Neural System Development
Introduction
Neural development is one of the earliest systems to begin and the last to be completed after birth. This development generates the most complex structure within the embryo and the long time period of development means in utero insult during pregnancy may have consequences to development of the nervous system.
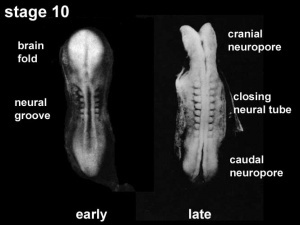
The early central nervous system begins as a simple neural plate that folds to form a groove then tube, open initially at each end. Failure of these opening to close contributes a major class of neural abnormalities (neural tube defects).
Sonic Hedgehog expression (white) in both the notocord (pale circular) and neural tube floorplate (bright triangle). (Image- Lance Davidson)
Within the neural tube stem cells generate the 2 major classes of cells that make the majority of the nervous system : neurons and glia. Both these classes of cells differentiate into many different types generated with highly specialized functions and shapes. This section covers the establishment of neural populations, the inductive influences of surrounding tissues and the sequential generation of neurons establishing the layered structure seen in the brain and spinal cord.
- Neural development beginnings quite early, therefore also look at notes covering Week 3- neural tube and Week 4-early nervous system.
- Development of the neural crest and sensory systems (hearing/vision/smell) are only introduced in these notes and are covered in other notes sections.
Some Recent Findings
Reading
- Human Embryology (3rd ed.) Chapter 5 p107-125
- The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology (6th ed.) Moore and Persaud Chapter 18 p451-489
- Essentials of Human Embryology Larson Chapter 5 p69-79
- Before We Are Born (5th ed.) Moore and Persaud Chapter 19 p423-458
- Human Embryology, Fitzgerald and Fitzgerald
- History of Science- Brain and Mind, Brain Structure, Camille Golgi, S. Ramon y Cajal
Objectives
- Understand early neural development.
- Understand the formation of spinal cord.
- Understand the formation of the brain; grey and white matter from the neural tube.
- Understand the role of migration of neurons during neural development.
- To know the main derivatives of the brain vesicles and their walls.
- To know how the nervous system is modelled, cell death etc.
- To understand the contribution of the neural crest.
- Understand the developmental basis of certain congenital anomalies of the nervous system, including hydrocephalus, spina bifida, anencephaly and encephalocele.
References
Search Pubmed: Neural System Development
| System Links: Introduction | Cardiovascular | Coelomic Cavity | Endocrine | Gastrointestinal Tract | Genital | Head | Immune | Integumentary | Musculoskeletal | Neural | Neural Crest | Placenta | Renal | Respiratory | Sensory | Birth |
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 30) Embryology Neural System Development. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Neural_System_Development
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G