User:Z5015534
Lab Attendance
--Z5015534 (talk) 13:45, 7 August 2015 (AEST) --Z5015534 (talk) 13:32, 14 August 2015 (AEST)--Z5015534 (talk) 13:14, 21 August 2015 (AEST)--Z5015534 (talk) 13:23, 28 August 2015 (AEST)--Z5015534 (talk) 12:15, 4 September 2015 (AEST)--Z5015534 (talk) 13:19, 11 September 2015 (AEST)--Z5015534 (talk) 13:04, 18 September 2015 (AEST)
--Mark Hill (talk) 17:24, 3 September 2015 (AEST) Where is he first assessment item? ANAT2341 Lab 1 - Online Assessment (0/5)
Lab 1 Assesment
PMID 26247832 <pubmed>26247832</pubmed>
- The study observed the effects of changing progesterone levels on the treatment outcome of in vitro fertilisation embryo transfer in patients with different ovarian responses; poor ovarian response group (oocyte retrieval <5), intermediate ovarian response group (5<oocyte retrieval <15) and high ovarian response group (oocyte retrieval >16). When the size of the follicle had reached more than 14mm, the fasting blood was collected to determine the various hormone levels, including progesterone. After 37 hours, the oocyte was retrieval was performed, progesterone was injected (intramuscularly) and 3-4hrs after, fertilisation occurred. 2-3 days after the oocyte retrieval, embryo transfer occurred. It was diagnosed as clinical pregnancy when when B-mode ultra sound showed gestation sac, embryo bud, or fetal heart beat 35 days after embryo transfer.
- The study found that in the poor ovarian response group, the pregnancy rate was not associated with the level of progesterone but in the intermediate and high groups the clinical pregnancy rate was inversely related with the progesterone levels. The experiment showed that progesterone levels are only associated with clinical pregnancy in patients with intermediate or high ovarian response rates.
PMID 23661780 <pubmed>23661780</pubmed>
- The study examined whether the environment that a sperm resides in, effects the subsequent functioning of the larvae in the broadcast spawning marine invertebrate Galeolaria gemineoa. The study approached the question by exposing portions of a males ejaculate to differing levels of salinity, normal salinity and reduced salinity. The solutions, containing the sperm, were then both returned to normal levels of salinity. Fertilization then took place as normal (in levels of normal salinity) and the developmental success (the proportion of zygotes that developed into larvae) was measured, as well as an exploration into whether offspring fertilised by sperm exposed to lower salinity levels were more resistant to lower salinity themselves.
- The results showed that larvae fertilised by sperm exposed to lower salinity levels had poorer developmental success then larvae fertilised by sperm exposed to normal levels of salinity. The study found that developmental performance was generally higher when the larvae and the sperm experienced the same environment, then if the sperm and larvae experienced an environment that differed.
Lab 2 Assesment
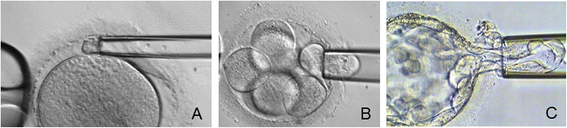
Polar body, Blastomere and Trophectoderm Biopsies [1]
PMID 25625041
--Mark Hill (talk) 17:26, 3 September 2015 (AEST) Uploaded image contains reference, copyright and student template. I would have used a simpler name for the image file. (5/5)
Lab 3 Assesment - Oncofertility articles
PMID 25284123 <pubmed>25284123</pubmed>
- A review article discussing the large effect cancer treatments have on cancer survivors, including infertility. The article discusses the effects of different treatments, and ways to protect fertility in women.
PMID 25191024
<pubmed>25191024</pubmed>
- A research article aiming to discover and explore differences in oocyte stimulation for fertility preservation (FP) patients based on cancer diagnosis. The study found that factors such as age, type of cancer and chemotherapy exposure, can influence response to ovarian stimulation.
PMID 24934638
<pubmed>24934638</pubmed>
- A review article discussing the methods and strategies to increasing fertility when undergoing chemotherapy treatments for early breast cancer patients.
--Mark Hill (talk) 17:26, 3 September 2015 (AEST) These are relevant to your group project. (5/5)
Lab 4 Assessment - Quiz
--Mark Hill (talk) 17:28, 3 September 2015 (AEST) I had asked for a sub-heading of the topic(s) covered by your quiz. Q1 is good. Q2 T/F questions are generally a guess and not good design. Q3 the question could be more clearly worded. There is no " villi cell " just chorionic villi if you wanted to be specific. (8/10)
References
PMID 26244658 look at this[2]
Please do not use your real name on this website, use only your student number.
- 2015 Course: Week 2 Lecture 1 Lecture 2 Lab 1 | Week 3 Lecture 3 Lecture 4 Lab 2 | Week 4 Lecture 5 Lecture 6 Lab 3 | Week 5 Lecture 7 Lecture 8 Lab 4 | Week 6 Lecture 9 Lecture 10 Lab 5 | Week 7 Lecture 11 Lecture 12 Lab 6 | Week 8 Lecture 13 Lecture 14 Lab 7 | Week 9 Lecture 15 Lecture 16 Lab 8 | Week 10 Lecture 17 Lecture 18 Lab 9 | Week 11 Lecture 19 Lecture 20 Lab 10 | Week 12 Lecture 21 Lecture 22 Lab 11 | Week 13 Lecture 23 Lecture 24 Lab 12 | 2015 Projects: Three Person Embryos | Ovarian Hyper-stimulation Syndrome | Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome | Male Infertility | Oncofertility | Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis | Students | Student Designed Quiz Questions | Moodle page