contractile properties of all associated myofibres.
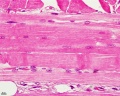
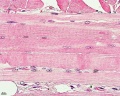
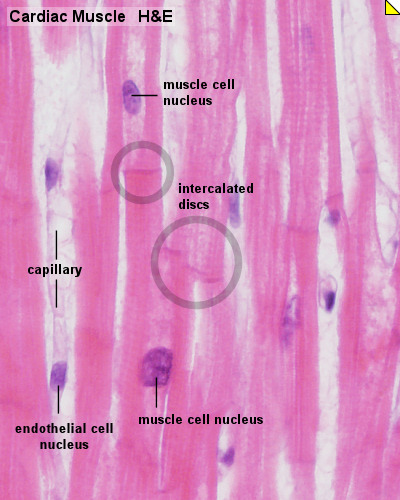
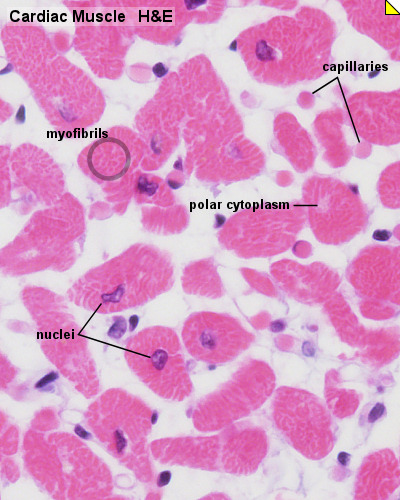
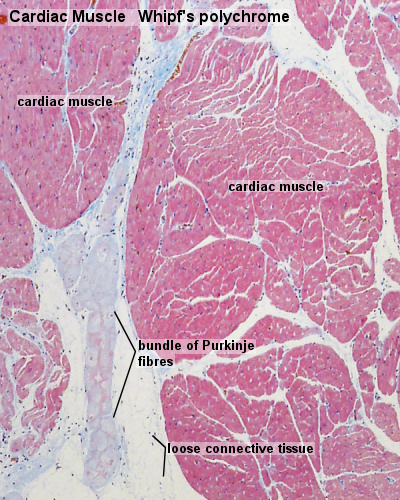
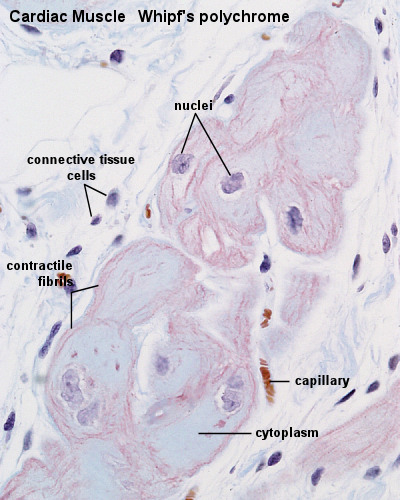
Cardiac Muscle Histology
Unlabeled Images
Electron Microscopy - Cardiac Muscle
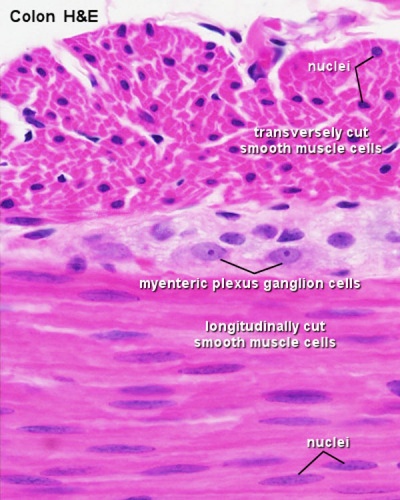
Smooth Muscle Histology
- Smooth Muscle Histology: Labeled Colon low | Labeled Colon high | Colon x40 | Colon x40 | Ileum x10 | Oesophagus x10 | Seminiferous tubule x40 | Uterus myometrium x10 | Uterus myometrium x40 |
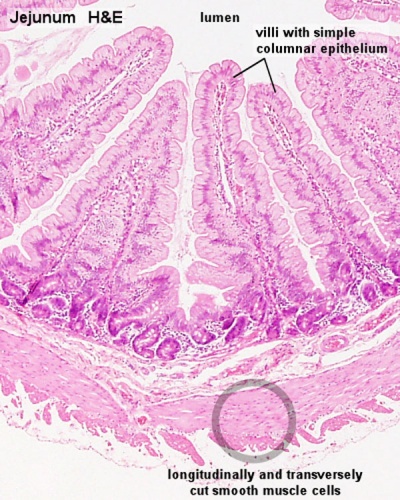
Gastrointestinal Tract Wall
The gastrointestinal tract consists of two thick outer muscle layers (longitudinal and circular) and a thin muscularis mucosa layer.
Course Links
- Histology Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | ANAT2241 Support | Histology | Histology Stains | Embryology Glossary
| Common Histology Stains | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Practical Support
- Pages can be accessed from any internet connected computer.
ANAT2241 Support Links: The Virtual Microscope | Covering and Lining Epithelia | Glandular Epithelia | CT Components | CT Types | Bone, Bone Formation and Joints | Muscle | Nervous | Blood | Eye | Cardiovascular | Respiratory | Integumentary | Gastrointestinal | Gastrointestinal Organs | Lymphatic and Immune | Endocrine | Urinary | Female Reproductive | Male Reproductive | Histology Stains | Histology Drawings | Practicals Health and Safety 2013 | Moodle - 2019
ANAT2241 This practical support page content is not part of the science practical class and provides only background information for student self-directed learning purposes.
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 28) Embryology ANAT2241 Muscle Tissue. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/ANAT2241_Muscle_Tissue
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G