2010 Lab 8
Introduction
This laboratory will study the early development of both the Renal and Genital systems, often grouped as the Urogenital System.
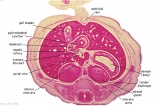
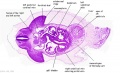
Mid-Embryonic (stage 13)
- Renal middle stage (mesonephros) and septating cloacal region.
- Gonad is present only as indifferent genital ridge stage.
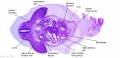
Late Embryonic (stage 22)
- Renal kidney developing (metanephros) and degenerating middle stage (mesonephros).
- Gonad is differentiating and the internal genital tract (mesonephric/paramesonephric duct) is differentiating.
Early Fetal
- Renal kidney has identifiable cortex and medulla and is retroperitoneal. Note the relative size of the kidney and adrenal gland.
- Gonad is now different for male and female and internal genital tract is developing. External genitalia is indifferent.
Links: Influence of Sry on gonad development | Comparative anatomy of adult male and female reproductive tracts
Stage 13
| ||||||
|
|
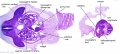
|
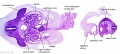
|
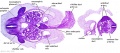
|
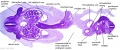
| |
| E1L | E2L | E3L | E4L | E5L | E6L | E7L |

|
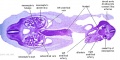
|
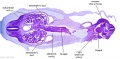
|
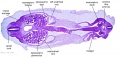
|
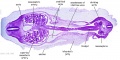
|
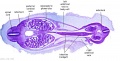
|
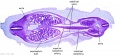
|
| F1L | F2L | F3L | F4L | F5L | F6L | F7L |
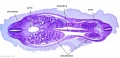
|
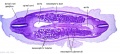
|
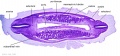
|
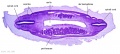
|
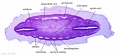
|
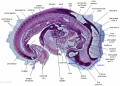
|
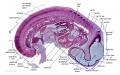
|
| G1L | G2L | G3L | G4L | G5L | G6L | G7L |
Introduction
| Movies - Embryo Carnegie stage 22 - This embryo animation rotates and show the relative position of internal renal system structures at the end of embryonic development. Compare these with the earlier stage 13 embryo.
The movies are based upon reconstruction of serial slice images. | |
| Urogenital |
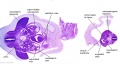
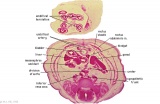
Stage 22 Renal Annotated
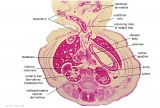
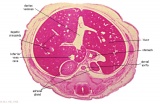 E6: R,L adrenal glands under diaphragm. E6: R,L adrenal glands under diaphragm.
|
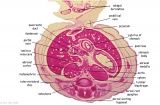
|
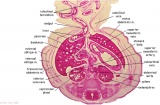
|
|
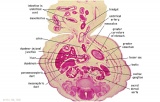
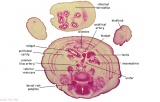
| Fl: Adrenal glands. R. Kidney. Autonomic ganglia (partly the adrenal medulla precursors). | F2: Kidneys (note retroperitoneal location). Cortex. Medulla. L. Adrenal gland. Superior mesenteric artery. Inferior vena cava. | F3: R testis (note its location relative to the R adrenal). L adrenal. R renal hilus. large channels are branches of ureteric tree. | |
|
|
|
|
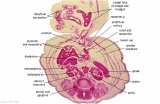
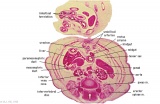
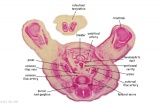
