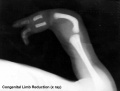
X-ray
| Embryology - 27 Feb 2026 |
|---|
| Google Translate - select your language from the list shown below (this will open a new external page) |
|
العربية | català | 中文 | 中國傳統的 | français | Deutsche | עִברִית | हिंदी | bahasa Indonesia | italiano | 日本語 | 한국어 | မြန်မာ | Pilipino | Polskie | português | ਪੰਜਾਬੀ ਦੇ | Română | русский | Español | Swahili | Svensk | ไทย | Türkçe | اردو | ייִדיש | Tiếng Việt These external translations are automated and may not be accurate. (More? About Translations) |
| Educational Use Only - Embryology is an educational resource for learning concepts in embryological development, no clinical information is provided and content should not be used for any other purpose. |
Introduction
There are a number of different neonatal screening (newborn screening) programs in different countries testing for various "common" congenital abnormalities and infections. Perinatally the infant is tested physically for hip displasia and may have an x-ray to establish the extent of musculoskeletal abnormality. There are also a number of other systems (renal, cardiovascular, respiratory, gastrointestinal, endocrine and genital) that can be assessed postnatally by x-ray alone or in combination with tracers or contrast agents.
Radiation is a known teratogen and can affect development, but there is ongoing discussion as to the associated fetal risk and that to maternal health of a range of conditions that are detected or analysed using x-radiation.[1]
Diagnosis Categories
- Prenatal diagnosis - number of different techniques (non-invasive, invasive) for determining normal development
- Neonatal diagnosis (APGAR test, Guthrie test, Hearing test)
- Maternal diagnosis - often pregnancy will expose maternal health problems
Some Recent Findings
|
| More recent papers |
|---|
|
This table allows an automated computer search of the external PubMed database using the listed "Search term" text link.
More? References | Discussion Page | Journal Searches | 2019 References | 2020 References Search term: Fetal X-ray | Neonatal X-ray |
Musculoskeletal Abnormalities
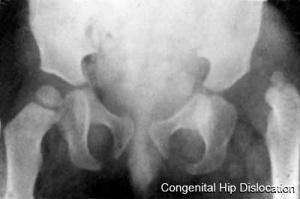
Congenital Hip Dislocation
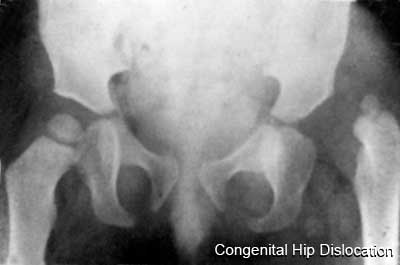
|
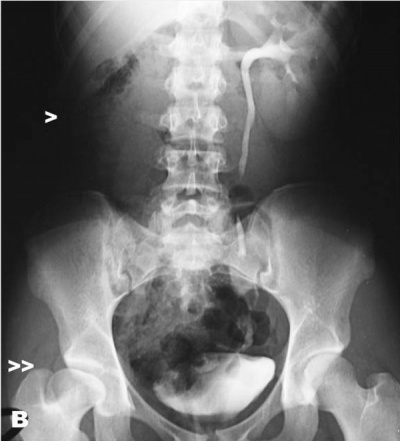
(>>) right hip dysplasia is shown. |
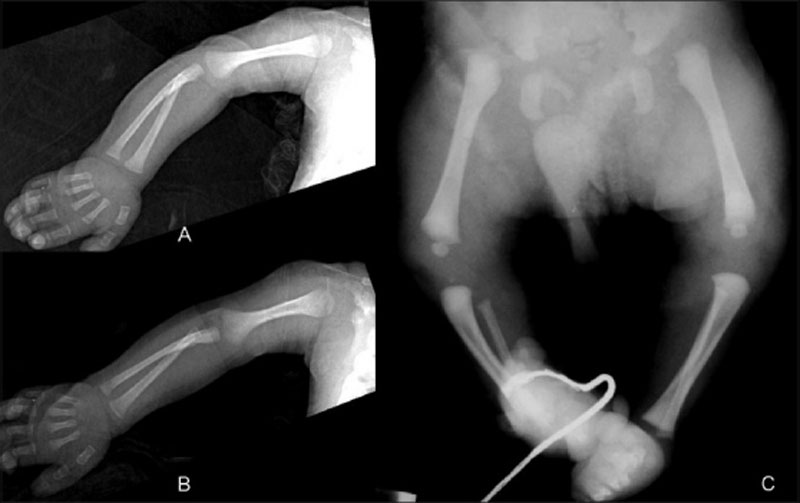
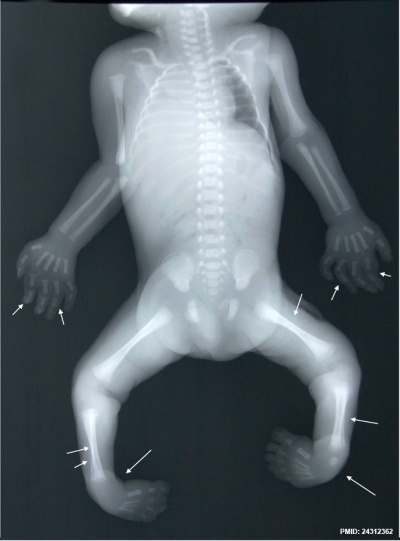
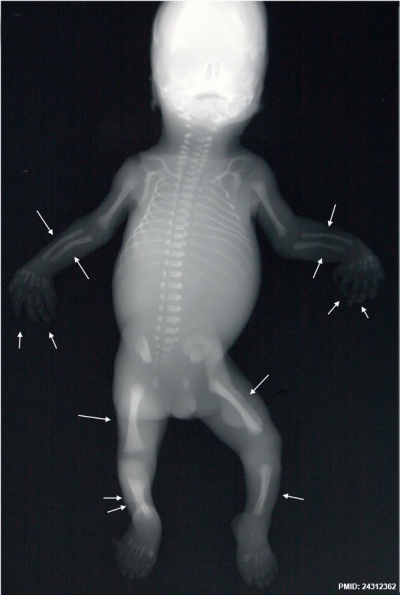
Skeletal Bowing
Fetal bowing and hypoplasia of the femur, tibia and fibula, and talipes equinovarus.[4]
|
|
