Hearing - Middle Ear Development: Difference between revisions
From Embryology
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
== References == | |||
<references/> | |||
===Reviews=== | |||
===Articles=== | |||
===Search PubMed=== | |||
'''Search Pubmed:''' [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?db=pubmed&cmd=search&term=Middle%20Ear%20Development Middle Ear Development] [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?db=pubmed&cmd=search&term=ossicle%20Development Ossicle Development] | |||
==External Links== | ==External Links== | ||
Revision as of 15:04, 4 June 2010
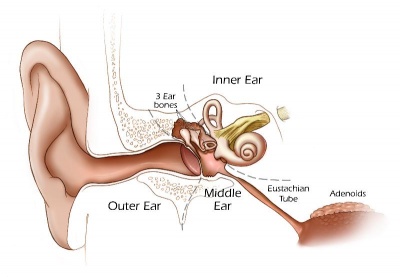
Introduction
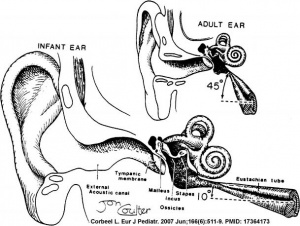
The middle ear ossicles (bones) are derived from 1st and 2nd arch mesenchyme. The space in which these bones sit is derived from the 1st pharyngeal pouch.
Tympanic Cavity
- derived from first pharyngeal pouch
- extends as tubotympanic recess - during week 5 recess contacts outer ear canal
- mesoderm between 2 canals forms tympanic membrane
- expands to form tympanic recess
- stalk of recess forms auditory tube(eustachian tube, pharyngotympanic tube)
Ossicles
- develop from first and second pharyngeal arches
- tympanic cavity enlarges to incorporate
- coats with epithelia
- first arch mesoderm
- tensor tympani muscle
- malleus and incus
- second arch mesoderm
- stapedius muscle and stapes
Middle Ear Genes - gooscoid, RARs, Prx1, Otx2, Hoxa1, Hoxb1, endothelian related molecules
Additional Images
References
Reviews
Articles
Search PubMed
Search Pubmed: Middle Ear Development Ossicle Development
External Links
- Neuroscience Neuroscience - The Middle Ear
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, May 2) Embryology Hearing - Middle Ear Development. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Hearing_-_Middle_Ear_Development
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G