| F4: R kidney and R ureter. Inferior vena cava. L. kidney, L renal hilus and L ureter. R testis with R mesonephric duct (precursor of vas deferens). L testis. Umbilical arteries passing into umbilical cord allantois between them. | F5: Kidneys. Ureters. Note umbilical arteries and allantois. Also note how R testis and mesonephric structures are attached to parietal peritoneum by a mesogonad. | F6: Kidneys. Ureters. Note umbilical arteries and allantois. Also note how R testis and mesonephric structures are attached to parietal peritoneum by a mesogonad. | F7: In F7, (dorsal to R testis and liver) note with the distinct lumen of the mesonephric duct, almost solid column of paramesonephric cells and remnants of mesonephric tubules. "mesogonad". Ureters. Bladder with submucosa and detrusor muscle. Umbilical arteries. Division of aorta. |
|
|
|
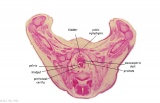
|
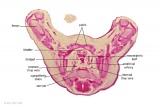
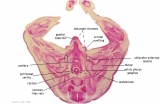
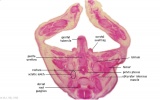
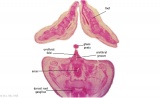
| G1: Ureters, Bladder. Umbilical arteries. Testis with remains of mesonephros (dorsal), mesonephric duct and paramesonephric cells. Sigmoid colon and mesocolon. | G2: Ureters being displaced ventrally, crossing common iliac arteries. Sigmoid colon. Bladder. Mesonephric ducts (lateral) and paramesonephric ducts (smaller, medial) located dorsal to bladder. | G3: Ureters (cut twice): descending dorsal to bladder and ascending ventrally to enter the bladder at trigone, through the submucosa). Fusion of paramesonephric ducts. Paired mesonephric ducts. Umbilical arteries looping off common iliac arteries. Pubic symphysis. Colon. | G4: Most caudal part of loop of ureters. Urethra emerging from bladder. Mesonephric ducts. Rectocolic junction. |
|
|
|
|
| G5: Urethra (in region of future prostate gland - note crescentic shape). Rectum. Rectovesical pouch. Between G4 and G5, each mesonephric duct (vas deferens) has joined the prostatic urethra (caudal to the ureters), thereby increasing the caliber of the latter. | G6: Penile urethra, emerging inferiorly to the glans penis. Scrotal swellings (appear before testis descends). | G7: Penile urethra, emerging inferiorly to the glans penis. Scrotal swellings (appear before testis descends). | Note F7 MS term: "inebriated Puffin" (dorsal to R testis and liver) lumen of the mesonephric duct (eye), almost solid column of paramesonephric cells (beak) and remnants of mesonephric tubules (body). |
Stage 22
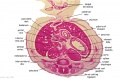
|
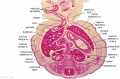
|
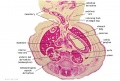
|
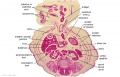
|
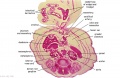
|
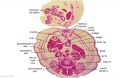
|
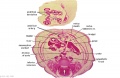
|
| F1L | F2L | F3L | F4L | F5L | F6L | F7L |
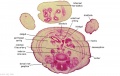
|
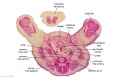
|
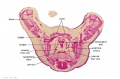
|
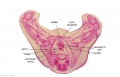
|
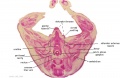
|
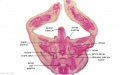
|
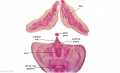
|
| G1L | G2L | G3L | G4L | G5L | G6L | G7L |
Stage 22 Selected (male)
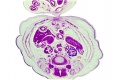
|
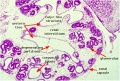
|
|
| |||
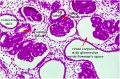
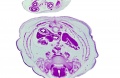
| F4 kidney | F5 renal pelvis | F6 nephron | F7 gonad | |||
|
|
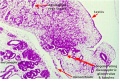
|
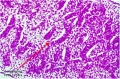
|
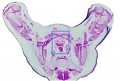
|
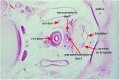
|
|
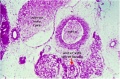
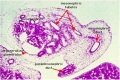
| G1 ureter | G2 mesonephros | G3 testis | G4 rete tesits | G5 urogenital | G6 urogenital | G7 urogenital |
Stage 22 Selected