- X-ray Links: Fetal skeleton | Fetal skeleton abnormal | Fetal skeleton abnormal | Musculoskeletal Abnormal | Musculoskeletal | X-ray
Arthrogryposis
Renal Abnormalities
Renal Agenesis
Ureteral Duplication
- Links: Renal Abnormalities | Renal Development
Gastrointestinal Tract Abnormalities
Duodenal atresia
Gene Tests
A new site developed by NIH "GeneTests" provides medical genetics information resources available at no cost to all interested persons. It contains educational information, a directory of genetic testing laboratories and links to other databases such as OMIM.
Links: Gene Tests
References
- ↑ Hodson K, Waugh J & Nelson-Piercy C. (2011). Early life radiation exposure. Withholding imaging in pregnancy may be hazardous. BMJ , 342, d1486. PMID: 21406518
- ↑ Franco EL & Turgeon GA. (2010). Radiodiagnostic imaging in pregnancy and the risk of childhood malignancy: raising the bar. PLoS Med. , 7, e1000338. PMID: 20838652 DOI.
- ↑ Dasenbrock C, Tillmann T, Ernst H, Behnke W, Kellner R, Hagemann G, Kaever V, Kohler M, Rittinghausen S, Mohr U & Tomatis L. (2005). Maternal effects and cancer risk in the progeny of mice exposed to X-rays before conception. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. , 56, 351-60. PMID: 15945274 DOI.
- ↑ ten Broek CM, Bots J, Varela-Lasheras I, Bugiani M, Galis F & Van Dongen S. (2013). Amniotic fluid deficiency and congenital abnormalities both influence fluctuating asymmetry in developing limbs of human deceased fetuses. PLoS ONE , 8, e81824. PMID: 24312362 DOI.
Reviews
{#pmid:19160197}}
{#pmid:18528700}}
Articles
{#pmid:16484148}}
{#pmid:14949062}}
{#pmid:14942747}}
{#pmid:15434757}}
Search PubMed
Search PubMed: x-ray neonatal diagnosis | x-ray neonatal screening | maternal x-ray risk
Additional Images
External Links
External Links Notice - The dynamic nature of the internet may mean that some of these listed links may no longer function. If the link no longer works search the web with the link text or name. Links to any external commercial sites are provided for information purposes only and should never be considered an endorsement. UNSW Embryology is provided as an educational resource with no clinical information or commercial affiliation.
- NIH PubMed Health Newborn Screening
- Nemours Foundation Newborn Screening Tests
- The Children's Hospital at Westmead NSW Newborn Screening
- Secondary School Resource biotechnology online
- PBS How the World Discovered the X-Ray
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2026, February 27) Embryology X-ray. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/X-ray
- © Dr Mark Hill 2026, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G