|

|

|

| |||
| F4 kidney | F5 renal pelvis | F6 nephron | F7 gonad | |||

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
| G1 ureter | G2 mesonephros | G3 testis | G4 rete tesits | G5 urogenital | G6 urogenital | G7 urogenital |
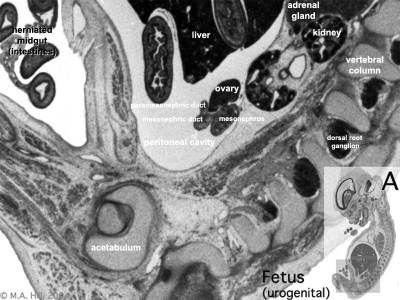
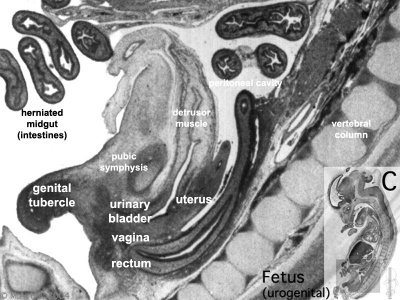
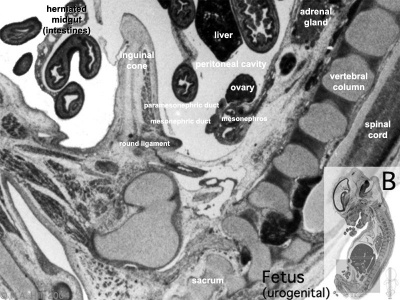
Fetal 10 Week (female)
|
|
|
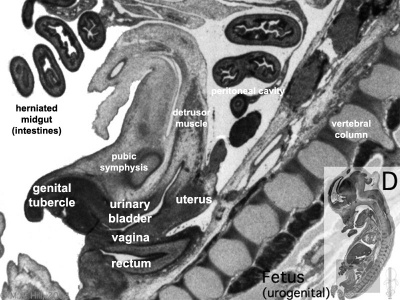
|
Urogenital Labelled - most lateral | lateral | medial | midline
Urogenital Movies
| Urogenital Sinus | Urogenital Septum | Trigone | Renal Nephron | ||
| Ovary | Testis | Female External | Male External | Uterus | Testis Descent |
| Migration 1 | Migration 2 | Migration 3 |
Group Project
--Mark Hill 15:01, 22 September 2010 (UTC) Any student who has not now added an assessment to every project discussion page and included a copy of all assessments given on their own page will a receive zero mark for this individual assessment item.
Group Projects (20% of your final mark). It is now week 9 and the projects should now have been peer assessed by your class. It is now time for your group to review the comments and constructive criticisms that have been added to your project discussion page.
Begin by collating the comments.
- What are the common criticisms?
- What were the best aspects identified within your project?
- What errors, typos, missing references were identified?
- Were there contributions from individual group members that were identified as good or poor parts of the overall project?
Then work on the changes.
- Develop priorities.
- Divide the changes and corrections between group members.
- Are there additional changes that should be made that were not identified by peer assessment.
You now have 2 weeks to complete all project work before final assessment.
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Course Content 2010
Embryology Introduction | Cell Division/Fertilization | Lab 1 | Week 1&2 Development | Week 3 Development | Lab 2 | Mesoderm Development | Ectoderm, Early Neural, Neural Crest | Lab 3 | Early Vascular Development | Placenta | Lab 4 | Endoderm, Early Gastrointestinal | Respiratory Development | Lab 5 | Head Development | Neural Crest Development | Lab 6 | Musculoskeletal Development | Limb Development | Lab 7 | Kidney | Genital | Lab 8 | Sensory | Stem Cells | Stem Cells | Endocrine | Lab 10 | Late Vascular Development | Integumentary | Lab 11 | Birth, Postnatal | Revision | Lab 12 | Lecture Audio | Course Timetable
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2026, March 1) Embryology 2010 Lab 8. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/2010_Lab_8
- © Dr Mark Hill 2026, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G